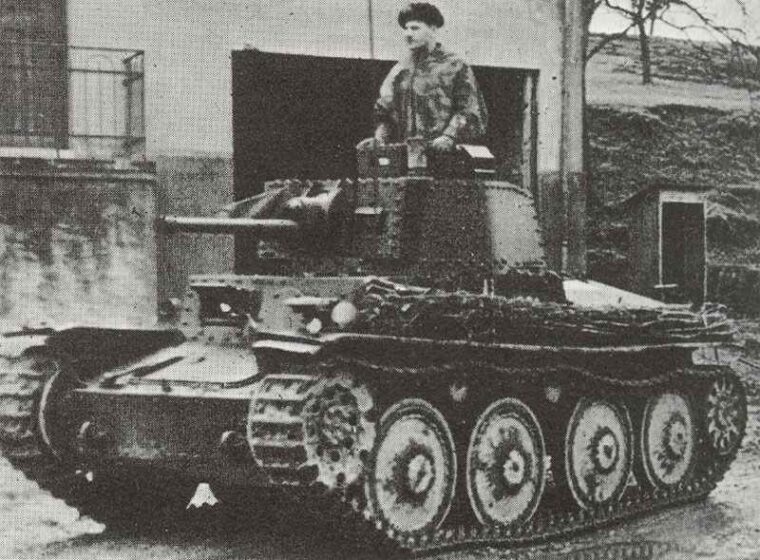
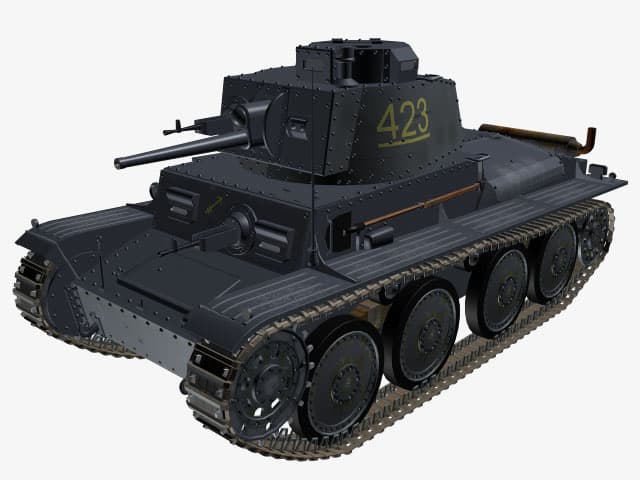
German ex-Czech light tank PzKpfw 38(t).
History, development, service, specifications, pictures and 3D model.
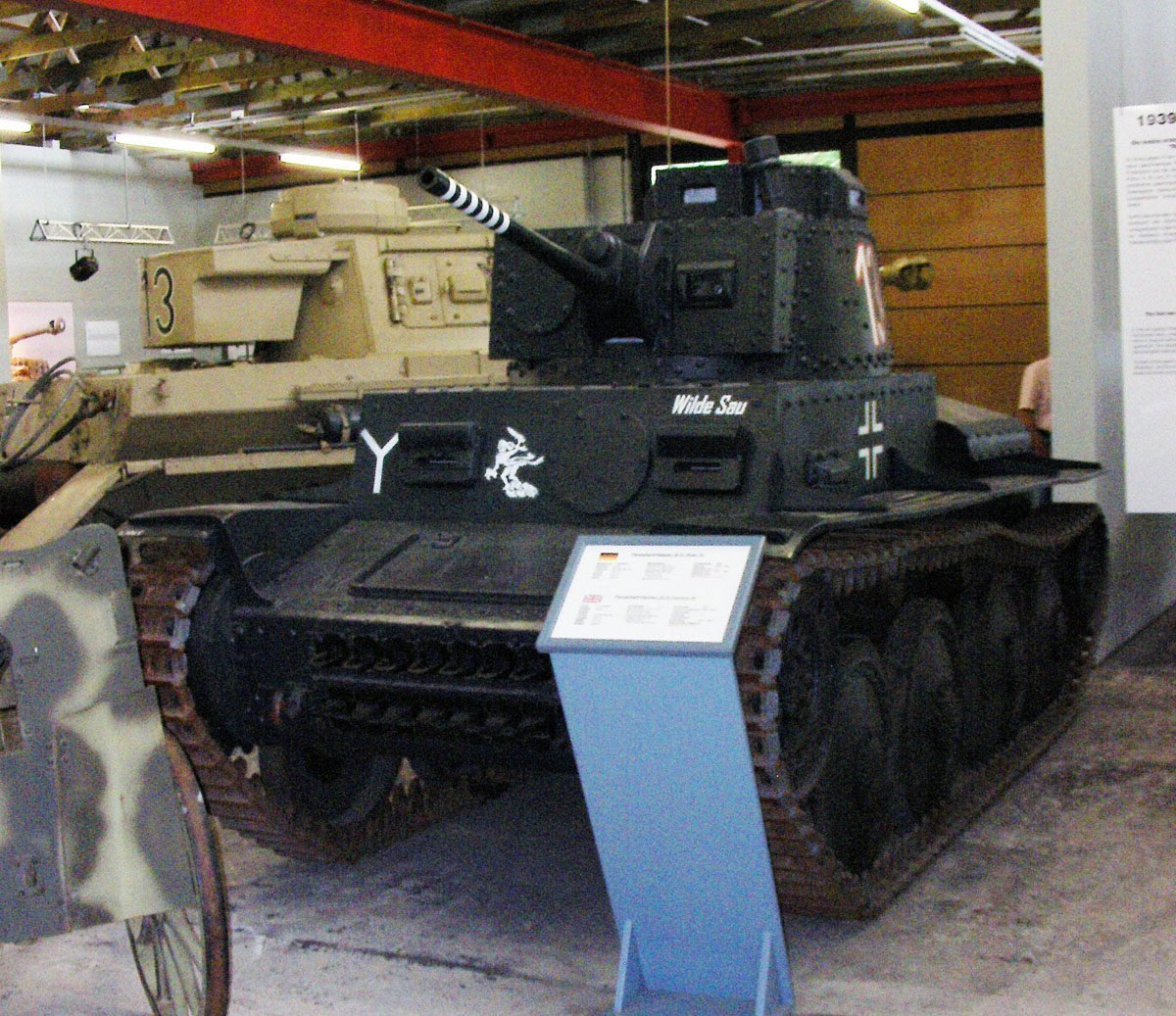

Panzer 38 (t)
Type: Light tank
History:
Table of Contents
The Panzer 38 (t) was, in fact, the Czech LT Vz 38 which was produced for the Wehrmacht after the annexation of the Czechoslovakian provinces of Bohemia and Moravia in March 1939.
Ordered as a prototype from CKD (Praga) in 1937, the Vz 38 was outright winner of competitive tests held in 1938. In July, an order was placed for 150 tanks to be manufactured immediately. The Munich Agreement forced the slow-down of this order and no production vehicles were delivered before March 1939. After the German occupation, an order was placed for the 150 incomplete tanks to be completed for the Wehrmacht as the PzKpfw 38 (t) Ausf A. Fifty-nine PzKpfw 38 (t) Ausf A served in the 67th Panzerabteilung of the 3rd Light Division in Poland, and 15 served in Norway in 1940. Thereafter, this tank served in most theaters of war except Africa.
The PzKpfw 38 (t) Ausf A ordered in May 1939, was a completion of the tanks already ordered for the Czech Army. The success of tests with the prototypes and the first production vehicles lead the Waffenamt to order a further 325. Three series were envisaged, Series II, III and IV, being basically similar apart from minor detail changes to suit German use. Both Ausf B and C served in France in 1940 with the 7th and 8th Panzer Divisions, and with the 8th Panzer Division in Greece in 1941. The Ausf D was introduced in September 1940.
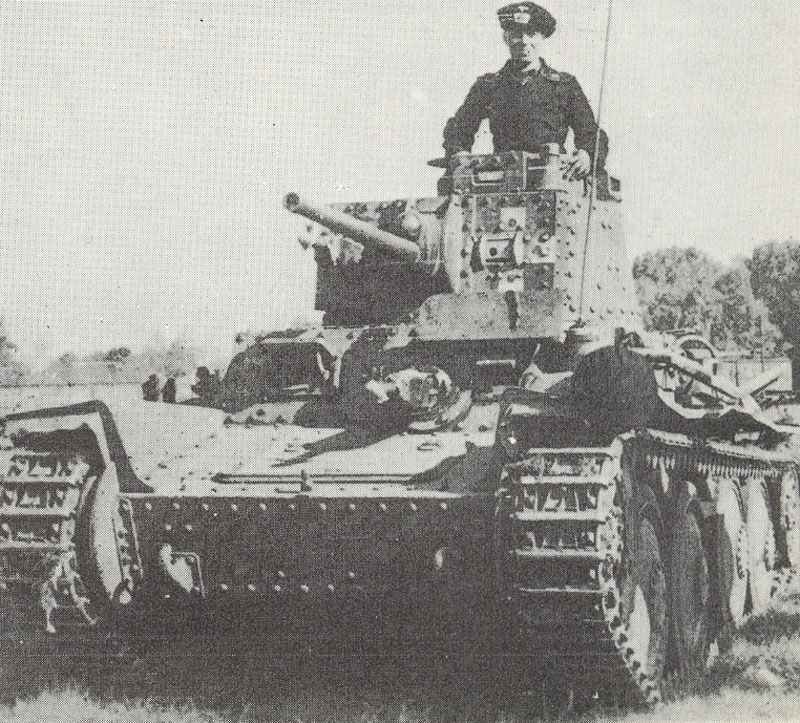
As a result of experience in Poland, greater protection was demanded, and from November 1940 the frontal armor of the tanks of Ausf E and F was increased to 50 mm by riveting two 25 mm plates together on all frontal surfaces. The armour on the turret sides and on the upper sides of the fighting compartment was also increased.
All models of the Panzer 38 served in Russia from June 1941. The Ausf D, E and F served mainly with the more recently formed 12th, 19th and 20th Panzer Divisions, as well as with the 7th and 8th Panzer Divisions which were the first divisions to be equipped with these tanks.
Before the German occupation of Czechoslovakia in March 1939, CKD (later known as BMM) had sought export orders for their tanks. In 1938/39, Sweden placed an order for 90 TNH-SV tanks. In the spring of 1940, the Germans commanded that all tanks under construction for Sweden be delivered to the Wehrmacht. Early in 1941, Sweden received a license to build the TNHPS tank, which she did, under the designation Strv m/41. Deliveries to the Swedish Army took place from February 1943. The Strv m/41 was basically similar to the PzKpfw 38 (t) Ausf G. The ‘Swedish’ vehicles were to have been assembled from February 1941, but difficulties arose because of their obsolete configuration, and because of the modifications which had been incorporated specifically for the export order. Tanks of this type were exported to the Slovak Free State and served with their Fast Division in southern Russia in 1941 and 1942.
The final outgrowth of the demand for heavier armor resulted in the PzKpfw 38 (t) Ausf G, which used basic 50 mm armor-plate for all frontal surfaces. More extensive use of welding was made in the construction of this model. The growing obsolescence of this tank against Russian T-34 and KV tank led Hitler to order that its chassis be used as the basis of a self-propelled anti-tank gun. A proportion of the output for March 1942, and all output for April were used for this purpose, The final 47 tanks were manufactured in May and June 1942.
Served mainly in Russia. Various models of the PzKpfw 38 (t) series were exported to the German allies, Hungary, Romania and Slovakia.
In 1943 the 15 cm heavy Infantry gun was also placed on the tank chassis of the Panzer 38 and was named Grille .
In September 1944, the PzKpfw 38 (t), despite being obsolete, was still in service mainly with armored train units, two tanks being carried on the flat cars of each train. At this time, 229 Pz Kpfw38 (t) of all models were listed as available.
Pictures Panzer 38(t)


Specifications for PzKpfw 38(t) Ausf E
Specifications:
PzKpfw 38(t) Ausf E | Specification |
|---|---|
Type | Light tank |
Engine | Praga EPA, water-cooled gasoline engine with 150 hp |
Gearbox | 5 forward, 1 reverse |
Crew | 4 |
Length | 4.61 m |
Width | 2.14 m |
Height | 2.40 m |
Weight | 9.85 tons |
Maximum speed | 26.25 mph |
Fuel consumption per 100 miles | 144 litres on road, 216 litres cross-country |
Fuel | 218 litres |
Road radius | 156 miles |
Cross-country radius | 100 miles |
Vertical obstacle | 0.79 m |
Trench crossing | 1.88 m |
Fording depth | 0.90 m |
Turning circle | 5.00 m |
Climbing power | 60° |
Armor:
PzKpfw 38(t) Ausf E | mm | angle |
|---|---|---|
Turret front | 50 | 10 ° |
Turret side | 30 | 10° |
Turret rear | 22 | 10° |
Turret top | 15 | 90° |
Superstructure front | 50 | 17° |
Superstructure side | 30 | 0° |
Superstructure rear | 10 | 60° |
Superstructure top | 15 | 90° |
Hull front | 50 | 16 ° |
Hull side | 15 | 0° |
Hull rear | 15 | 12 ° |
Hull bottom | 8 | 90° |
Gun mantlet | 25 | round |
Armament and Equipment:
PzKpfw 38(t) Ausf E | Specification |
|---|---|
Main armament | 3.7 cm KwK38(t) L/47.8 |
Rounds | 42 |
Traverse | 360° |
Elevation | -10° to +25° |
Muzzle velocity Pzgr | 750 m/s |
Muzzle velocity Pzgr40 | 1,040 m/s |
Shell weight Pzgr | 0.815 kg |
Shell weight Pzgr40 | 0.368 kg |
Secondary armament | 1 x 7.92mm MG37(t) coaxially to gun (traverse 10° left to 10° right, elevation -14° to +25°), 1 x 7.92mm MG37(t) in front (traverse 35° left to 11° right, elevation -14° to +25°); together 2,400 rounds |
Radio | FuG37(t) (up to 3.1 miles range) |
Telescopic sight | TZF(t) (up to 1.25 miles aiming) |
Penetration mm at 30° armor plates of the gun:
Range | Pzgr | Pzgr40 |
|---|---|---|
Penetration 100 meters | 41 | 64 |
Penetration 500 meters | 35 | 34 |
Penetration 1,000 meters | 29 | - |
Penetration 1,500 meters | 24 | - |
Penetration 2,000 meters | - | - |
Production:
PzKpfw 38(t) | figures |
|---|---|
Production | from May 1939 to June 1942, Ausf E from November 1940 and ending before October 1941 |
Combat delivery | June 1914 (Ausf E) |
Price per tank | ? |
Total production figure | 1,411 (of these 525 Ausf E and Ausf F) |
Service statistics of PzKpfw 38(t):
Year | Available | Production | Losses |
|---|---|---|---|
before 1939 | - | - | - |
1939 | 59 (Sep) | 150 | ? |
1940 | ? | 370 | ? |
1941 | 754 (Jun) | 698 | 773 |
1942 | 381 (Jan) | 193 | 196 |
1943 | 287 (Jan) | - | 96 |
1944 | 227 (Jan) | - | ? |
1945 | - | - | - |
Total | - | 1,411 "1 | 065" |
Animated 3D model Panzer 38 (t)
References and literature
Kraftfahrzeuge und Panzer der Reichswehr, Wehrmacht und Bundeswehr (Werner Oswald)
Encyclopedia of German Tanks of World War Two (P.Chamberlain, H.L.Doyle)
Panzer und andere Kampffahrzeuge von 1916 bis heute (Christopher F. Foss, John F. Milsom, Colonel John Stafford Weeks, Captain Georffrey Tillotson, Richard M. Ogorkiewicz)
Panzerkampfwagen des 1. und 2. Weltkrieges (Andrew Kershaw)
Krieg der Panzer (Piekalkiewicz)
The Encyclopedia of Weapons of World War II (Chris Bishop)














