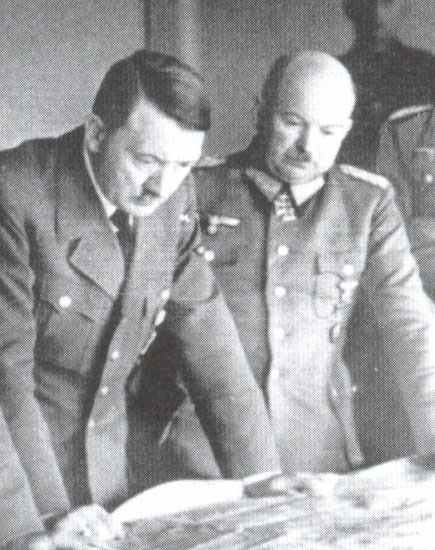
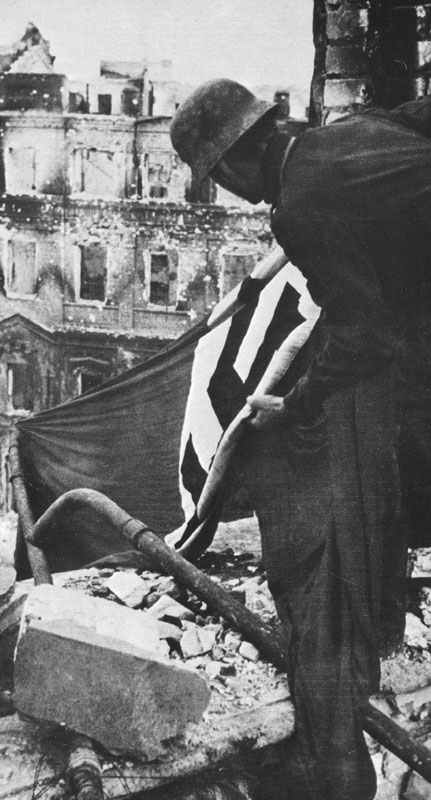
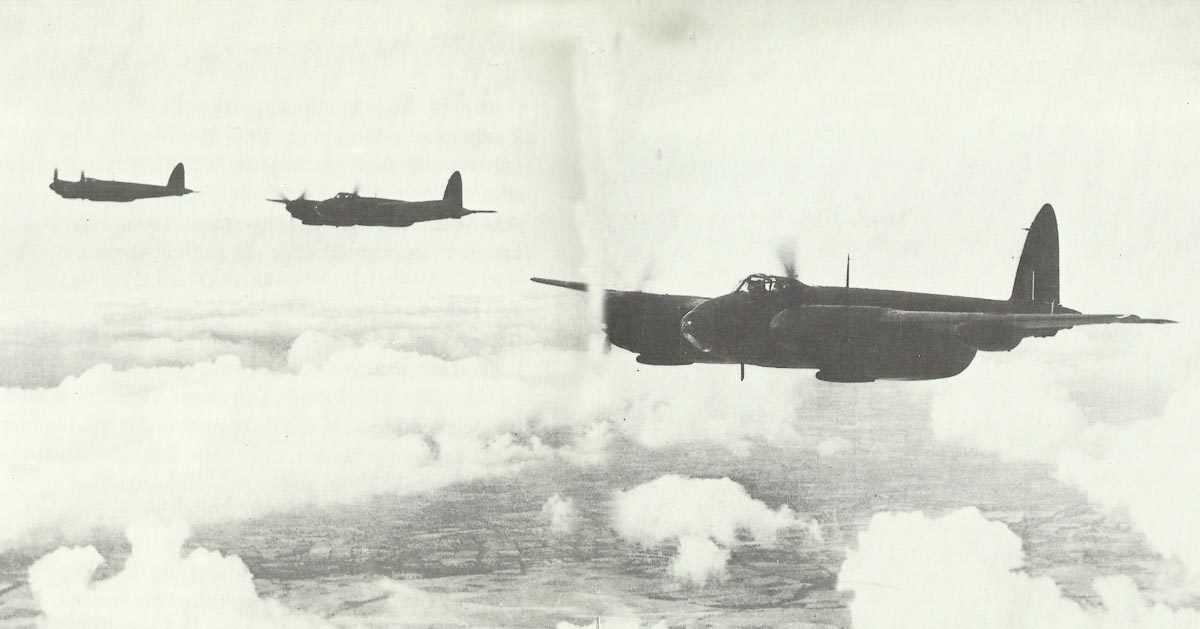
The World Wars 1914-18 and 1939-45.
Recent reports:
About WW2 Weapons
WW2 affected virtually almost any corner of the globe. In the six years between 1939 and 1945, some kind of 50 million people lost their lives, and hardly any who survived were not affected. It was the costliest and utmost widespread conflict the world has forever obtained.
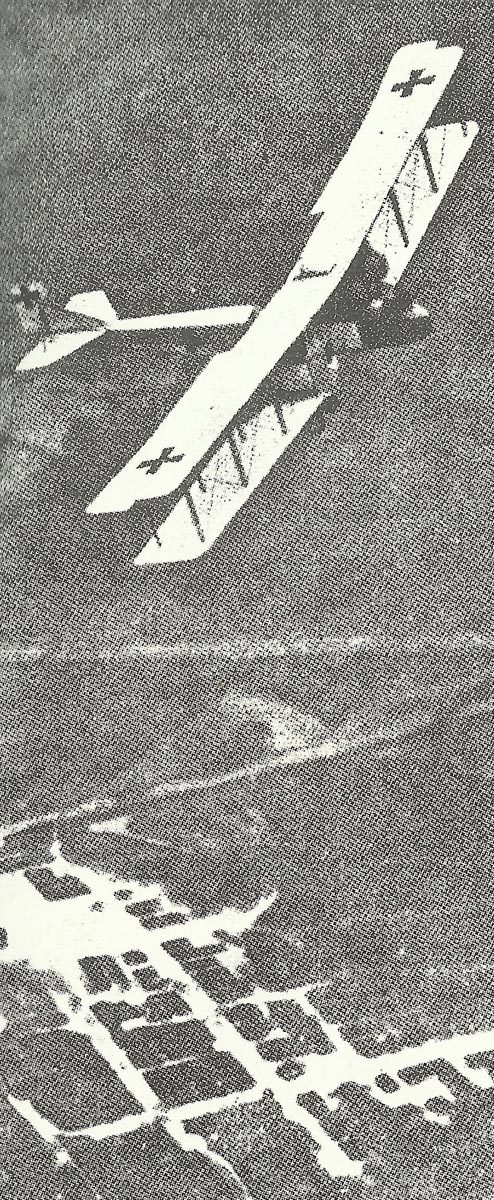
It was subsequently battled on ground, sea and in the air with weapons which in fact had first been used in World War One of 1914-18. Ironically, a far greater conflict was to come out from the burning embers of these ‘war to end all wars’, and with it huge innovations in technologies.
The countries engaged in WW2 finally owned the techniques, potential and weapons to fight every other in a much more powerful – and more deadly – manner.
However only Britain, her Empire allies as well as Germany were engaged during the full period (as well as, in fact, Japan and China since 1937). For all the other nations the conflict was of a shorter duration. The US and Japan, for example, were at war from December 1941 to August 1945 (and the USA was at the same time at war with Germany, until Hitler‘s defeat in May 1945).
The state of affairs was so complex, the skeins of partnerships and enmity so connected that it would require a really huge document in fact to illustrate the prospect.
Only one factor was less complicated and widespread to all the nations involved: the nature of the weapons that the soldier used to struggle their way to triumph – or defeat.
Of course, there were differences in detail of the WW2 weapons: the German Panzer V Panther was a very different tank from the US M4 Sherman, the Russian T-34, or the English Cromwell. But in fact they were all much the same – armored vehicles mounting powerful guns running on tracks.
The small arms with which the various opponent countries equipped their armies were totally different weapons in details too, but basically these were all guns for launching projectiles at high speed.
Simply speaking, lots of people would just say that guns are guns, bombs are bombs, aircraft are planes, and so on. But there is definitely even more to it than that, for the abilities to obtain victory or lose a war actually rested on these kinds of WW2 weapons’ qualities, just as a lot of as it did on the fighting abilities of those who employed them and on the strategic sense of those who directed them in their use.

General about WW2 Weapons:
All information, data, specifications and statistics used on the website WW2 Weapons have been compiled from a variety of sources and the large library of the author – who now lives on Crete for a long time – about military history and history, especially about the world wars, which has been built up over decades.
The most important source references and notes about additional literature can be found at the end for the most articles. To the best of our knowledge and belief, the most secure and reliable information and sources were used, which are also constantly updated and improved.
These data and specifications are used among other things for as accurate as possible historical military simulations, such as the war game WW2 Total. The photos are mostly ‘public domain’, but partly also property of the author.
The author therefore asks for understanding that he can’t handle additional requests for the sources or pictures beyond that due to time constraints and provides the information and its sources to the internet community as ‘as published’, i.e. either the visitor of this website considers it helpful and agrees with it over, or just leaves it.
Discussions and suggestions for improvement are nevertheless welcome and can be held below the respective reports.