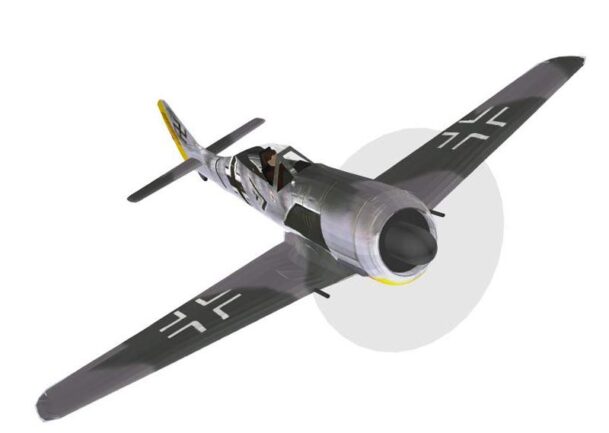
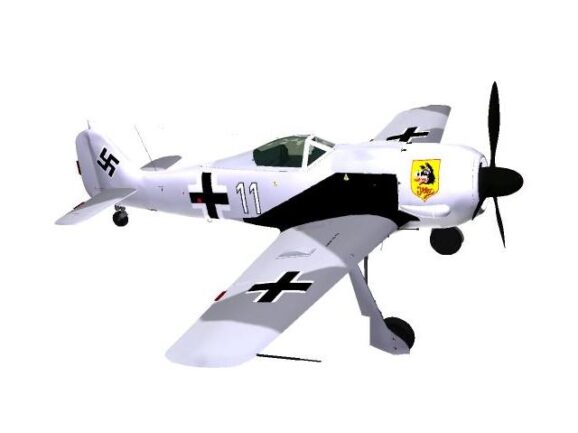
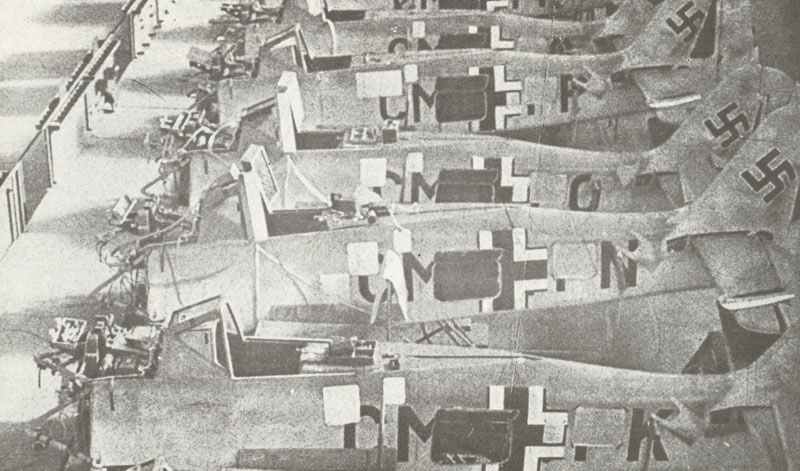
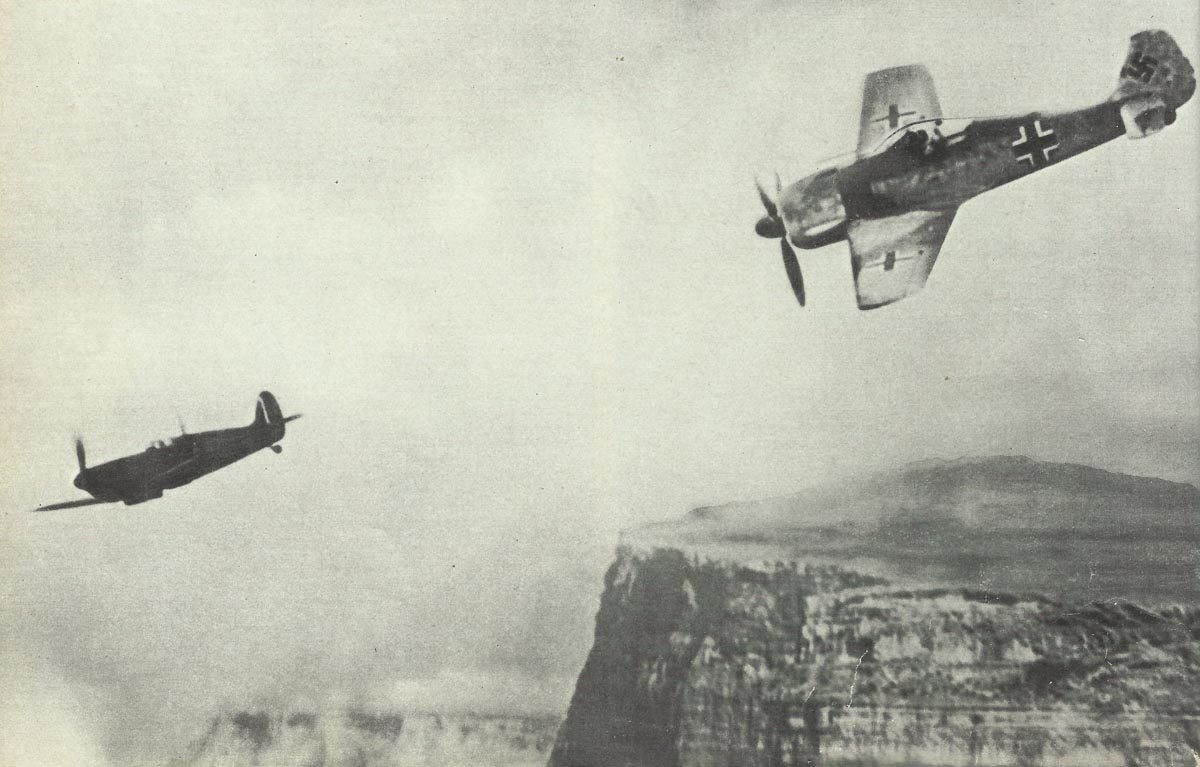
Focke-Wulf A fighter planes from the German Luftwaffe in World War II.
History, development, service, specifications, pictures and 3D model.
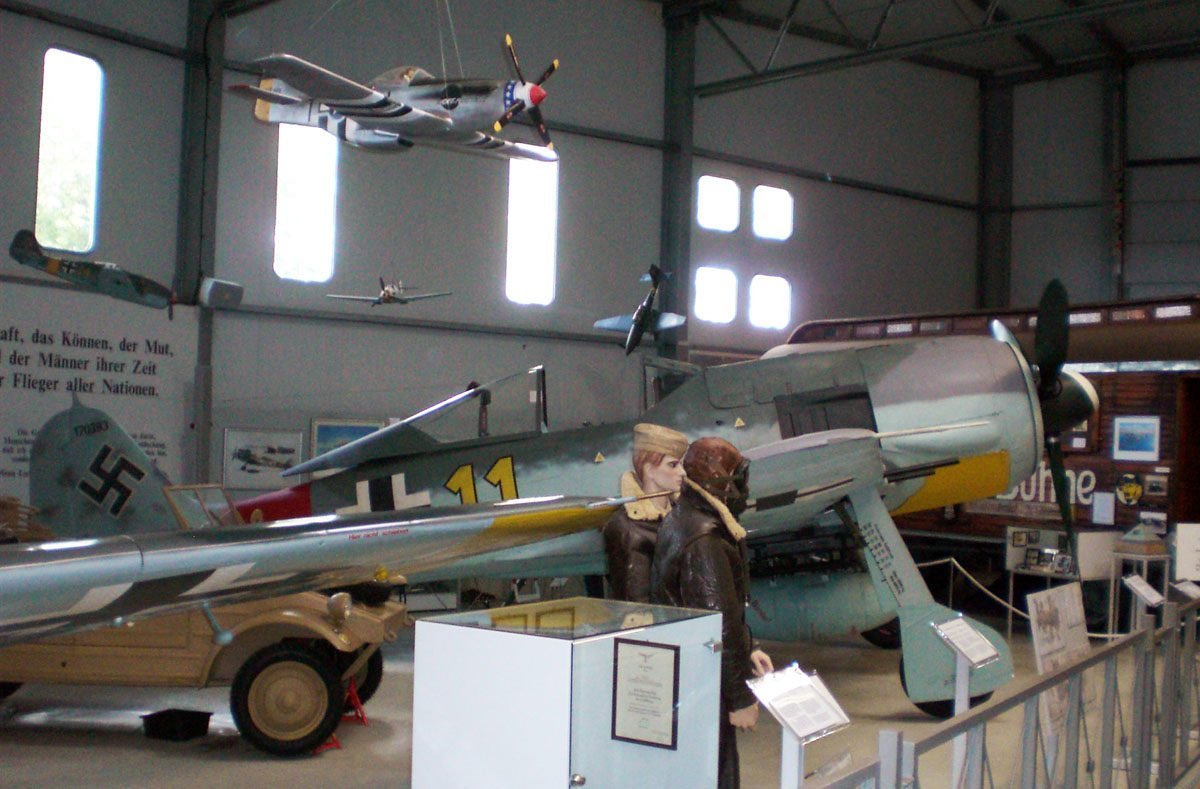

Focke-Wulf Fw 190 A
Table of Contents
Focke-Wulf Fw 190 A-series
Type: German Luftwaffe fighter plane and fighter-bomber.
The Focke-Wulf Fw 190 was a German single-seat, single-engine fighter aircraft designed by Kurt Tank in the late 1930s and widely used during World War II. Along with its well-known counterpart, the Messerschmitt Bf 109, the Fw 190 became the backbone of the Luftwaffe’s Jagdwaffe (Fighter Force).
The ‘A’ series was the first version of the Fw 190 to be produced, and was powered by the BMW 801 radial engine. The Fw 190A was well-liked by its pilots due to its maneuverability and powerful armament, which typically consisted of four wing-mounted MG 151 20mm cannons and two MG 131 13mm machine guns mounted in the engine cowling.
Overview
– It was in service from 1941 to 1945, serving in all European theaters of the war.
– The Fw 190A was particularly effective as a fighter-bomber (Jabo), and specialized attack versions like the Fw 190F and G were developed.
– It was one of the first fighters to feature a wide-track retractable landing gear, which improved ground handling and stability.
– Noted Fw 190 pilots included Otto Kittel, Walter Nowotny, and Erich Rudorffer.
– The Fw 190A was also used by the air forces of Hungary, Turkey, and Romania during WWII.
The Fw 190A proved to be a formidable opponent to Allied fighters, particularly at low and medium altitudes, and it continued to be developed and improved throughout the war.
History
The Fw 190 V1 (D-OPZE), developed by Dipl-Ing Kurt Tank and Oberingenieur R Blaser to a 1938 RLM demand, initially flew on 1 June 1939, this plane and also the V2 equally being operated by a 1,550 hp BMW 139 two-row radial power plant. Following planes, using the bigger and more potent BMW 801C engine, contained 40 pre-series Fw 190 A-0s requested in 1940, the majority of them with a 3 ft 3.4in increased wing span which afterward became common.
Full-scale manufacturing began with 100 4-gun Fw 190 A-1s, which joined operation with II./JG26 in summer 1941, and ongoing using the better-armed A-2 and A-3, the second getting 6 guns (2 MG 151/20 and 4 MG 17) along with a BMW 801D-2 power plant.
Despite the fact that flown some time before WW2 this slim small fighter had been unidentified to the Allies and prompted an unpleasant shock when initial encountered over France in 1941. Undoubtedly, it had been so significantly better than the larger and much slower Spitfire V that the first time the RAF believed not just outnumbered, however crushed technically.
It was faster compared to every Allied fighter operating, got a good deal stronger armament, had been incredibly robust, had superb power of maneuver and excellent pilot view. It had been furthermore a really tiny target, much lighter than every Allied fighter, together with a reliable wide track landing gear in contrast to the Me 109. Luckily for the Allies, it never replaced the Me 109G, however aside from the fighter-bomber Fw 190 F the majority of them were in action in the West or Mediterranean.
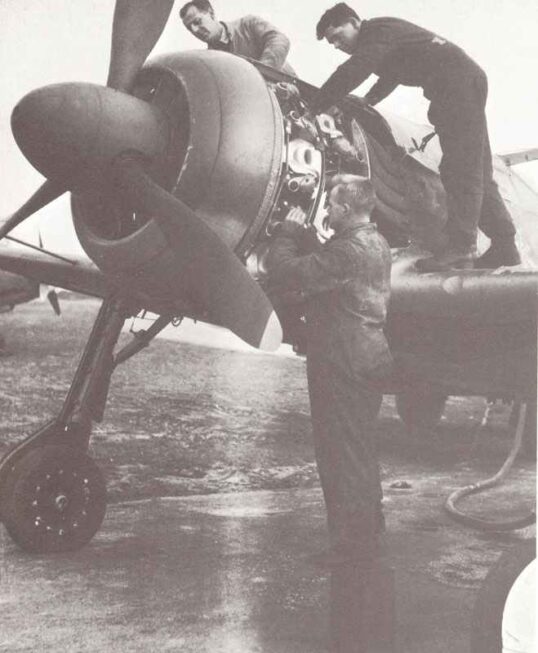


Initial operational use was made of the Focke-Wulf 190 in the fighter-bomber role, in low-level hit-and-run raids over southern England throughout 1942. The A-4 models (2,100 hp boosted BMW 801D-2) provided the A-4/U8 fighter-bomber (carrying a drop-tank and 1,102 lb (500 kg) of bombs, with armament decreased) and the A-4/R6 bomber interceptor with under-wing rocket projectiles.
By the end of the year 1942 around 2,000 Focke-Wulf 190 were produced and had been in extensive action in Europe, the Mediterranean as well as on the Eastern Front.
The A-5 was manufactured mainly for close support; the A-6 and A-7 consisted of more advancements in firepower; the A-8s were largely bomber interceptors or Zerstörer, however some were used as all-weather fighters while others as 2-seat trainers.
The Focke-Wulf 190 B and C models had been rejected, soon after prototypes with boosted BMW 801D or DB 603A engines, in preference to the long-nosed Fw 190 D or ‘Dora’.
Users: Germany (Luftwaffe), Croatia, Slovakia, Turkey (during WW2).
Animated 3D model Focke-Wulf A-3
Specifications Focke-Wulf Fw 190 A-6, A-8
Specifications:
A-6, A-8 | Specification |
|---|---|
Type | fighter, fighter-bomber |
Power plant | one 1,700 hp (2,100 hp boosted) BMW 801D-2 18-cylinder two-row radial engine (A-8), BMW 801TS (A-6) |
Accommodation | 1 |
Wing span | 34 ft 5.6 in (10.51 m) |
Length overall | 29 ft 4.4 in (8.95 m) |
Height overall | 12 ft 11.9 in (3.96 m) |
Wing area | 196.98 sq/ft (18.30 m²) |
Weight empty equipped | 7,650 lb (3,470 kg) |
Weight loaded | 9,656 lb (4,380 kg) |
Maximum wing loading | 49.02 lb/sq ft (239.34 kg/m²) |
Maximum power loading | 5.68 lb/hp (2.57 kg/PS) |
Maximum speed | A-8: 408 mph at 20,670 ft (657 km/hr at 6,300 m); A-6: 424 mp at 34,450 ft (683 km/hr at 10,500 m) |
Initial climb | 2,350 ft/min (716 m/min) |
Service ceiling | 37,400 ft (11,410 m) |
Range | 497 miles (800 km) |
Armament:
Specification | A-6 | A-8 |
|---|---|---|
above engine | 2 x 7,92mm MG17 (1,200 rpm, velocity 2,477 ft.sec) | 2 x 13mm MG131 (930 rpm, velocity 2,461 ft.sec) |
in wing roots | 2 x 20mm MG151/20 (720 rpm, velocity 1,920 ft.sec) | 2 x 20mm MG151/20 (720 rpm, velocity 1,920 ft.sec) |
in outer wings | 2 x 20mm MG151/20 (720 rpm, velocity 1,920 ft.sec) | 2 x 20mm MG151/20 or 2 x 30mm MK108 (650 rpm, velocity 1,705 ft.sec) |
external load | 1 x 2,200 lb (1,100 kg) bomb (fighter-bombers) | 1 x 1,100 lb (500 kg) bomb on centreline |
Service statistics:
Focke-Wulf 190 | figures |
|---|---|
First flight V1 | 1 June 1939 |
Production delivery (A-1) | September 1940 |
Service delivery (A-1) | summer 1941 |
Production delivery (A-6) | June 1943 |
Production delivery (A-8) | end of 1943 |
Final delivery | 1945 (in France 1946) |
Total production figure (all) | 20,001 (2,000 end of 1942) |
Accepted by Luftwaffe 1/39-12/44 | 16,724 |
Production 1941 (all fighters) | 228 |
Production 1942 (all fighters) | 1,850 |
Production 1943 (all fighters) | 2,171 |
Production 1944 (all fighters) | 7,488 |
Production 1945 (all fighters) | 1,630 |
in First Line Units 20.9.42 | 509 |
in First Line Units 31.12.42 | 580 |
in First Line Units 10.1.45 | 1,561 |
References and literature
Combat Aircraft of World War II (Bill Gunston)
Technik und Einsatz der Kampfflugzeuge vom 1. Weltkrieg bis heute (Ian Parsons)
Das große Buch der Luftkämpfe (Ian Parsons)
Luftkrieg (Piekalkiewicz)
Flugzeuge des 2. Weltkrieges (Andrew Kershaw)
German Aircraft of World War 2 in Colour (Kenneth Munson)
Warplanes of the Luftwaffe (David Donald)
The Luftwaffe Album, Bomber and Fighter Aircraft of the German Air Force 1933-1945 (Joachim Dressel, Manfred Griehl)
Luftwaffe Handbook (Dr Alfred Price)
The Encyclopedia of Weapons of World War II (Chris Bishop)
Focke-Wulf Fw 190 Aces of the Western Front (J. Weal)