German super heavy battle tank Maus (‘Mouse’).
History, development, service, specifications, statistics and pictures.
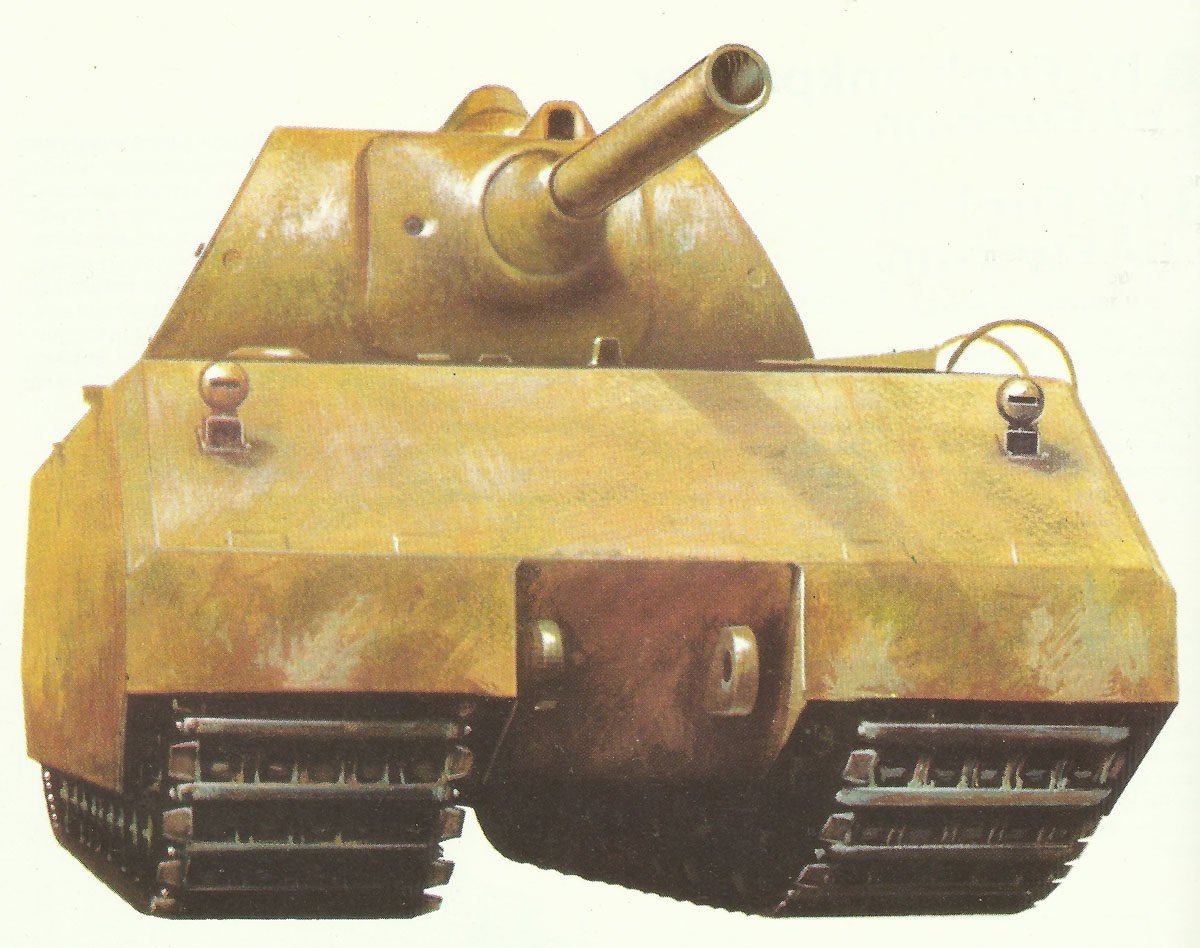

Panzerkampfwagen Maus (Mouse).
Type: Super heavy battle tank.
History
Table of Contents

On June 8, 1942, Dr Ferdinand Porsche in Stuttgart received an order from Hitler to begin designing a super heavy main battle tank armed with a 12.8-cm cannon and a coaxial 7.5-cm cannon in a turret, which would have the largest possible armor.
Porsche was head of the German Panzer Commission at that time and also personally had a great influence on Hitler, who was fascinated by his technical ingenuity. So he was successfully urged by Dr Porsche to develop a super heavy tank.
However, Porsche’s technical refinements were often too complex for combat vehicles for the battlefield, which already turned out in his design for the Tiger tank and later King Tiger tank and also led to the super heavy Ferdinand tank destroyer (or ‘Elefant’ = ‘Elephant’). The majority of German tank designers and tacticians were also not very enthusiastic about this project.
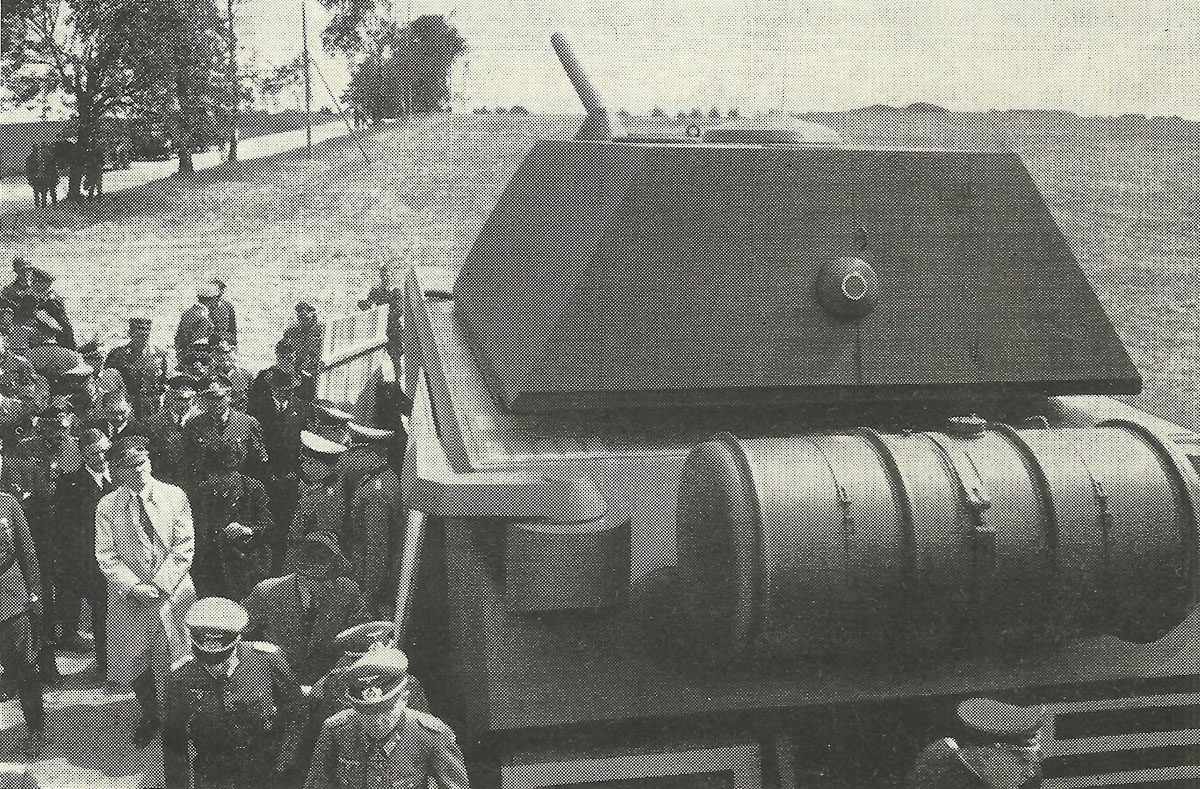
At the beginning the vehicle was called Mammut (‘Mammoth’) or ‘Porsche project number 205’. Trials with prototypes were to begin as early as May 1943, but many difficulties arose. For example, the planned air-cooled engine could not be delivered, so that the prototype V1 had to be equipped with a modified MB509 aircraft engine and the V2 with a MB517 diesel engine. The longitudinal torsion bar suspension planned by Porsche had to be abandoned, because there was not enough space for the number of necessary stations to carry the constantly increasing weight of the vehicle.
Nevertheless, an order was placed for the construction of 150 series vehicles, which was cancelled soon in October 1943.
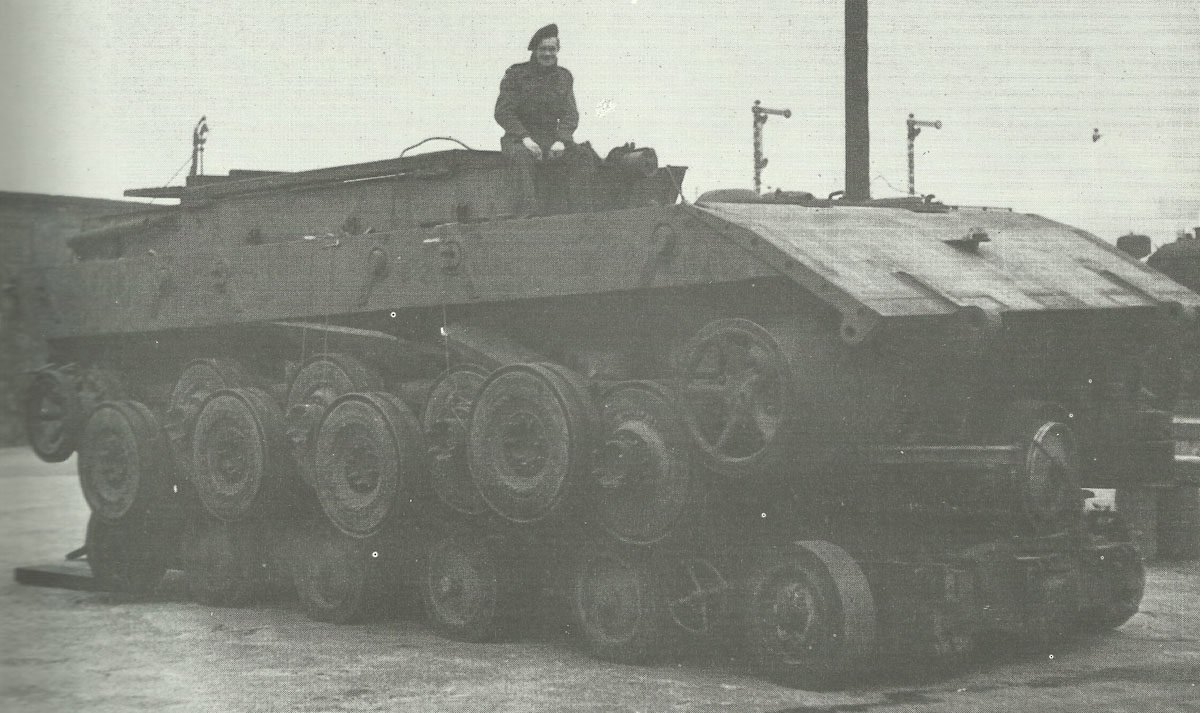

In June 1943, the Heereswaffenamt (Weapons office of the German Army) also ordered the so-called super heavy E-100 main battle tank from the Adler factories as a competitor product to the Maus. Hitler ordered the company to stop further development work on super heavy main battle tanks in 1944, however, and the work progressed only slowly. Only three men worked on the prototype, the chassis of which was finished until the end of the war.
However, construction of the first super heavy Maus main battle tank began at Alkett on August 1, 1943, and Krupp delivered the vehicle hull by mid-September. The first test drive with a turret dummy then took place on December 23, 1943, at Alkett, whereupon the vehicle was brought to Boeblingen near Stuttgart on January 10, 1944, for detailed tests.
Apart from the problems with the running gear, the testing was even quite successful and Hitler demanded the completion of the prototype with turret and armament. In June 1944 the vehicle was tested with a real turret and armament.
Also, these tests were very successful and so the prototype V1, called Maus I, went to the test site in Kummersdorf.
The prototype V2 without a turret, called Maus II, started trials in September 1944, but the engine was destroyed in an accident and could not be replaced before April 1945. Both prototypes were blown up before the arrival of the Red Army at Kummersdorf.
Nevertheless, at the end of the war there were nine prototypes with different construction progress and production plans for 150 units had been prepared.
The Maus ran on a spiral spring drive designed by Skoda and was designed to be armed with the 15-cm-KwK44 or 17-cm-KwK44 cannon.
To cross rivers – and since the mouse was too heavy for most bridges – the vehicle should be able to pass through them to a depth of 26.25 ft (8 meters) simply on the ground, whereby the power for an electric motor should be transmitted by a cable from another mouse on the river bank.
Specifications for Panzerkampfwagen Maus
Specifications:
Maus (Porsche 205) | Specification |
|---|---|
Type | super heavy battle tank |
Engine | MB509 V12 1,080 PS or MB517 Diesel |
Gearbox | 2 forward, 2 reverse |
Crew | 5 |
Turret crew | 3 |
Length | 33.1 ft (10.09 m) |
Width | 12 ft (3.67 m) |
Height | 12 ft (3.66 m) |
Weight | 188 tons |
Maximum speed | 12.4 mph (20 km/hr) |
Cross-country speed | ? |
Fuel consumption per 100 km | ? |
Fuel | ? |
Road radius | 115 miles (186 km) |
Cross-country radius | ? |
Vertical obstacle | 2.36 ft (0.72 m) |
Trench crossing | 14.75 ft (4.50 m) |
Fording depth | 26.25 ft (8.00 m) diving |
Turning circle | ? |
Climbing power | 30 ° |
Armor:
Maus (Porsche 205) | mm | angle |
|---|---|---|
Turret front | 240 | round |
Turret side | 200 | 30° |
Turret rear | 200 | 7° |
Turret top | 40 | 90° |
Upper hull front | 200 | 55° |
Upper hull side | 180+100 | 0° |
Upper hull rear | 180 | 38° |
Hull top | 40-80 | 90° |
Lower hull front | 200 | 35° |
Lower hull side | 180 | 0° |
Lower hull rear | 180 | 30° |
Hull bottom | 40-100 | 90° |
Gun mantlet | 240 | (Saukopfblende/round) |
Armament and Equipment:
Maus (Porsche 205) | Specification |
|---|---|
Main armament | 12.8-cm KwK44 L/55 (alternative 15cm KwK44 or 17cm KwK44) |
Rounds | 32 |
Traverse | 360° (electric power) |
Elevation | -7° bis +23° |
Muzzle velocity Pzgr | 2.821 ft/sec (860 m/sec) |
Muzzle velocity Pzgr43 | 2.772 ft/sec (845 m/sec) |
Shell weight Pzgr | 58.3 lb (26.4 kg) |
Shell weight Pzgr43 | 62.5 lb (28.3 kg) |
Secondary armament | 7.5-cm-KwK44 L/30.5 (200 rounds) and 1x7.92mm machine gun or 1x20mm cannon (each coaxial) |
Telescopic sight | ZF |
Radio | ? |
Penetration mm at 30° armor plates of 12,8-cm KwK44 L/55:
Range | Pzgr | Pzgr43 |
|---|---|---|
Penetration 100 meters | 189 mm | 187 mm |
Penetration 500 meters | 166 mm | 178 mm |
Penetration 1000 meters | 143 mm | 167 mm |
Penetration 1500 meters | 127 mm | 157 mm |
Penetration 2000 meters | 117 mm | 148 mm |
Video of the ‘Maus’ in action with computer games
In addition, the following video to the deployment of the Maus, Horten Ho 229 and Sturmpanzer II in a ‘realistic land battle’ of the free2play game War Thunder:
Who does not know the F2P tank and plane war game War Thunder can download it from here for free:
References and literature
Kraftfahrzeuge und Panzer der Reichswehr, Wehrmacht und Bundeswehr (Werner Oswald)
Encyclopedia of German Tanks of World War Two (P.Chamberlain, H.L.Doyle)
Panzer und andere Kampffahrzeuge von 1916 bis heute (Christopher F. Foss, John F. Milsom, Colonel John Stafford Weeks, Captain Georffrey Tillotson, Richard M. Ogorkiewicz)
Krieg der Panzer (Piekalkiewicz)











