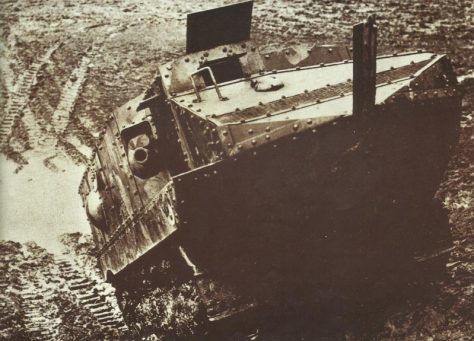
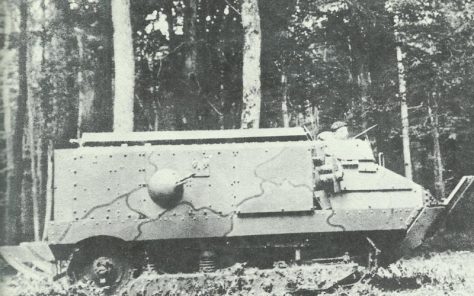
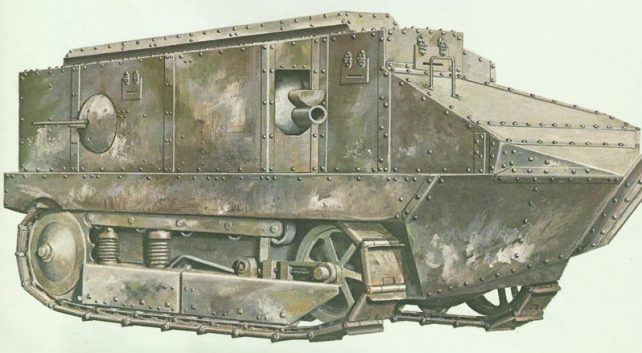
French Schneider assault tank Char d’Assaut (CA) of World War One.
History, development, service, specifications, pictures and 3D model.

French tanks in WW1
Table of Contents
During World War I, the French military developed and deployed several types of tanks. The best known are:
Schneider CA1: The first French tank to be built and used in combat, the Schneider CA1 was designed as an artillery support vehicle. It was heavily armored but slow and had limited off-road capabilities.
Saint-Chamond: Developed alongside the Schneider CA1, the St Chamond assault tank was larger and equipped with a more powerful 75mm gun. However, it suffered from poor mobility and mechanical issues.
Renault FT: The FT-17, introduced in 1917, was the first tank with a fully rotating turret. Its design became the archetype for future tank development. The FT was small, lightweight, and more maneuverable than its predecessors, making it suitable for mass production.
Char 2C: The Char 2C, designed near the end of the war, was the largest and heaviest tank produced by any country during World War I. However, it did not see combat in the war as it was not completed until after the armistice.
The French military’s use of tanks in World War I helped to establish the tank’s role as a key weapon in modern warfare. The Renault FT, in particular, had a significant impact on tank design and tactics in the following decades. Despite initial mechanical issues and limited success, these early French tanks paved the way for more advanced and effective armored vehicles in the future.
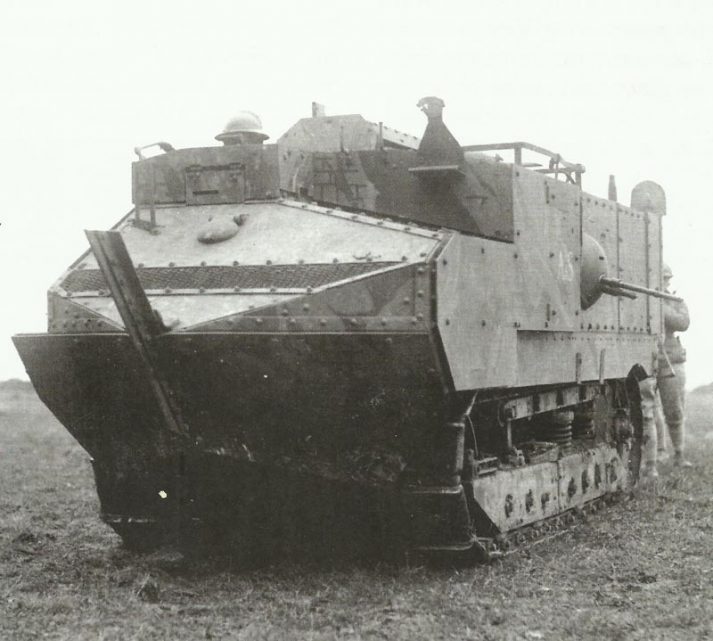
Char d’Assaut Schneider CA1
Char d’Assaut Schneider
Type: Assault tank.
History:
The idea of the Char d’Assaut Schneider (or Schneider CA) had been developed under the aegis of General Estienne, who imagined an armored tractor to tow armored sledges carrying troops across the Western Front battlefields in a shock strike on German ditches.
For the groundwork of the armored tractor Estienne suggested making use of the track and chassis of the U.s. Holt farming tractor which at these days in 1915 turning into an extensively employed artillery tractor.
By simply speaking straight to General Joffre, the French C-inC, Estienne managed to get assistance for his proposal, and the armament company Schneider became associated as the development bureau.
The initial plans required 200 Schneider CA’s by the end of 1916, nevertheless design and manufacturing were so time-consuming that it was not before the middle of 1917 that significant tanks were ready for action.
The Schneider CA appeared as what was fundamentally an armored container placed over a basically unaltered Holt tractor suspension and track. The container equipped a pair of machine guns along with a short 75-mm M1897 (2.95-in) gun to the right side forward. The engine produced 55 hp (41 kW) and was supplied from a pair of petrol tanks which were placed close to the machine-gun mountings.
These tanks turned out extremely vulnerable to German fire, to the degree that one armor-piercing round could set the tank burning, a destiny that befell numerous Schneider CA’s after they moved into battle.
Top armor thickness was 11.5 mm (0.45 in), improved to 19.5 mm (0.77 in) on later tanks.
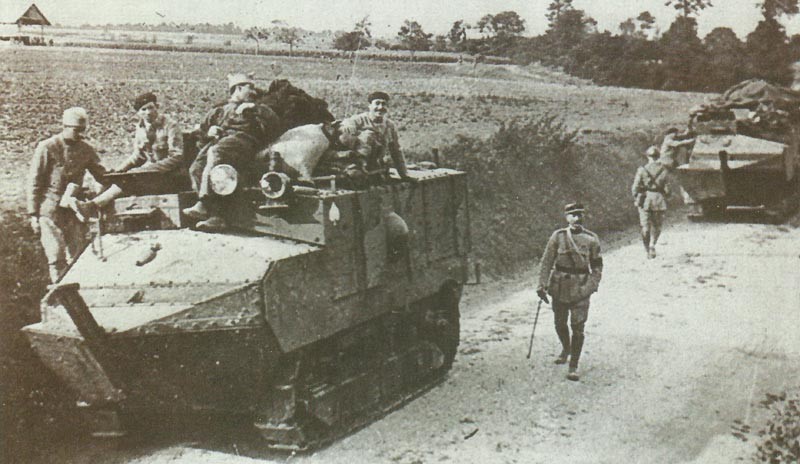
The concept of the armored personnel-carrying sledge had been abandoned, and the Schneiders were used primarily for infantry support in the way of the day. They demonstrated to be below effective in this purpose, for their cross-country characteristics were seriously limited.
By May 1917 a number of 300 had been manufactured, but afterwards the gun model was exchanged in manufacturing by the Schneider Char de Ravitaillement stores-carrying model, on which the right-hand gun position was exchanged by a door opening into the stores-carrying section. Extra 8-mm (0.31-in) armor was put onto the sides of most tanks as the response of experience in battle, and possibly the best element expressed by the Schneider CA was that as the consequence of rough experience the French army discovered how to apply and maintain armored vehicles in the field.
The French established their first armor school at Champlieu in October 1916 and very quickly found out that insufficient maintenance and absence of spare parts could eliminate a tank from the field as effectively as enemy fire.
A number of the first missions were fiascos as the consequence of insufficient schooling and maintenance, a popular of these being the assault on the Chemin des Dames in April 1917, when Seventy-six out of a total of 132 Schneider CAs engaging were sacrificed.
The last Schneider CA was produced in August 1918, but at that time, attrition and progress towards the Renault FT-17 had minimized the numbers operating to below One hundred.
Many of these were the unarmed transport model, however the gun Schneiders had taken their part in several missions during 1918, having an amount of good results in a few. However, the Schneider CA was an unsound and indifferent tank on the Western Front and turned out too vulnerable to getting fire when hit.
The most beneficial that may certainly be mentioned of them is that they educated the French army considerably concerning the restrictions and possibilities of armored warfare.
Animated 3D model Schneider Char d’Assaut (CA)
Specifications Schneider Char d’Assaut (CA)
Specifications:
Schneider CA | Specification |
|---|---|
Type | assault tank |
Crew | 7 |
Main Armament | 1 x 75-mm (2.95-inch) howitzer right side forward |
Secondary Armament | 2 x 8-mm-Hotchkiss machine guns (one each side) |
Length | 19 ft 8 in (6.00 m; with ramps 6.32 m) |
Width | 6 ft 6 2/3 in (2.00 m) |
Height | 7 ft 10 in (2.39 m) |
Armour | max 0.45 in (11.5 mm); later max 0.77 in (17-19.5 mm) |
Battle weight | 16.6 tons (14,600 kg) |
Ground pressure | 0.72 kg/cm² |
Power to weight ratio | 3.83 hp/t |
Engine | one 55-hp (41-kW) Schneider four-cylinder petrol engine |
Maximum speed | 3.7 mph (6 km/hr) |
Road range | 30 miles (48 km) |
Vertical obstacle | 2 ft 59 in (0.79 m) |
Trench crossing | 5 ft 75 in (1.75 m) |
Climbing power | 57% |
Service delivery | 1917 |
Final delivery | August 1918 |
Total production figure | c. 400 |
References and literature
An Illustrated History of the Weapons of World War One (Ian Westwell)
The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Weapons of World War I (Chris Bishop)
Panzer und andere Kampffahrzeuge von 1916 bis heute (Christopher F. Foss, John F. Milsom, Colonel John Stafford Weeks, Captain Georffrey Tillotson, Richard M. Ogorkiewicz)
Panzerkampfwagen des 1. und 2. Weltkrieges (Andrew Kershaw)