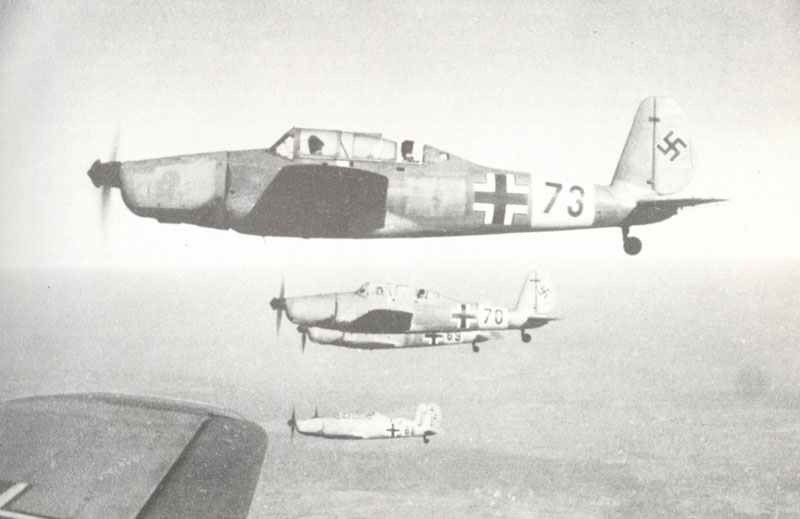
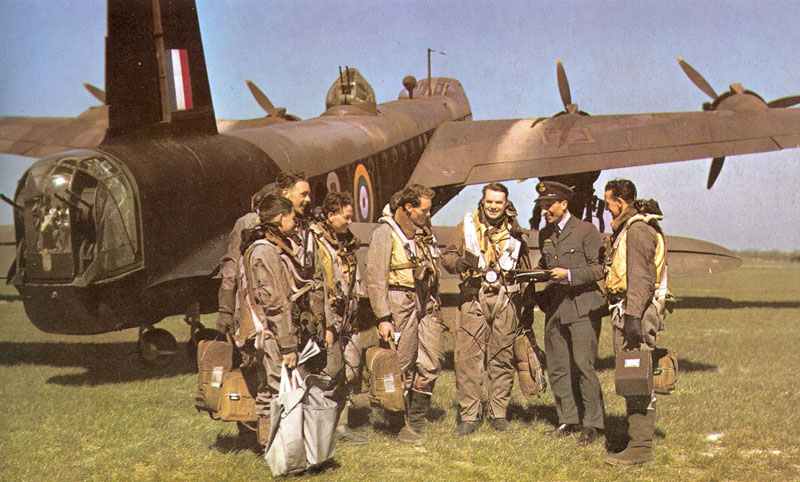
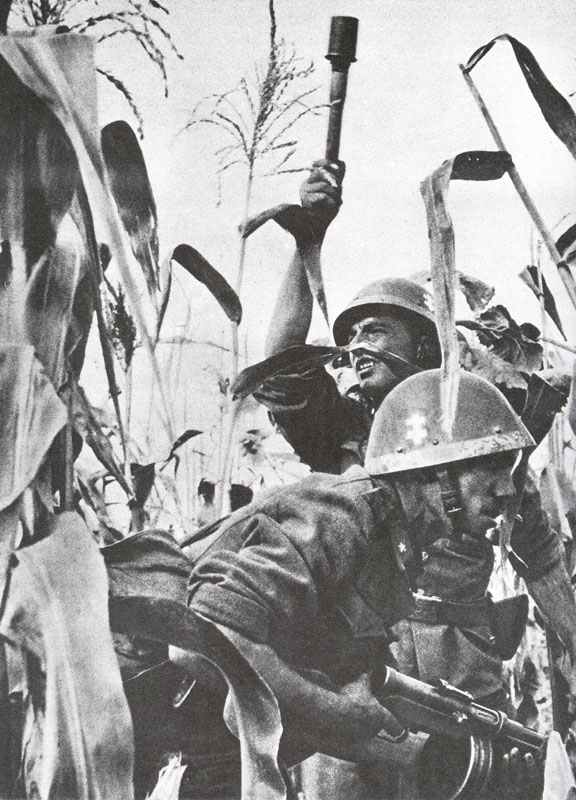
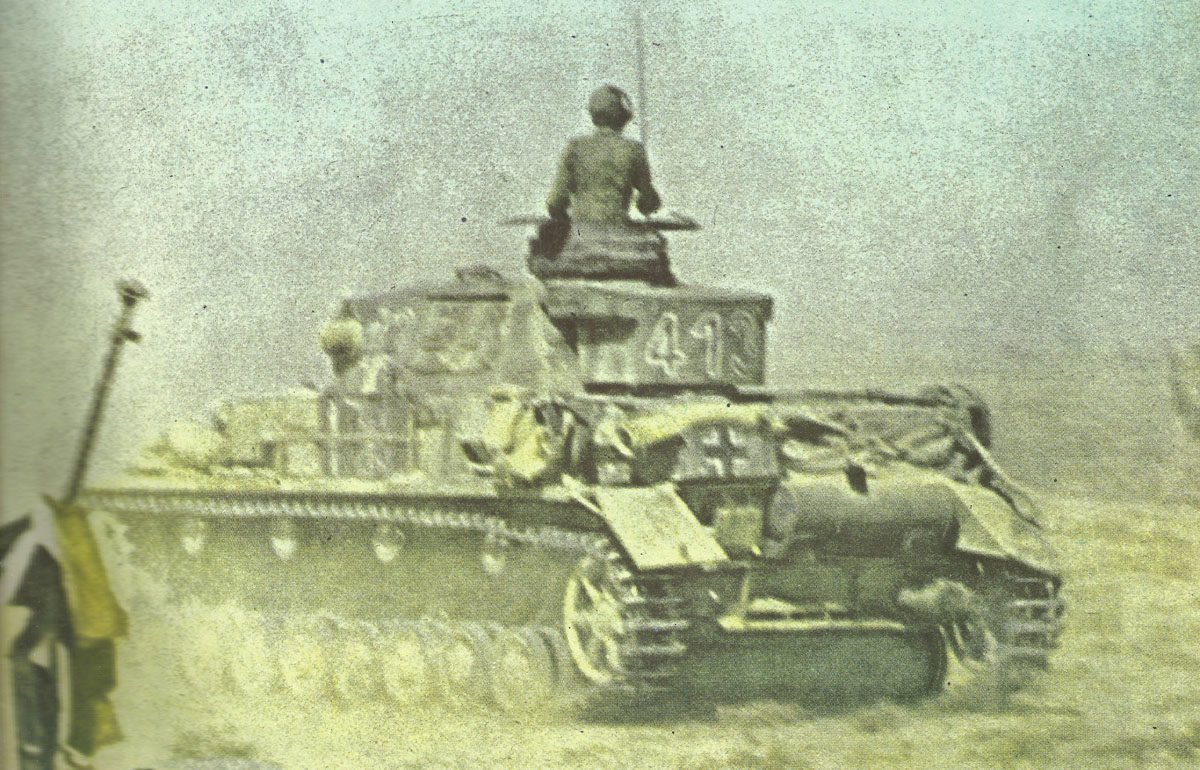
The Armed Forces of the Second World War 1939-45.
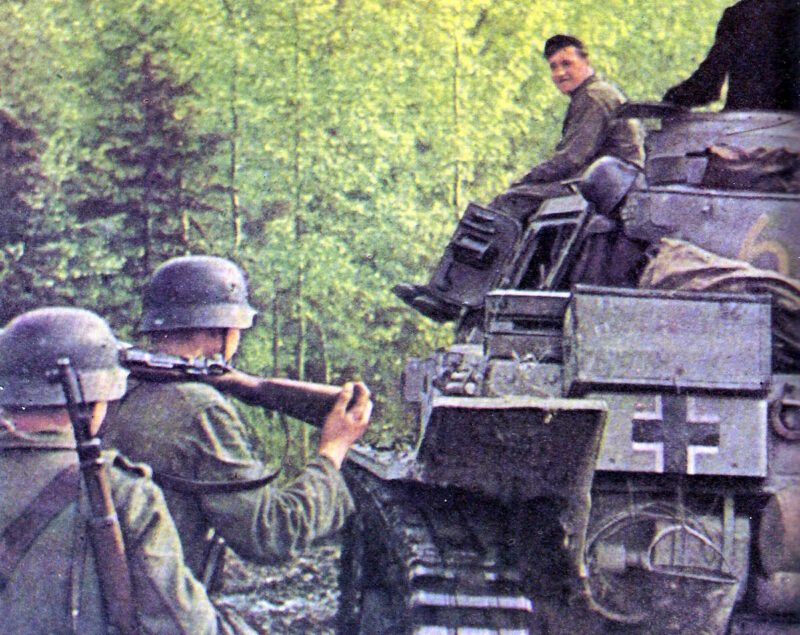

Armed Forces of World War II
Table of Contents
World War II was a monumental conflict that spanned the globe, involving countless nations and resulting in significant developments in military strategy and technology. The armed forces of the participating nations were diverse, consisting of land, air, and sea units, each playing crucial roles in the numerous campaigns that defined the war.
The main combatants, the Axis powers—Germany, Italy, and Japan—and the Allied forces—primarily France, Great Britain, the United States, the Soviet Union, and China—mobilized millions of soldiers and state-of-the-art weaponry in a struggle for power and survival.
The military history of the United States during World War II illustrates a complex and transformative period for American armed forces.
Initially, American citizens volunteered to fight against the Axis powers in other nations’ forces, despite such actions being against U.S. law at the time. However, with the attack on Pearl Harbor in December 1941, the United States officially entered the war, committing its vast industrial and human resources to the Allied cause.
This would lead to significant change within the U.S. military, confronting and challenging the nation’s perspectives on race and gender, as more than one million African Americans served, alongside many other marginalized groups.
At the onset of war, the European combatants possessed varying levels of preparation and capability.
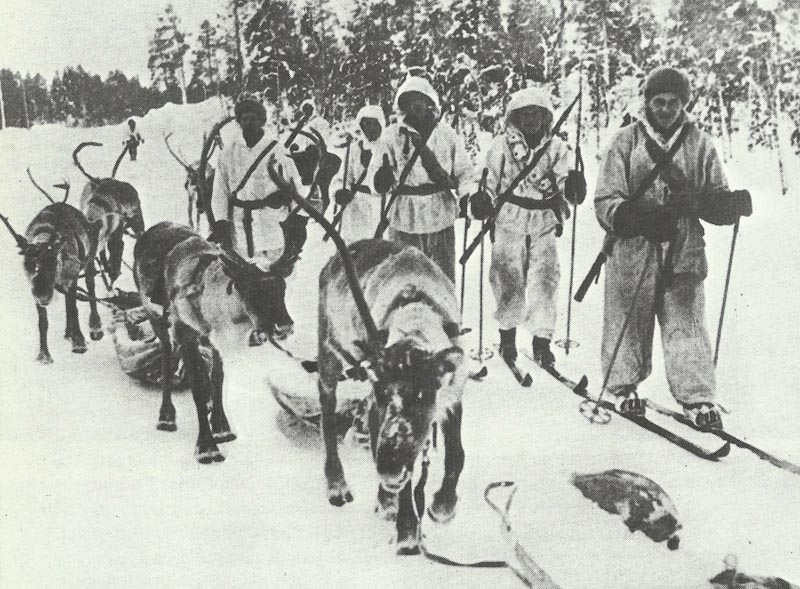
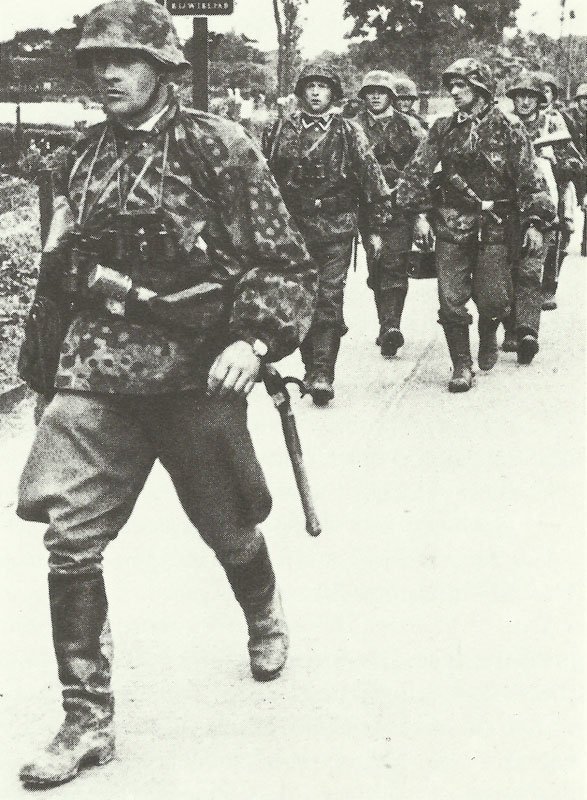
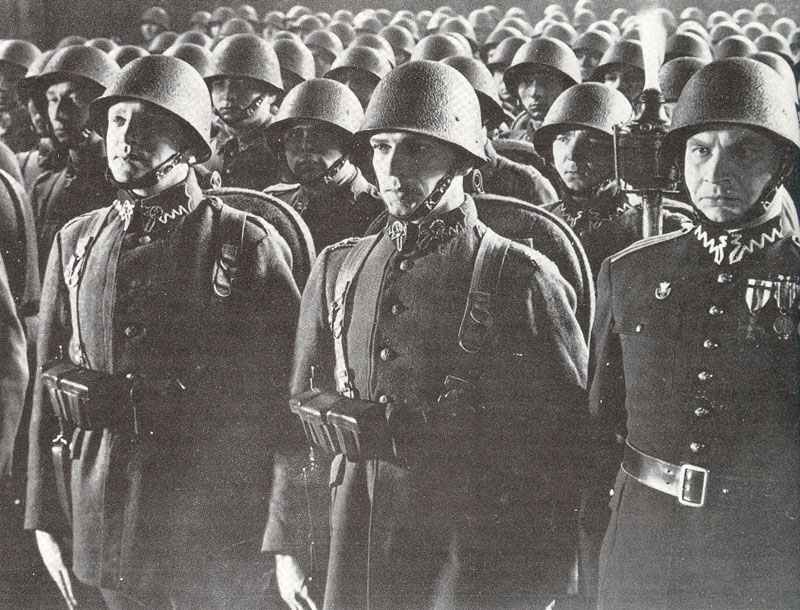
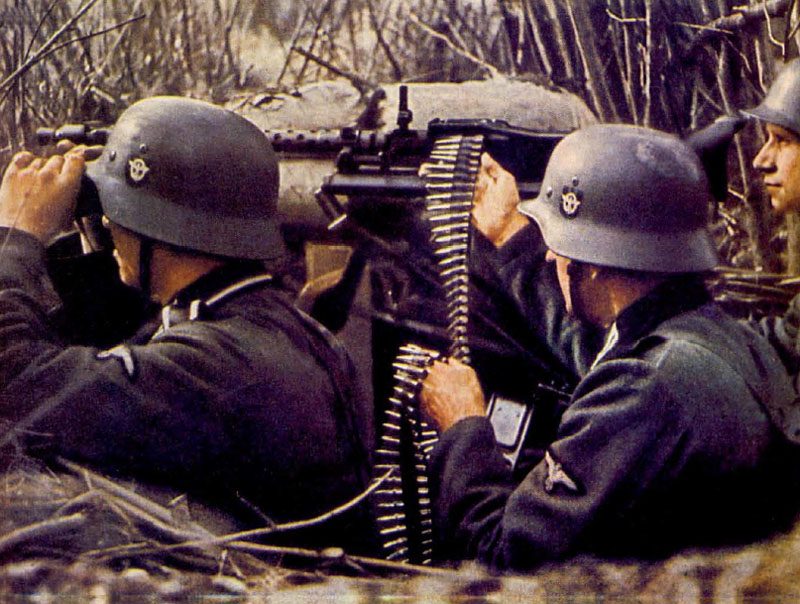
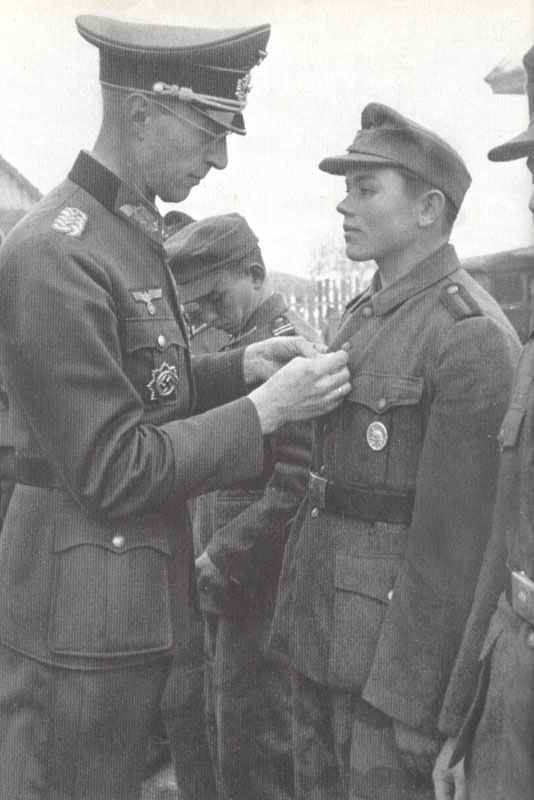
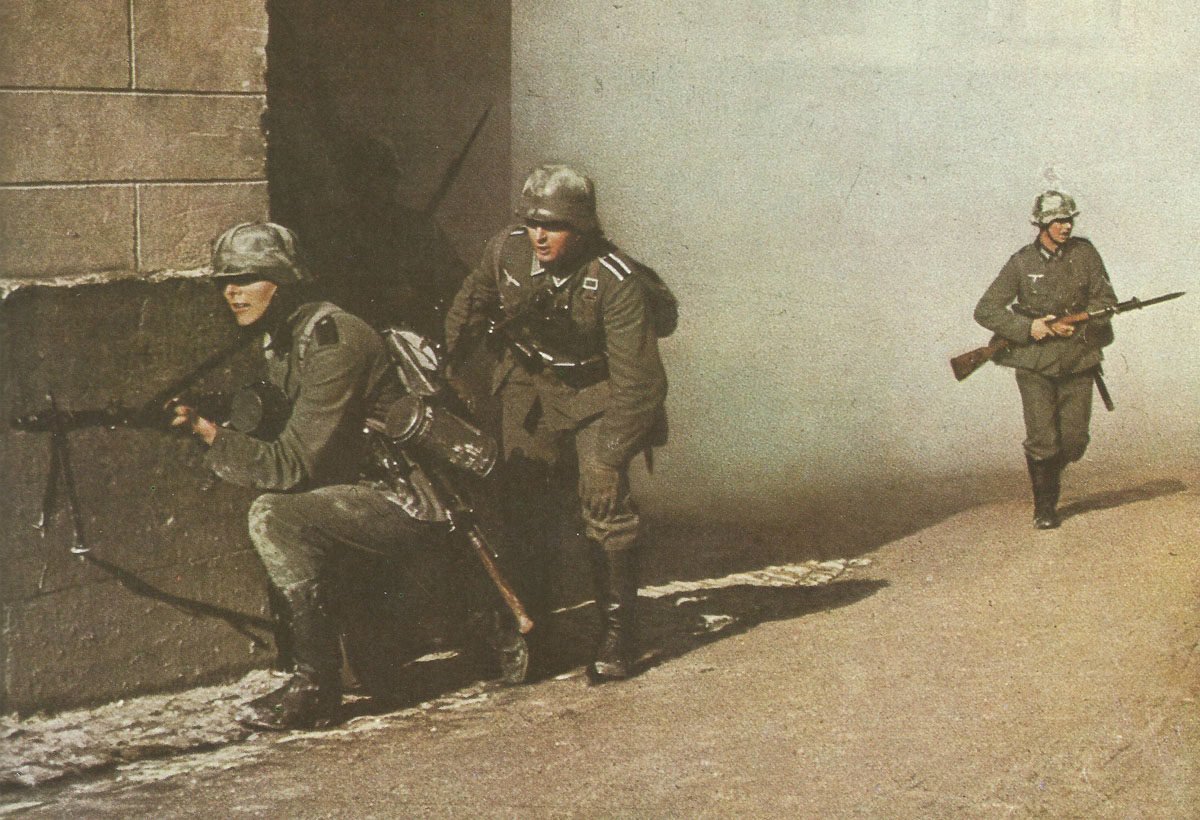
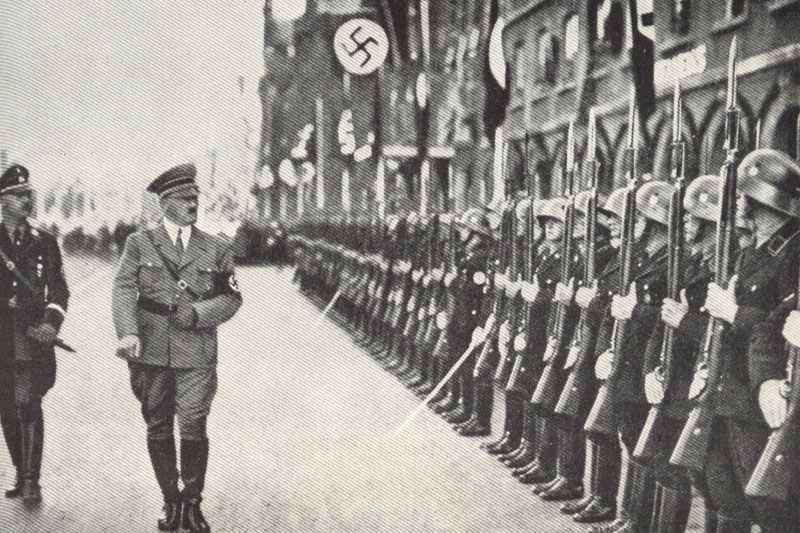
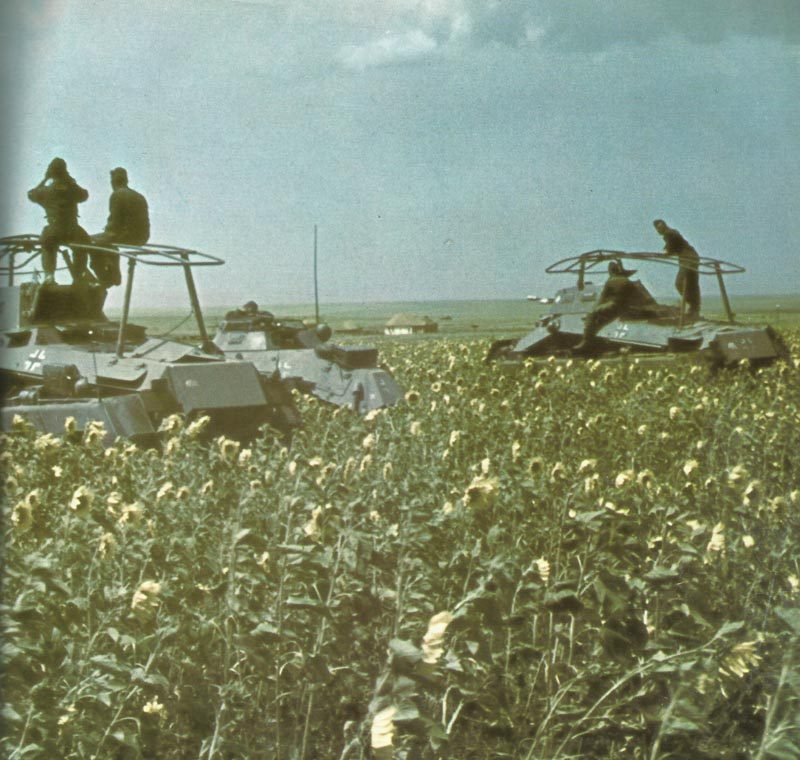
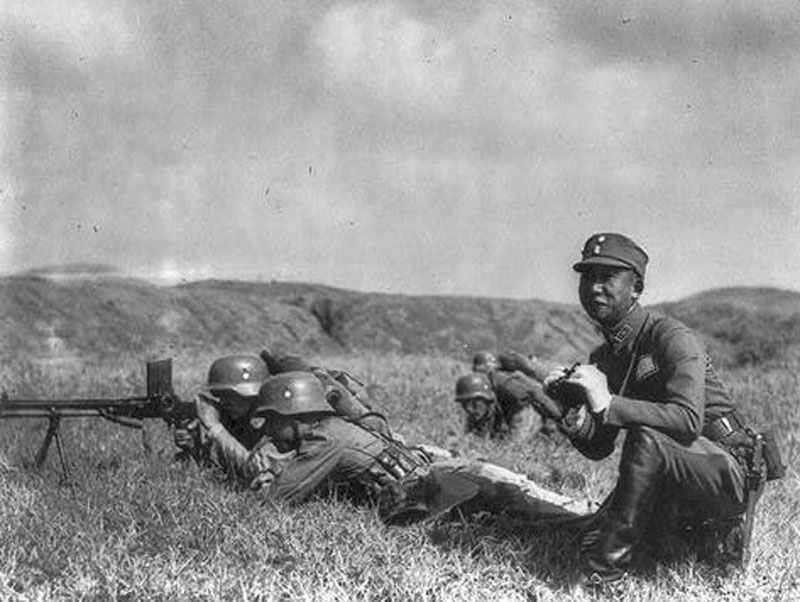
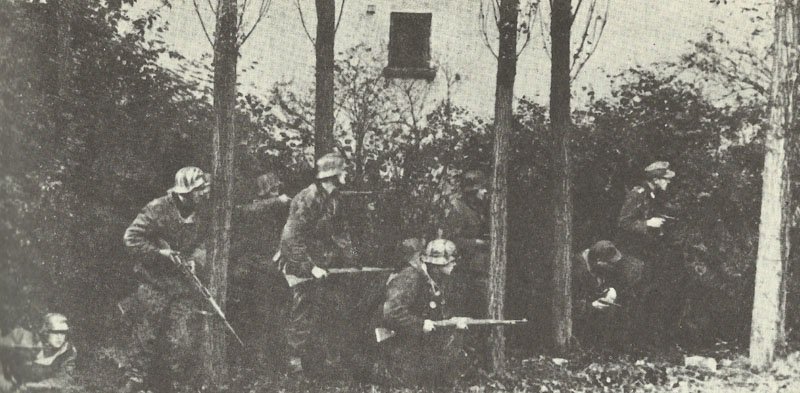
The German army, known as the Wehrmacht, was recognized for its efficiency and modern tactics, comprising a formidable force early in the war.
In contrast, the Allies were initially disparate but grew increasingly cohesive, combining their industrial capacities and strategic advantages, such as radar technology, to counter the Axis.
Each nation’s military contribution was vital, and understanding these forces provides insight into the broader narratives of World War II, including the geopolitical aftermath that shaped the modern world.
Articles about the armed forces of the Second World War
Overview of the armed forces of the Second World War 1939 to 1945
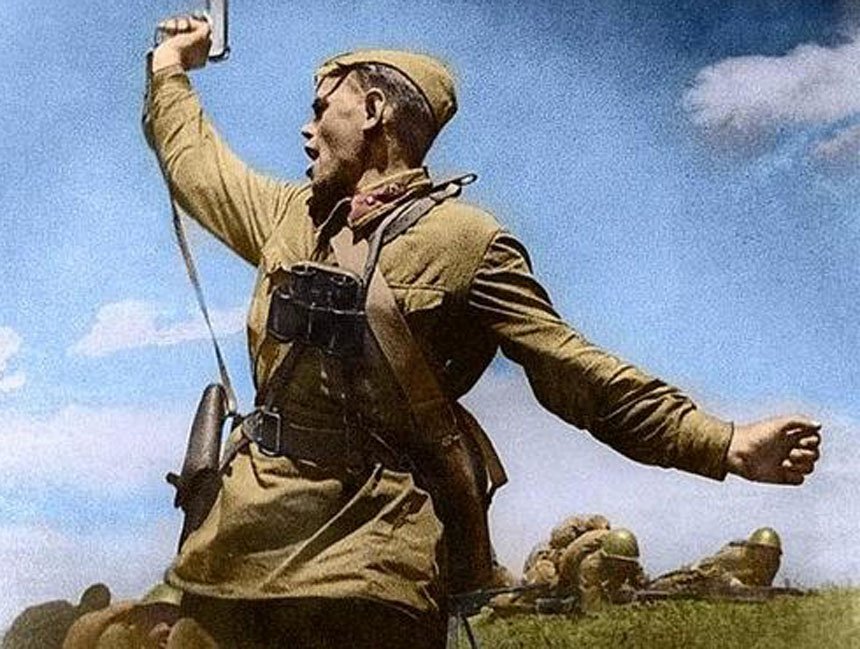

World War II was a monumental conflict that spanned the globe, involving countless nations and resulting in significant developments in military strategy and technology. The armed forces of the participating nations were diverse, consisting of land, air, and sea units, each playing crucial roles in the numerous campaigns that defined the war.
Axis Forces
The Axis powers consisted of Germany, Italy, and Japan. These nations formed alliances and coordinated their military efforts to achieve their expansionist goals.
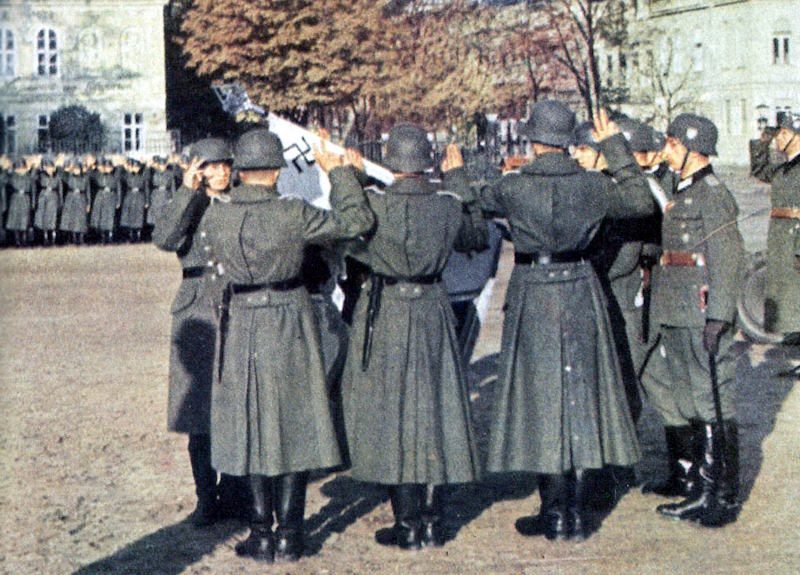

German Armed Forces
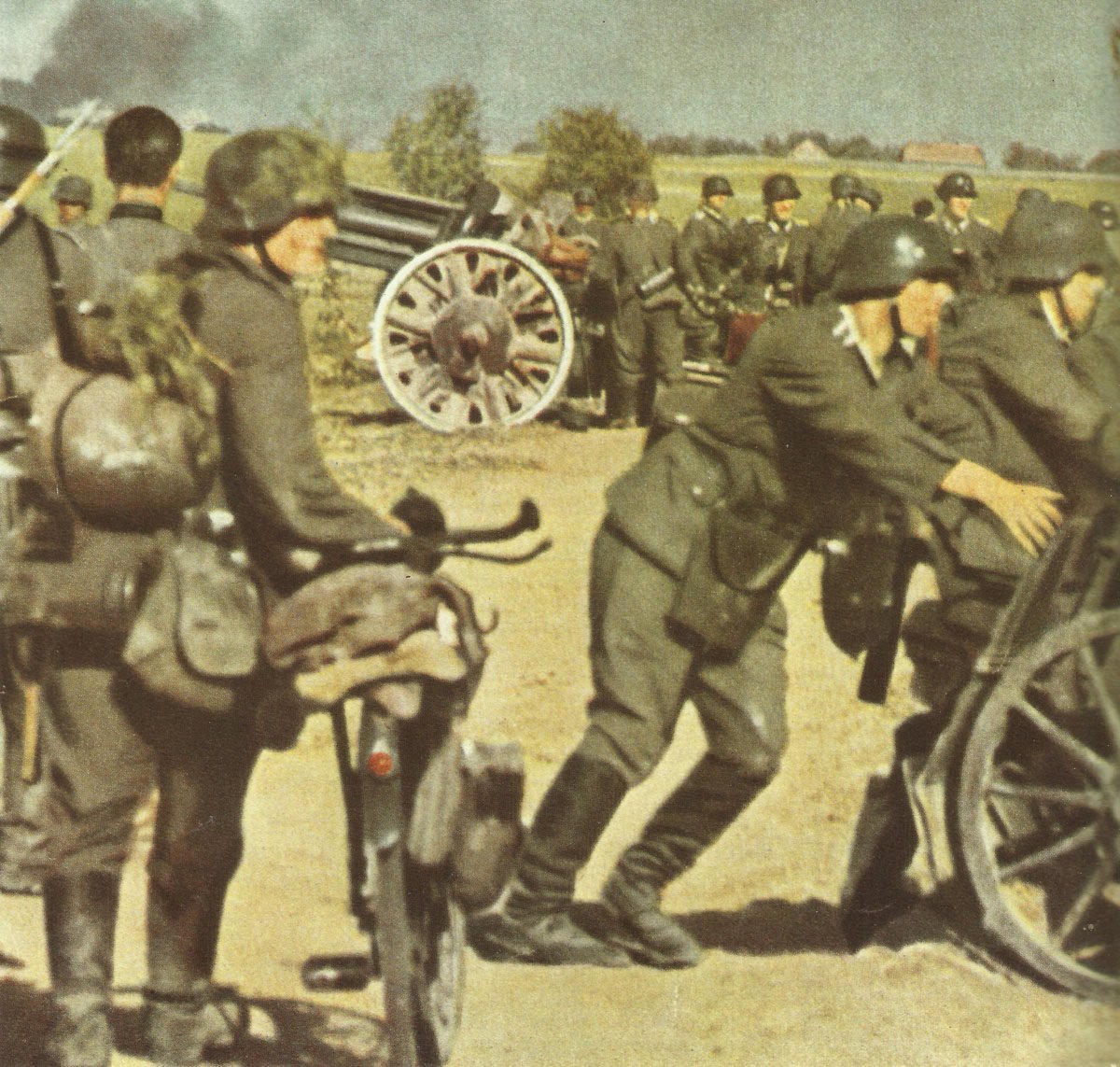
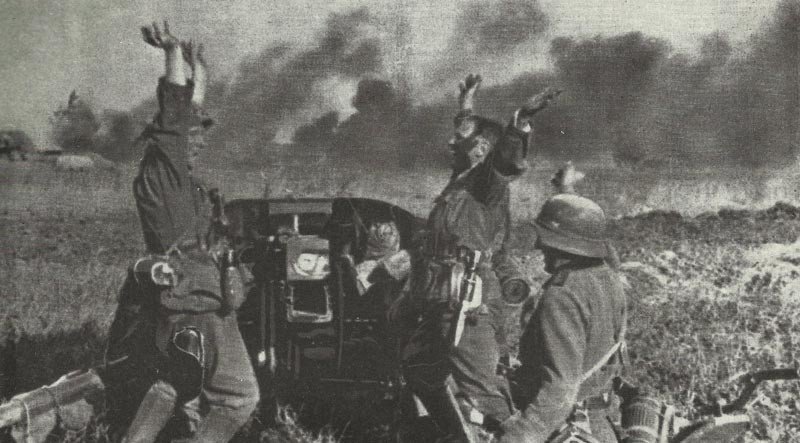
The German armed forces, known as the Wehrmacht, were highly disciplined and well-equipped. They consisted of the Army, Navy, and Air Force. The German Army, under the leadership of Adolf Hitler, launched several successful military campaigns in the early years of the war, but ultimately faced defeat on multiple fronts.
Italian Armed Forces
The Italian armed forces were initially ill-prepared for the demands of a global conflict. However, they played a significant role in the Mediterranean theater, particularly in North Africa. The Italian Army, Navy, and Air Force fought alongside their German counterparts but faced numerous setbacks.
Japanese Armed Forces
The Japanese armed forces, including the Imperial Japanese Army and Navy, were highly aggressive and expansionist. They launched surprise attacks on Pearl Harbor, the Philippines, and other territories, bringing the United States into the war. The Japanese forces fought fiercely in the Pacific theater but were ultimately defeated by the combined efforts of the Allied forces.
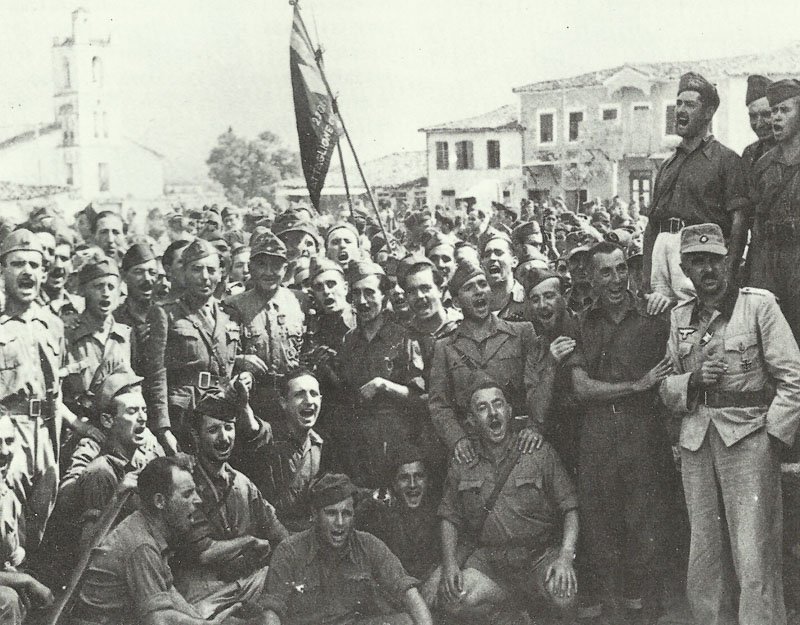
Allied Forces
The Allied forces were composed of nations that opposed the Axis powers, primarily Germany, Italy, and Japan. The major Allied powers included the United States, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and China.
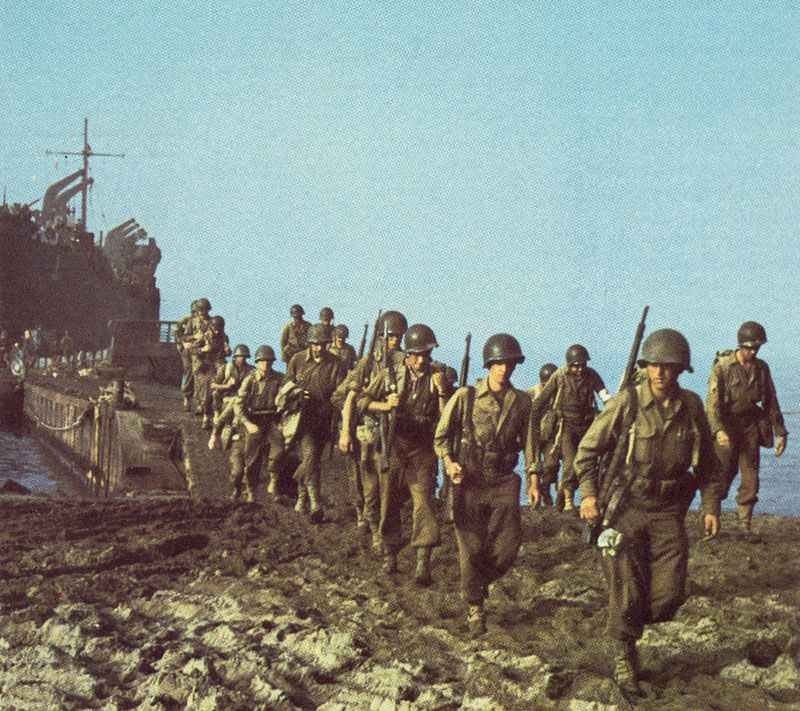

United States Armed Forces
The United States played a pivotal role in the Second World War, both in terms of manpower and resources. Its armed forces consisted of the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, and Army Air Forces. The Army was responsible for ground operations, while the Navy and Marine Corps focused on naval warfare and amphibious assaults. The Army Air Forces provided air support and conducted strategic bombing campaigns.
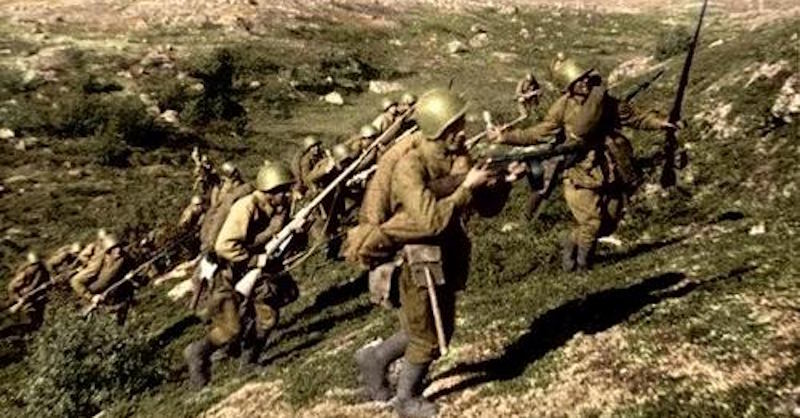
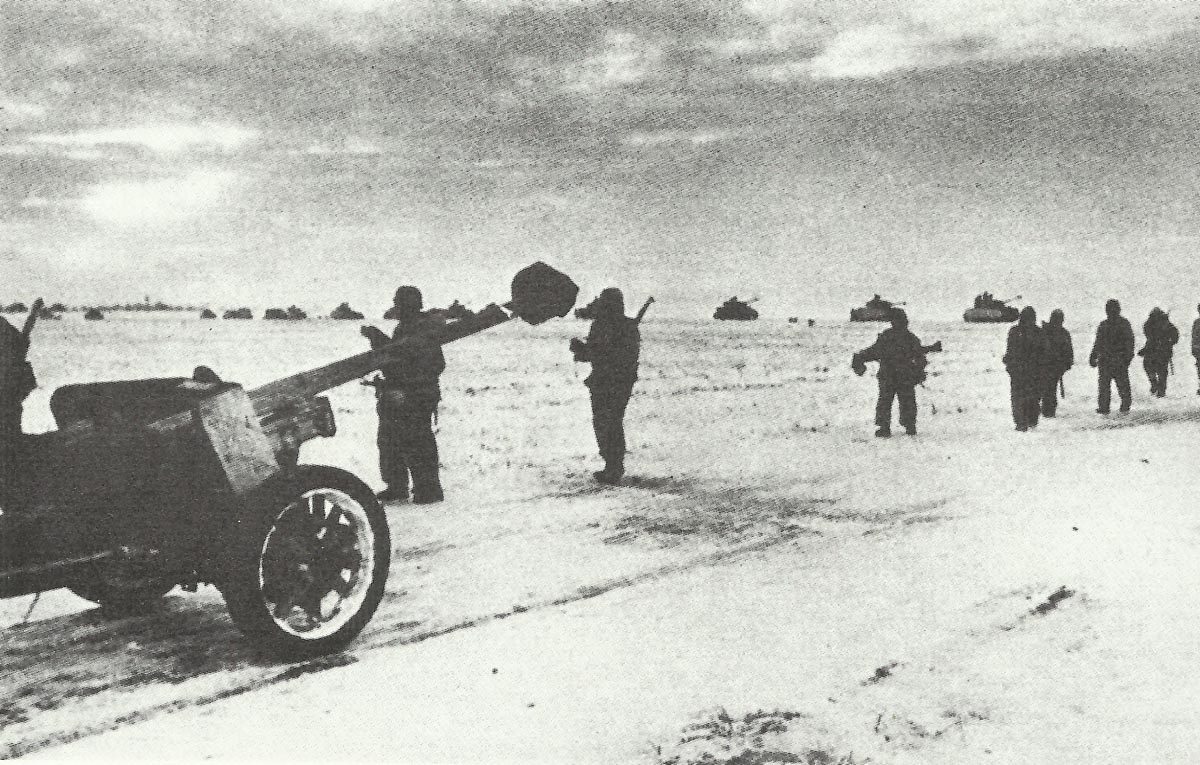
Soviet Armed Forces
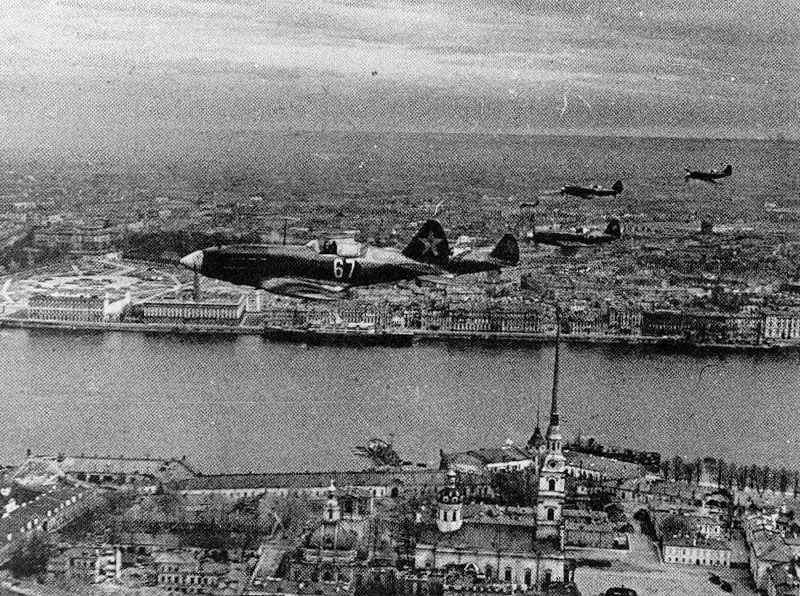
The Soviet Union had the largest armed forces in the world during the Second World War. The Red Army, as it was known, played a crucial role in the Eastern Front, where the majority of the fighting against Germany took place. The Soviet armed forces consisted of the Army, Air Force, and Navy.
British Armed Forces
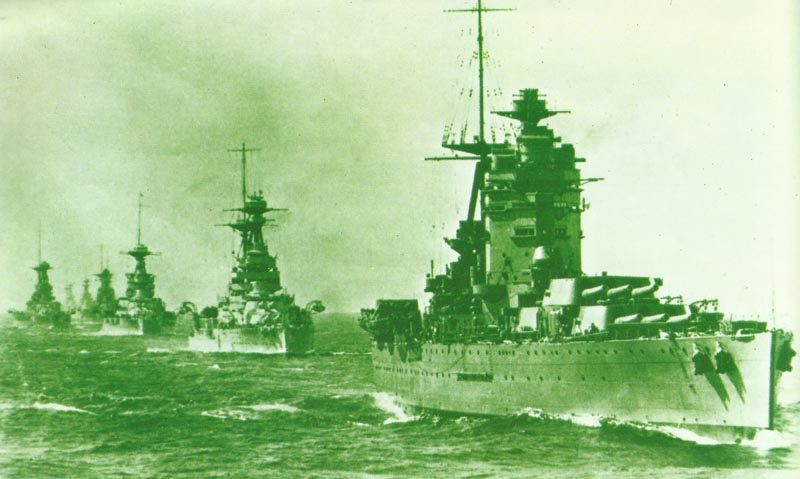
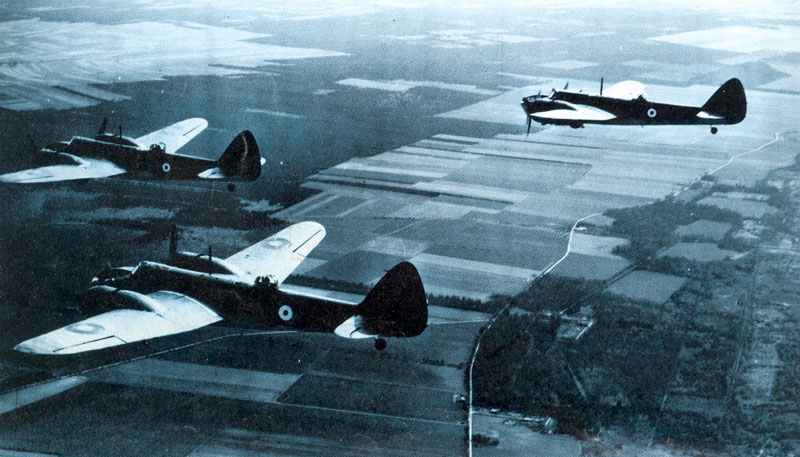
The British armed forces were instrumental in the Allied victory. The British Army fought in various theaters of the war, including North Africa, Italy, and Northwest Europe. The Royal Navy played a vital role in protecting supply lines and conducting naval operations. The Royal Air Force provided air support and played a significant role in the Battle of Britain.
Chinese Armed Forces
The Chinese armed forces, primarily the National Revolutionary Army, fought against Japanese aggression in the Pacific theater. Despite facing numerous challenges, they played a crucial role in tying down Japanese forces and diverting their attention from other fronts.
Other Allied Powers
Nations such as Canada, Australia, New Zealand, India, South Africa, Poland, Greece, Belgium, Norway, the Netherlands, and others also contributed troops and resources to the Allied cause.
Major Belligerents and Leaders
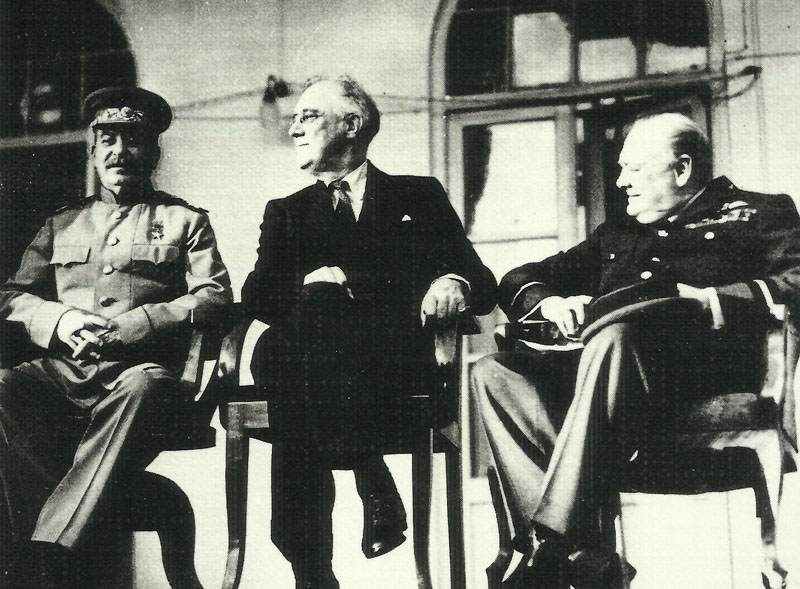

World War II was characterized by the monumental struggle between the Allied Powers, which included some of the world’s major powers, and the Axis Powers, recognized for their militaristic expansions and aggressive tactics. The leaders of these alliances became iconic figures who symbolized their nations’ ideologies and war efforts.
Allied Powers: Leadership and Coalition
The Allied Powers were led by a coalition of countries primarily including the United States, Great Britain, Soviet Union, France, and China.
Their leadership was marked by significant figures such as Winston Churchill of Britain, Franklin D. Roosevelt followed by Harry S. Truman of the United States, Joseph Stalin of the Soviet Union, Charles de Gaulle of France, and Chiang Kai-shek of China.
- United States: Roosevelt and then Truman
- Great Britain: Winston Churchill
- Soviet Union: Joseph Stalin
- France: Charles de Gaulle
- China: Chiang Kai-shek
Axis Powers: Expansion and Aggression
Conversely, the Axis Powers comprised a trio of nations led by dictatorial regimes including Germany, Italy, and Japan.
These countries were directed by Adolf Hitler, Benito Mussolini, and a militarist leadership in Japan, respectively. The Axis leaders aimed to expand their territories and influence, and their aggressive actions across various continents initiated and intensified global conflict.
- Germany: Adolf Hitler
- Italy: Benito Mussolini
- Japan: Emperor Hirohito and the militarist government
Key Military Operations
The effectiveness of military operations during World War II was instrumental in shaping the outcome of the war. These operations were complex, large-scale, and often pivotal in the various theaters of battle including Europe, the Pacific, and North Africa.
European Strategic Campaigns
-
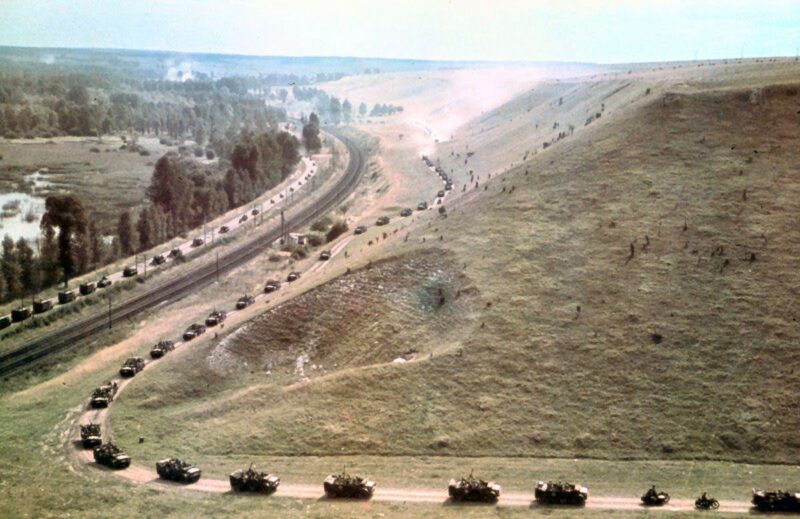
Operation Barbarossa: Initiated on June 22, 1941, this was Nazi Germany’s invasion of the Soviet Union and marked one of the largest military operations in history.
It involved around 4 million Axis powers’ troops and spanned across a front that exceeded 2,900 kilometers.
-
Battle of Britain: Fought predominantly in the air from July to October 1940, the Royal Air Force defended the United Kingdom against large-scale attacks by Nazi Germany’s air force, the Luftwaffe. It was the first major campaign to be fought entirely by air forces.
-
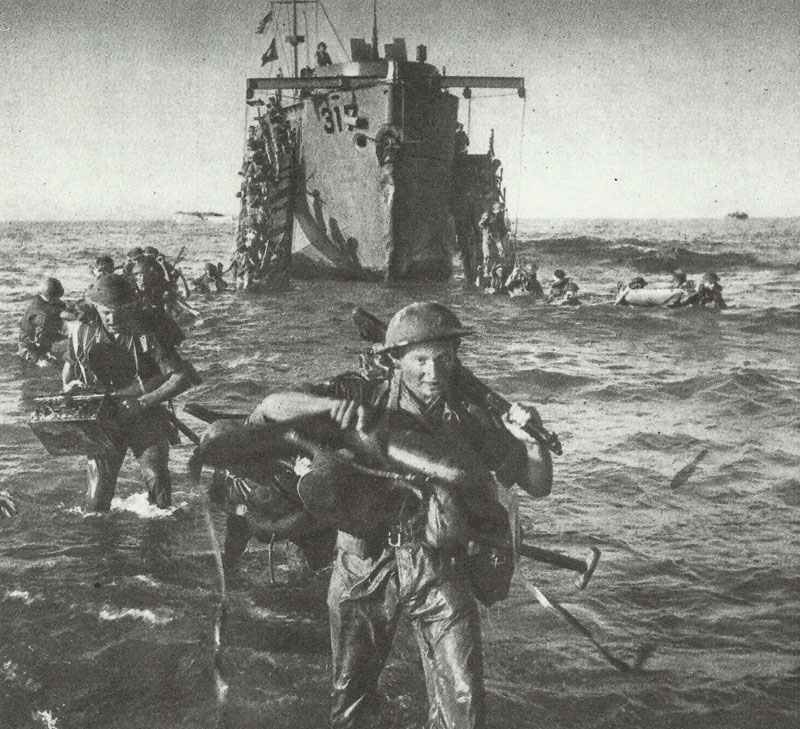
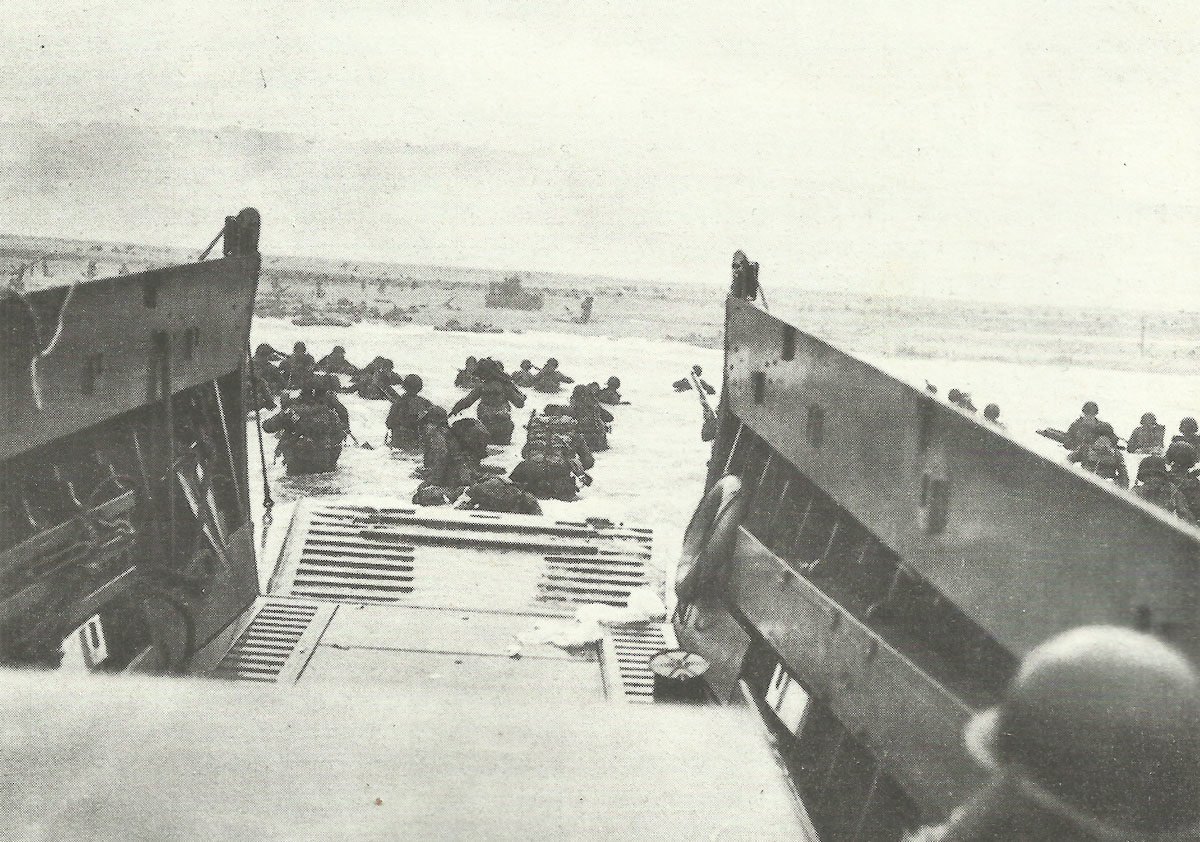
Normandy Invasion (D-Day): On June 6, 1944, Allied forces launched a combined naval, air, and land assault on Nazi-occupied France. Referred to often as D-Day, this operation marked the start of the liberation of Western Europe from Nazi control.
-
Battle of the Bulge: This major German offensive campaign launched through the densely forested Ardennes region of Wallonia in Belgium, France, and Luxembourg on the Western Front toward the end of the war, in December 1944.
Pacific Island Campaigns
-
Pearl Harbor: The surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service against the United States naval base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, on December 7, 1941, led the United States to officially enter the Pacific War.
-
Hiroshima and Nagasaki: The United States dropped atomic bombs on these two Japanese cities on August 6 and August 9, 1945. They were the only instances of nuclear weapons used in war to date and contributed to the end of the Pacific War.
North African and Italian Campaigns
-
North African Campaign: From 1940 to 1943, this campaign was a series of battles for control of the Suez Canal and the access to oil from the Middle East and raw materials from Asia.
-
It included operations in the Libyan and Egyptian deserts (Western Desert Campaign or Desert War) and in Morocco and Algeria (Operation Torch).
-
Italian Campaign: Starting with the Allies’ invasion of Sicily in July 1943, this campaign aimed to remove Fascist Italy from the war, secure the central Mediterranean, and divert German divisions from the northwest Europe campaign. The fall of Sicily led to the ousting of Mussolini and Italy’s eventual surrender.
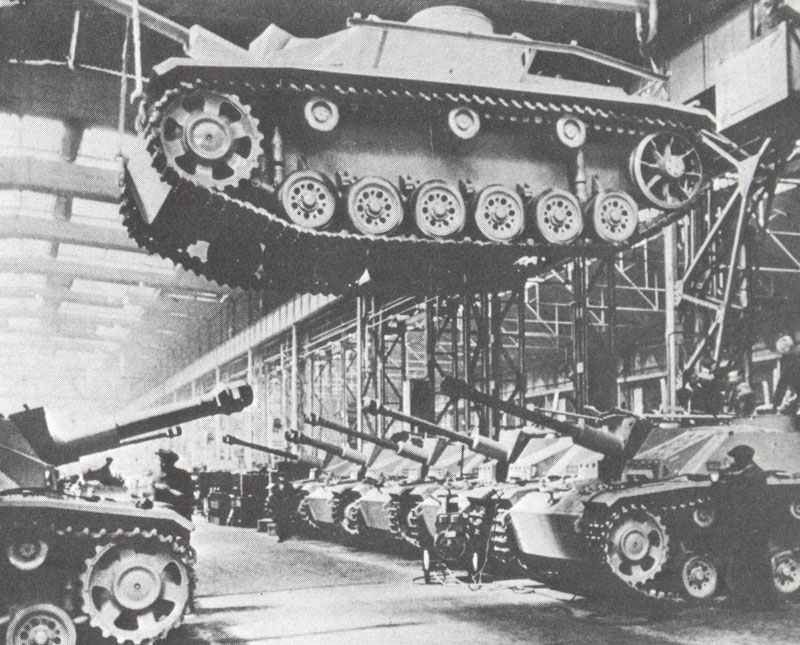
Armed Forces and Warfare Evolution
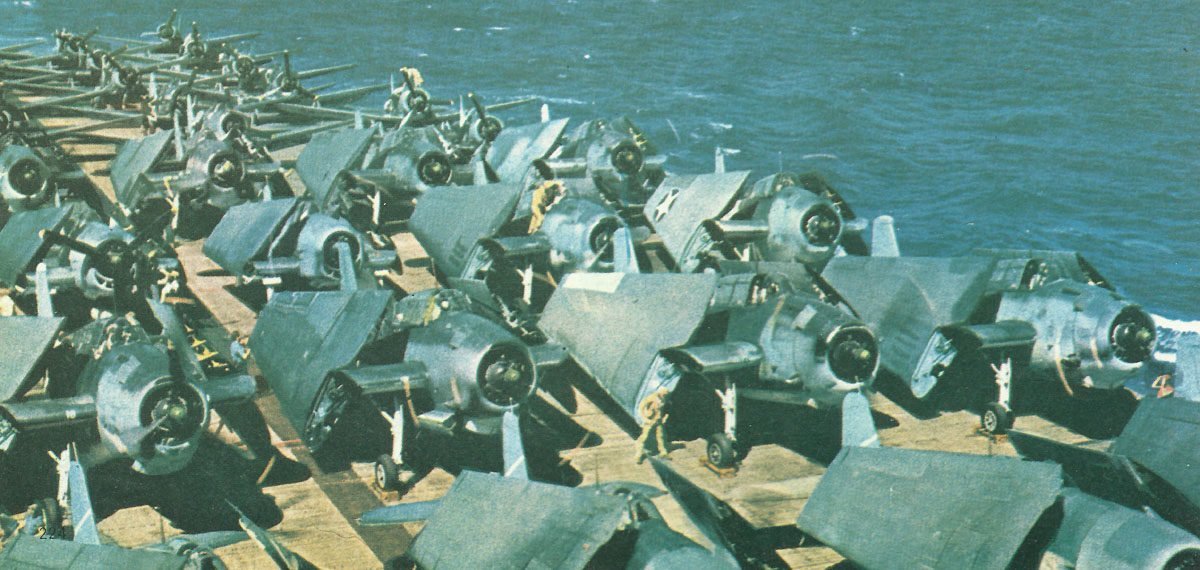

The evolution of armed forces during World War II brought significant advancements in technology and strategy that profoundly affected naval and aerial capabilities, infantry tactics, and intelligence systems.
Advancements in Navy and Aviation
The Navy and air forces underwent extensive technological and tactical transformations in World War II.
Aircraft carriers became the principal vessels, projecting power far beyond the range of traditional battleships.
The utilization and development of aircraft such as bombers and fighter planes advanced rapidly, with the Army Air Forces playing vital roles in aerial warfare.
Technologies like radar vastly improved fleet defense and permitted air attacks at night and in bad weather, altering naval strategies.
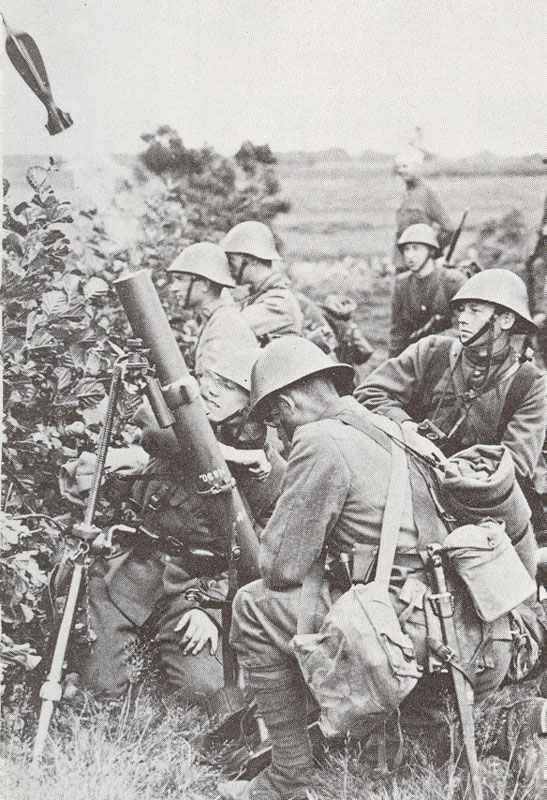
Infantry and Ground Strategies
Ground forces saw an overhaul in organization and combat tactics. The integration of infantry, artillery, and mechanized units led to highly effective combined arms strategies.
Armies adopted new formations to respond to the fast-paced and destructive nature of the conflict.
The evolution of maps and reconnaissance enabled ground units to maneuver more effectively in diverse terrains, and this knowledge was crucial in major battles such as the defense of the Suez Canal.
Intelligence and Communication
World War II marked a leap in intelligence gathering and communication, impacting military operations and outcomes.
Encryption technologies like the Enigma machine and subsequent code-breaking efforts by Allied forces were crucial.
Intelligence shaped decisions from high command to individual soldiers on the ground, affecting both the grand strategy and minor tactics that dictated the control or surrender of territories, impacting sovereignty across nations.
The organization and distribution of intelligence became as vital as the information itself.
Conclusion
The armed forces of the Second World War played a crucial role in shaping the outcome of the conflict. The Allied forces, led by the United States, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and China, ultimately emerged victorious over the Axis powers. The sacrifices and determination of these armed forces are a testament to the resilience of the human spirit in the face of adversity.
It is important to remember and honor the brave men and women who served in these armed forces, as their contributions paved the way for a more peaceful world.
References and literature
The Armed Forces of World War II (Andrew Mollo)
Operation Barbarossa: the Complete Organisational and Statistical Analysis, and Military Simulation, Volume I – IIIB (Nigel Askey)
Verbände und Truppen der deutschen Wehrmacht und Waffen-SS im Zweiten Weltkrieg 1939-1945 (Bundesarchiv-Militärarchiv und Arbeitskreis Wehrforschung)
World War II – A Statistical Survey (John Ellis)
Das Deutsche Reich und der Zweite Weltkrieg (10 Bände, Zentrum für Militärgeschichte)
Krieg der Panzer (Piekalkiewicz)
Luftkrieg (Piekalkiewicz)