The Best Fighter Planes of World War 2: A Comprehensive Overview.
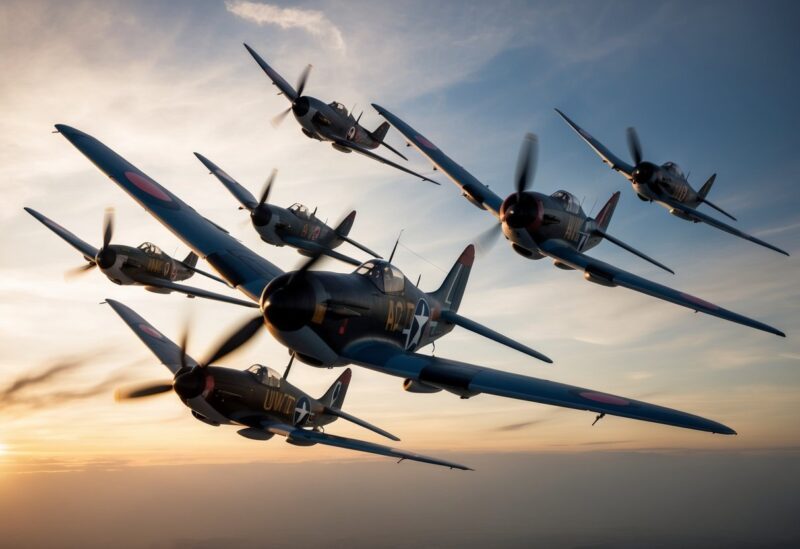

What were the best fighters of the Second World War?
Table of Contents
World War II saw the skies dominated by some of the most iconic fighter planes in history. These aircraft were crucial to both Axis and Allied powers, shaping the outcome of numerous battles. Advanced designs and engineering made them formidable weapons that continue to be recognized for their contributions to the war effort.
From the Pacific to the European theaters, these planes showcased remarkable speed, agility, and firepower. Many of these fighters were produced in large numbers and played significant roles in establishing air superiority. Their legacy lives on, continuing to influence aviation technology and popular culture today.
Supermarine Spitfire
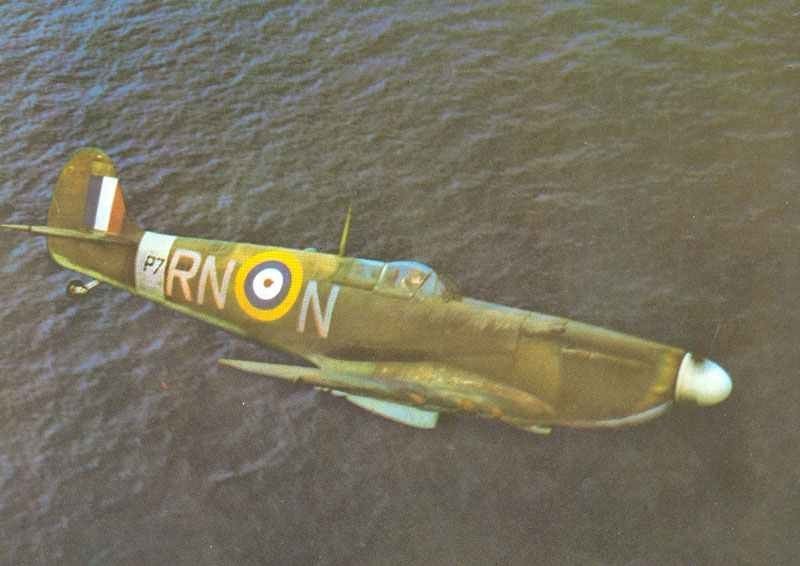

The Supermarine Spitfire is one of the most celebrated fighter planes of World War II. Designed by R.J. Mitchell in the 1930s, it played a crucial role in many battles.
Its sleek design made it an iconic symbol. The plane is praised for its speed, agility, and effectiveness. It was powered by the Rolls-Royce Merlin engine.
The Spitfire had a wingspan of 36 feet 10 inches. This contributed to its excellent flight performance. It excelled in aerial dogfights and was a favorite of pilots.
The Spitfire was used by the Royal Air Force, gaining fame during the Battle of Britain. It became a symbol of British resilience.
Many variants of the Spitfire were produced, each improving upon the last. Its adaptability ensured its use throughout the war.

North American P-51 Mustang
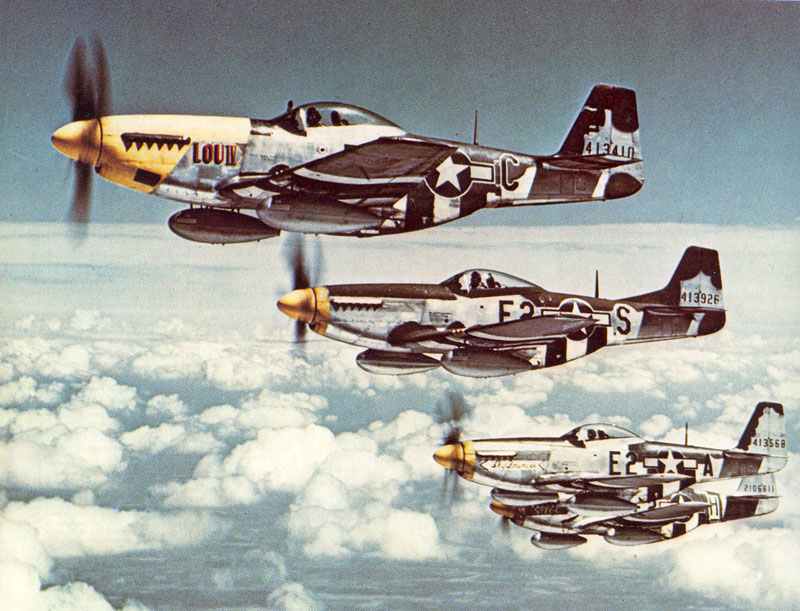

The North American P-51 Mustang is widely regarded as one of the best fighter planes of World War II. It was designed by North American Aviation in 1940. The British Purchasing Commission needed a new fighter, leading to its creation.
This aircraft quickly proved its worth through its impressive performance. It was capable of long-range missions, escorting bombers deep into enemy territory. The P-51 had a top speed of about 438 mph and was powered by a 1,490 horsepower engine.
Its range extended between 500 to 1,000 miles with drop tanks. This capability allowed it to fly missions across Europe and the Pacific. It carried 90 gallons of fuel in each wing, consuming about 60 gallons per hour.
The Mustang gained fame not only for its speed and range but also for its impact in combat. P-51 pilots shot down nearly 5,000 enemy aircraft during the war. Many pilots achieved “ace” status, marking the P-51 as a formidable opponent in the skies.

Messerschmitt Bf 109
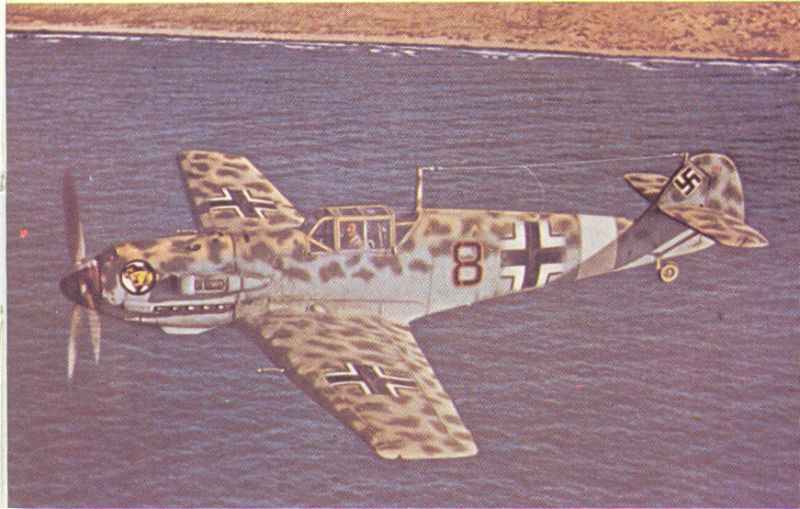

The Messerschmitt Bf 109 was a key fighter plane in World War II. It first flew in 1935 and quickly became vital for Germany’s Luftwaffe. It remained in service until the war ended in 1945. This aircraft was noted for its sleek design and advanced features for its time.
Developed by Wilhelm Messerschmitt, the Bf 109 combined speed, agility, and firepower. It became known as a symbol of German air superiority. The plane was a single-seater, designed to provide excellent performance in aerial combat.
Throughout the war, the Bf 109 participated in numerous battles across different theaters. It played a significant role in the Spanish Civil War before seeing extensive action in World War II. The German government funded its development as part of military rearmament efforts.
The Bf 109 was produced in large numbers, which allowed it to become a staple of the German air force. It shared the spotlight with other fighters like the Focke-Wulf Fw 190. Its impact on the war effort was significant, making it one of the most important fighter planes of its era.

Focke-Wulf Fw 190
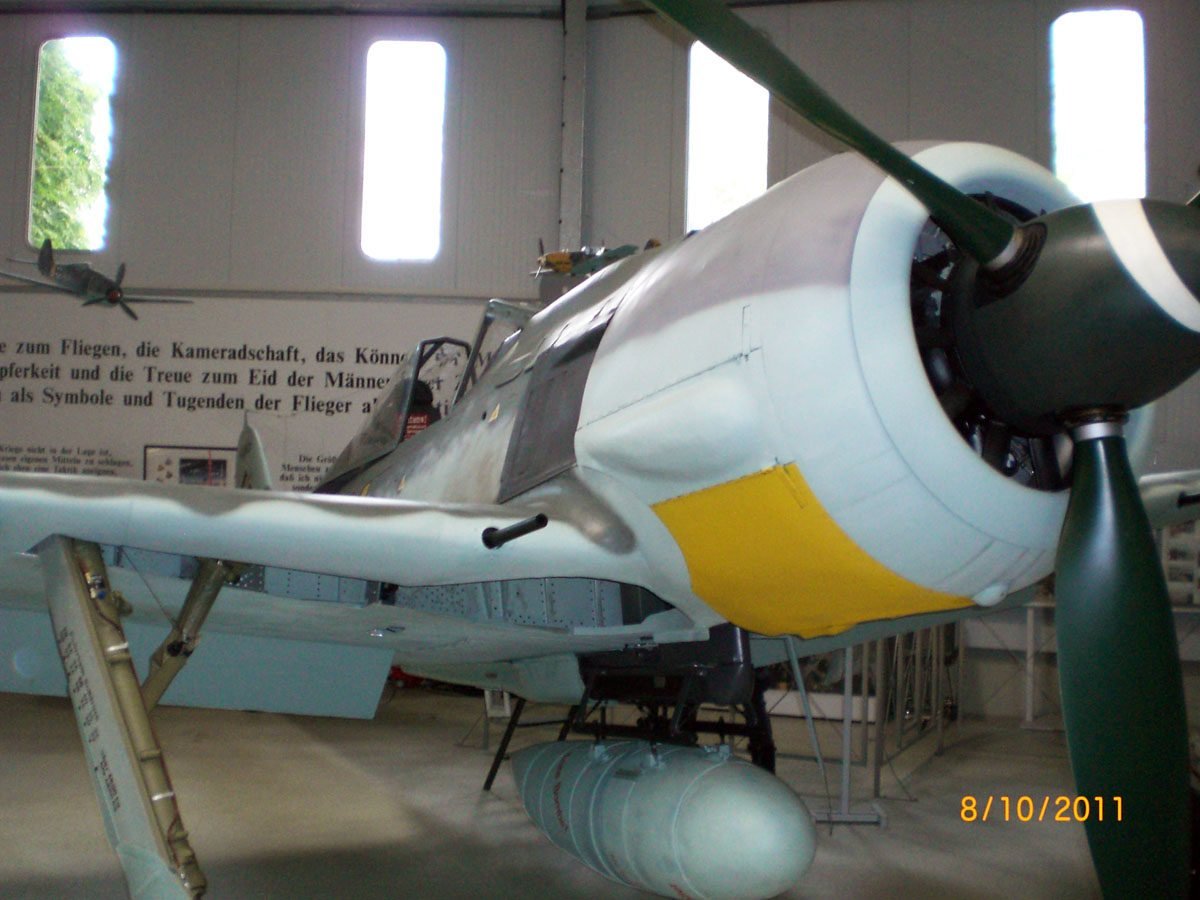

The Focke-Wulf Fw 190 was a prominent German fighter plane during World War II. Designed by Kurt Tank, it was celebrated for its performance and adaptability. Its popularity stemmed from its powerful BMW 801 radial engine and robust design.
The Fw 190 was often compared to the Messerschmitt Bf 109, another key German fighter. However, many pilots favored the Fw 190 due to its superior firepower and maneuverability. It was nicknamed the “Butcher Bird” because of its effectiveness in combat.
Throughout the war, the Fw 190 underwent numerous upgrades, improving its capabilities. Its versatility allowed it to serve in various roles, including as a bomber interceptor and ground-attack aircraft. This flexibility made it a vital component of the Luftwaffe’s arsenal.
Pilots appreciated the Fw 190’s cockpit design, which offered good visibility and controls. It became particularly feared by the Allies when it first appeared in combat, often outperforming earlier Allied fighters.
The Fw 190’s impact on air battles was significant, with many Allied aircraft succumbing to its firepower. Its presence on the battlefield marked a notable advancement in aviation technology during the war period. The Fw 190 remains one of the most famous fighter planes from World War II history.

Yakovlev Yak-3
The Yakovlev Yak-3 was a Soviet fighter that played a crucial role during World War II. Known for its excellent agility and speed, the Yak-3 was one of the lightest and most compact fighters of its time. Its small size and high power-to-weight ratio allowed it to outmaneuver many opponents in dogfights.
Pilots and ground crews praised the Yak-3 for its robustness and ease of maintenance. Its simple design made repairs straightforward, even in challenging conditions. This reliability contributed to the Yak-3’s success and popularity among Soviet pilots.
The Yak-3 stood out for its performance and played a significant role in various air battles. It was especially effective against German aircraft, proving to be a major asset to the Soviet air force.
Its streamlined design and effective power made the Yak-3 a formidable aircraft. This plane is remembered as one of the best Soviet fighters of the war, combining practicality with effective performance in combat situations. The Yak-3’s legacy continues to be admired by aviation enthusiasts and historians alike.
Mitsubishi A6M Zero
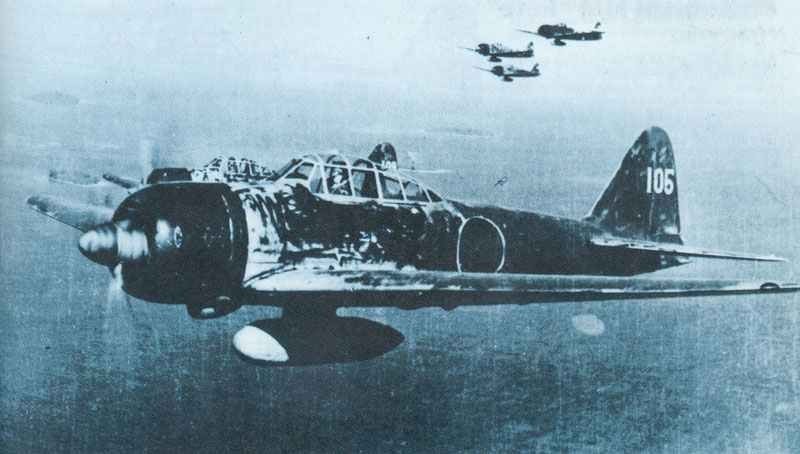
The Mitsubishi A6M Zero was a prominent fighter aircraft during World War II. It was developed by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries in Japan. Introduced in 1940, it quickly became the primary aircraft of the Imperial Japanese Navy.
Known for its agility and lightweight design, the Zero was armed with a powerful engine. It could reach impressive speeds, making it a formidable opponent in air combat. Its maneuverability gave it an advantage in dogfights against other aircraft.
Initially, the Zero outperformed many Allied planes, mainly due to its excellent handling and climb rate. It was crucial during campaigns in the Pacific, including battles at Pearl Harbor and throughout Southeast Asia.
The aircraft, however, had limited armor and fuel capacity. These weaknesses became more apparent as Allied forces improved their tactics and technology. Despite this, its early successes marked it as one of the most significant fighters of the era.
Production continued until the end of the war, with various models being developed. Though its influence waned as the war progressed, the Mitsubishi A6M Zero remains a symbol of early Japanese air superiority.

Vought F4U Corsair
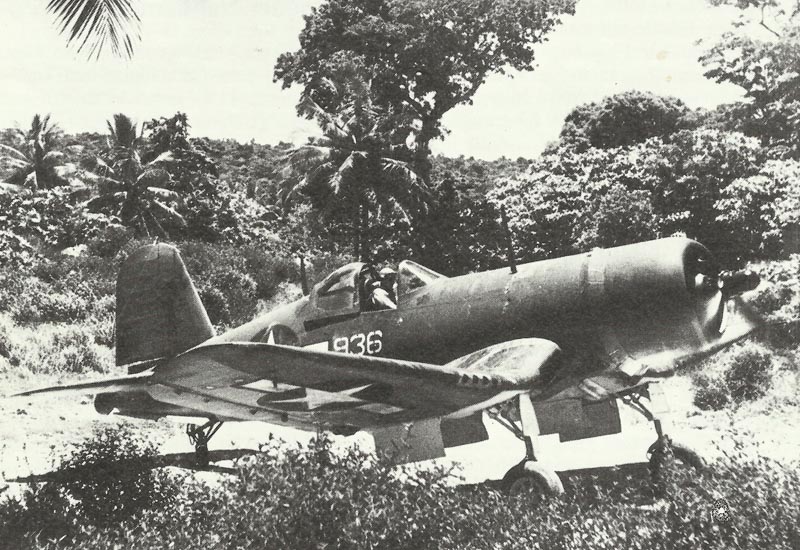

The Vought F4U Corsair was a standout fighter plane during World War II. Known for its unique gull-wing design, it was introduced in 1940 and quickly recognized for its speed and power. This airplane was powered by a strong engine, allowing it to reach speeds over 400 mph, making it one of the fastest fighters of its time.
The Corsair was heavily armed with six .50 caliber machine guns. This made it effective in both air-to-air combat and ground attacks. Its ability to deliver substantial firepower made it a favorite among pilots during intense battles.
Initially designed for the U.S. Navy, the Corsair also played a key role in the Korean War. Despite being intended for carrier operations, its long nose made deck landings challenging, and it was mostly used by land-based forces initially.
Pilots often referred to it as the “Whistling Death” due to the distinct sound it made. Additionally, during the Battle of Okinawa, it earned the nickname “Angels of Okinawa” for its effectiveness against enemy aircraft. The F4U Corsair remains an iconic symbol of air superiority during WWII.

Lockheed P-38 Lightning
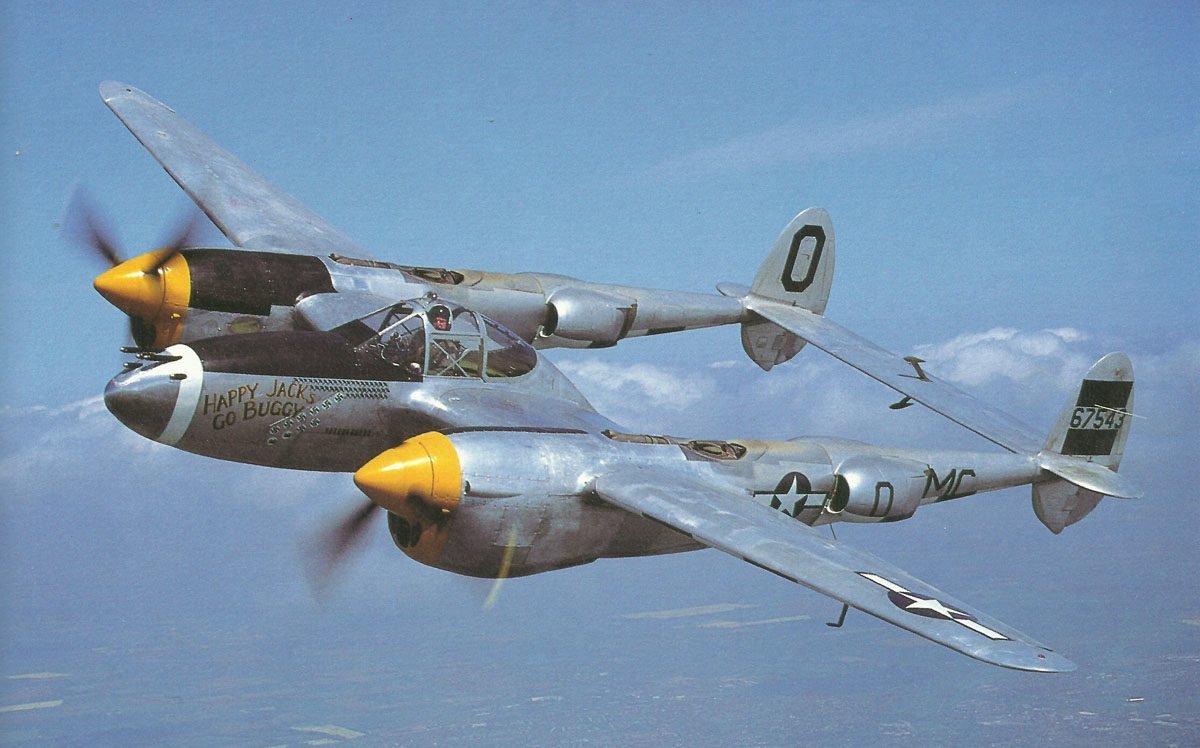

The Lockheed P-38 Lightning was a key fighter plane during World War II, known for its unique twin-boom design. Engineered as a twin-engine fighter by Lockheed for the United States Army Air Corps, the P-38 stood out with its central nacelle that housed the cockpit and weaponry.
This aircraft was originally designed for tasks like bomber interception. Nevertheless, it became celebrated for its flexibility in combat. The P-38 was capable of performing multiple roles, including dive bombing, ground attacks, and aerial reconnaissance.
Despite its success in many theaters, the P-38 had mixed results in Europe, where it faced operational challenges. In the Pacific, it excelled due to its long range and powerful twin engines. This made it effective in vast stretches of oceanic combat.
The Lightning’s versatility also came from its speed and high-altitude performance. As it dived, it could approach Mach speeds, which was quite advanced for the time. This adaptability ensured it remained significant throughout the war.
Used by famous aces and playing roles in critical missions, the Lockheed P-38 Lightning remains a remarkable example of World War II aviation history.

Grumman F6F Hellcat
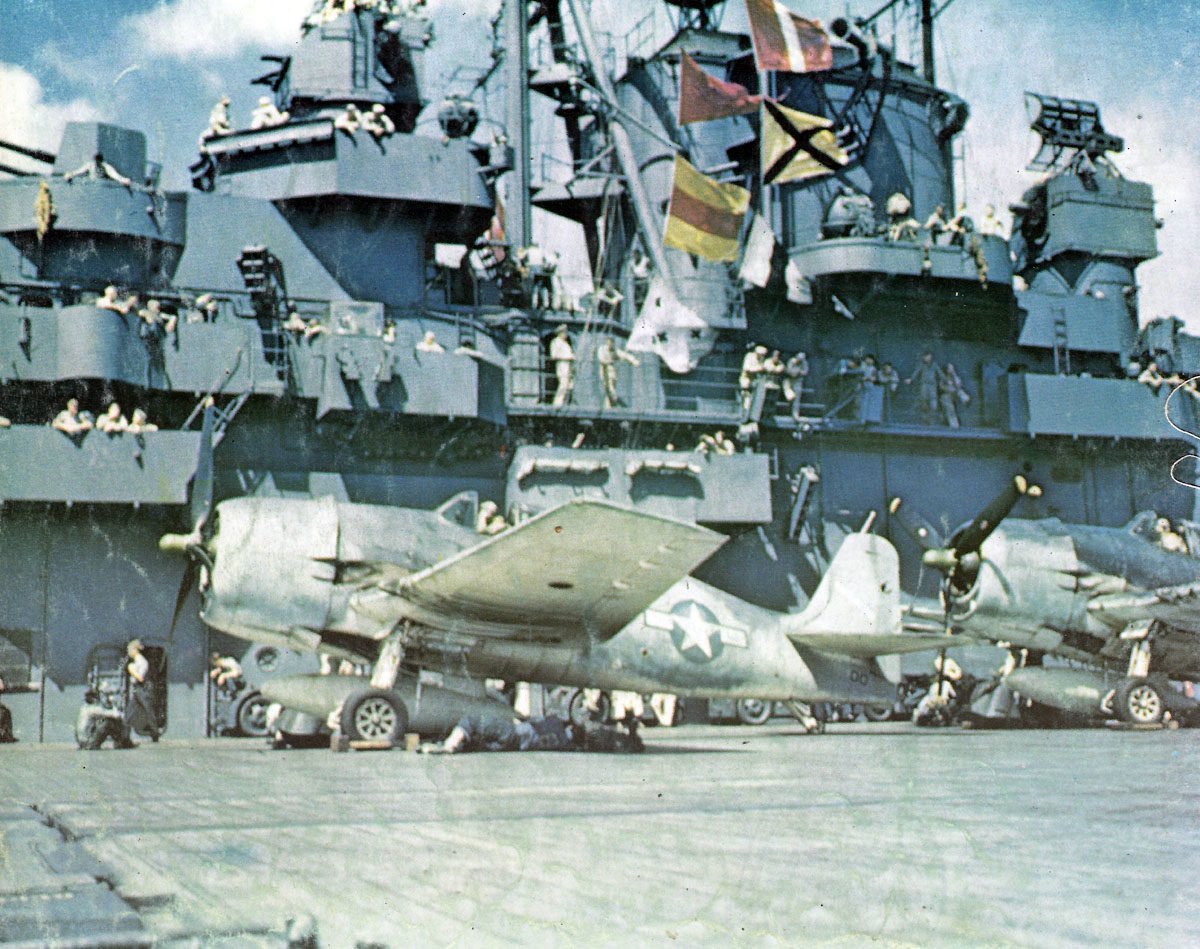

The Grumman F6F Hellcat was a carrier-based fighter aircraft used by the United States Navy during World War II. It was designed to replace the earlier F4F Wildcat and counter the Japanese Mitsubishi A6M Zero.
The Hellcat first flew in June 1942 and was introduced to service the following year. It quickly became a key asset in the Pacific Theater, known for its robust design and effectiveness in combat.
Powered by a 2,000-horsepower engine, the Hellcat could reach speeds of up to 380 miles per hour. Its performance was crucial in major battles, helping to secure air superiority for the Allies.
Over 12,000 Hellcats were produced during the war. Their use extended beyond just regular fighter duties; they also served as night fighters and photo-reconnaissance aircraft.
After World War II, the Hellcat continued to serve in the U.S. Navy and with reserve squadrons until the early 1950s. Its legacy as a reliable and powerful aircraft remains well-regarded in aviation history.
Hawker Hurricane
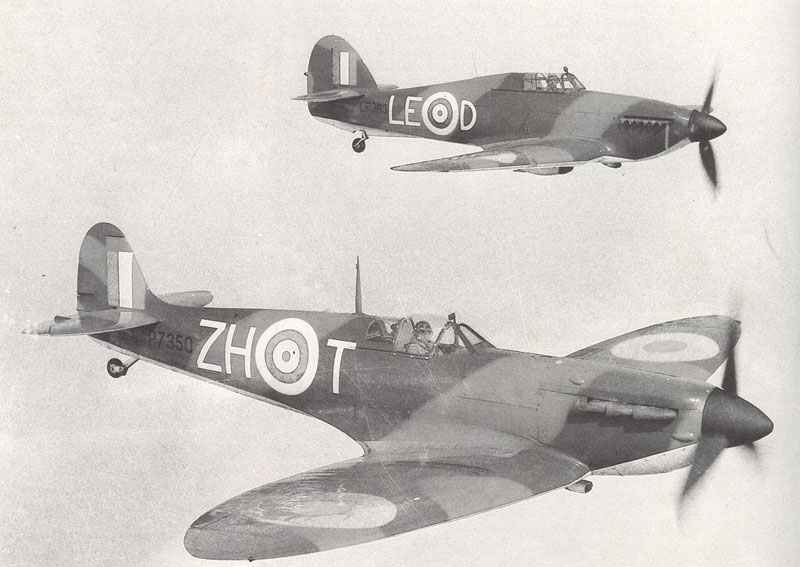

The Hawker Hurricane was a key fighter aircraft for Britain during World War II. Designed by Sydney Camm, this single-seat plane played a crucial role in the Battle of Britain. It was powered by the reliable Rolls-Royce Merlin engine.
It achieved notable success against the German Luftwaffe. The Hurricane was involved in 60% of the Luftwaffe’s losses during the Battle of Britain. This performance made it a standout aircraft in the conflict.
While often overshadowed by the Spitfire, the Hurricane was the first Royal Air Force aircraft to fly over 300 mph. Its impact and reliability were invaluable to the Allies during the war. Its simpler construction also made it easier to produce and repair compared to other aircraft.
The Hurricane boasted strong firepower with its machine guns, and its sturdy design could withstand significant damage. These features made it effective in various combat roles beyond dogfights, including ground attacks. As a vital component of the RAF’s arsenal, the Hurricane has earned its place in aviation history as a formidable fighter plane.

Technological Advancements

World War II was a time of rapid growth in aircraft technology. Fighter planes saw major improvements in engineering and aerodynamics. These advancements had a significant influence on their speed and combat effectiveness.
Engineering Innovations
During World War II, fighter planes experienced significant engineering changes that improved their performance and effectiveness. One notable innovation was the shift from wood and fabric construction to all-metal bodies. This made the planes more durable and capable of withstanding the stresses of combat.
Armament systems also saw advancements. Fighters were equipped with more powerful and reliable weapons. Some planes, like the American P-47 Thunderbolt, carried eight .50 caliber machine guns, allowing them to unleash a heavy barrage.
The introduction of radar was another important development. It improved targeting and navigation during missions, especially at night. These engineering innovations set new standards for military aviation, laying the groundwork for future advancements.
Aerodynamics and Speed
During the war, a focus on aerodynamics greatly enhanced the speed and maneuverability of fighter planes. Streamlined designs minimized air resistance, allowing many planes to reach speeds over 400 mph. The North American P-51 Mustang exemplified these improvements with its sleek design and powerful engine.
The development of the jet engine marked a revolutionary change in speed capabilities. Though late in the war, the Me 262 became the first operational jet fighter. It significantly outpaced its propeller-driven counterparts.
The increased speed and agility of these fighters improved their combat performance and survivability. These advancements played a critical role in shaping modern aerial warfare, setting the stage for future aircraft design.
Impact on Air Warfare
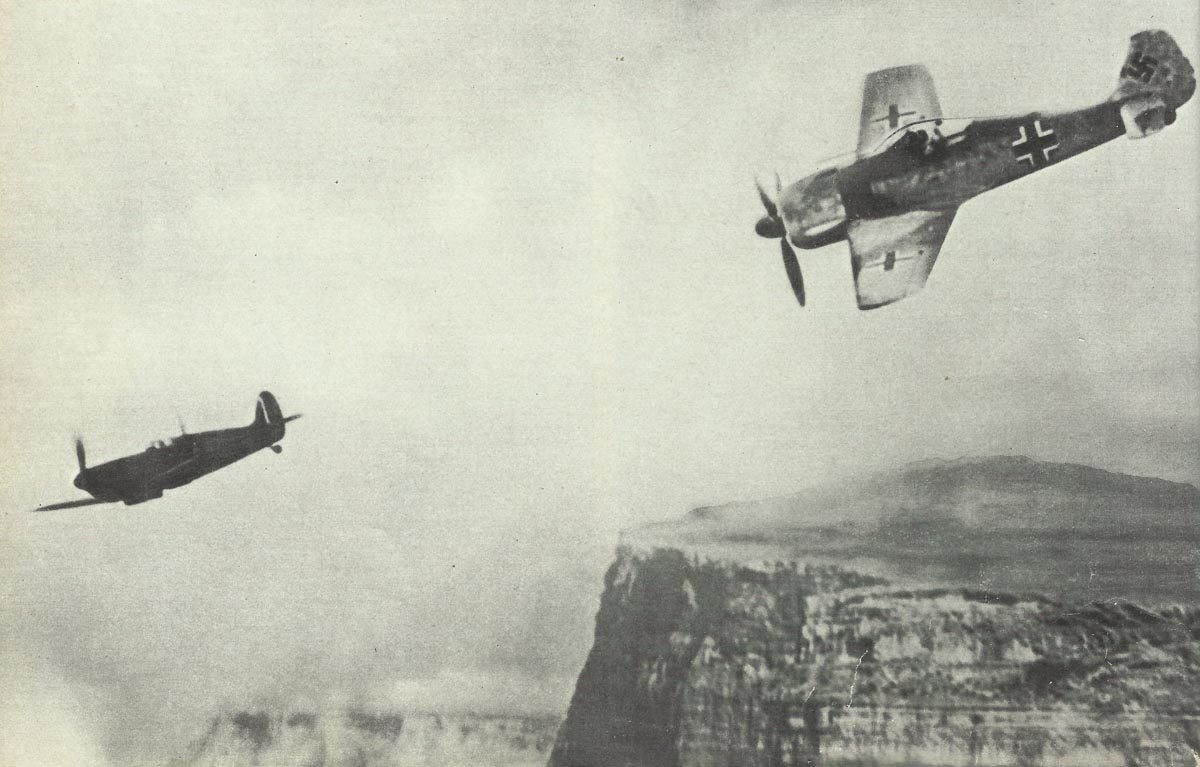
World War II fighter planes like the Messerschmitt Bf 109, Mitsubishi A6M Zero, and P-51 Mustang transformed how air battles were fought. These planes introduced new tactical maneuvers and emphasized air superiority as a strategic goal, shaping future military aviation strategies.
Tactical Developments
During World War II, fighter planes brought significant changes to tactics in air warfare. Speed and agility became crucial as aircraft like the P-51 Mustang and Bf 109 were designed to engage in dogfights more effectively. Dogfighting tactics evolved to include maneuvers like the “Thach Weave” or “Boom and Zoom,” which focused on leveraging altitude, speed, and surprise advantages.
These planes supported ground forces through close-air support, facilitating attacks on enemy locations. Coordinated air raids, using formations of bombers protected by fighter escorts, were instrumental. Pilots had to master new skills such as aerial gunnery and teamwork. The introduction of radar also enhanced strategic planning and intercept capabilities, allowing pilots to effectively locate and target enemy planes.
Strategic Importance
Fighter planes were essential in achieving air superiority during the war, which became a key strategic objective. Aircraft like the Spitfire and Zero dominated the skies in their respective theaters due to their advanced designs. The Allies’ control of airspace was crucial in numerous operations, cutting off enemy supply lines and providing air cover for ground troops.
The long-range capabilities of planes like the P-51 Mustang enabled deep strikes into enemy territories, supporting missions such as the critical bombing campaigns in Europe and the Pacific. Fighter planes also provided reconnaissance, gathering intelligence on enemy movements, which helped plan large-scale operations. Their ability to adapt to various roles—fighter, interceptor, escort—proved indispensable in maintaining strategic advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions

World War II was an era of remarkable aviation advancements. Fighter planes, like the Supermarine Spitfire and the Messerschmitt Bf 109, played critical roles in many battles. This section addresses common questions about their performance, technology, and pilot experience.
Which WWII fighter aircraft had the highest number of confirmed air-to-air combat victories?
The Messerschmitt Bf 109 was credited with the highest number of confirmed combat victories during World War II. This German fighter plane‘s design and capabilities allowed it to excel in numerous theaters of war.
What attributes were considered when determining the best fighter planes of WWII?
The speed, agility, firepower, and range were key attributes when assessing fighter planes. Effectiveness in combat, ease of maneuverability, and technological advancements also played significant roles in evaluating these aircraft.
How did different countries’ fighter planes compare in terms of performance during WWII?
Allies and Axis powers had varied strengths in their aircraft. The Supermarine Spitfire was known for its agility and speed, while the P-51 Mustang offered long-range capabilities. Conversely, the Bf 109 and Fw 190 were notable for their firepower and speed.
What advancements in aviation technology were made during WWII?
World War II spurred various technological advances in aviation, including jet engines, radar, and improved aerodynamics. These innovations significantly enhanced the performance and capabilities of fighter planes.
In terms of kill-to-loss ratio, which WWII fighter plane was most effective?
The F4U Corsair was able to shoot down 2,140 Japanese aircraft with a loss of only 189 Corsairs in 64,051 sorties, making it arguably the most effective fighter aircraft of the Second World War.
The P-51 Mustang also had an impressive kill-to-loss ratio, making it one of the most effective fighters. Its combination of speed, range, and maneuverability allowed it to excel in air combat.
Which WWII fighter planes were the easiest for pilots to handle and maneuver in combat?
The Yakovlev Yak-3 was lauded for its ease of handling and agility in combat. It was favored by pilots for its ability to turn quickly and engage in dogfights effectively. The P-51 Mustang was also known for its user-friendly controls.







