Did Hitler really invent sex dolls? What’s behind the myth?

Nowadays, everyone is aware that Hitler is responsible for a number of terrible events. But did you also know that there is a rumour going around that Adolf Hitler allegedly invented sex dolls?
What is the Borghild project all about?
Table of Contents
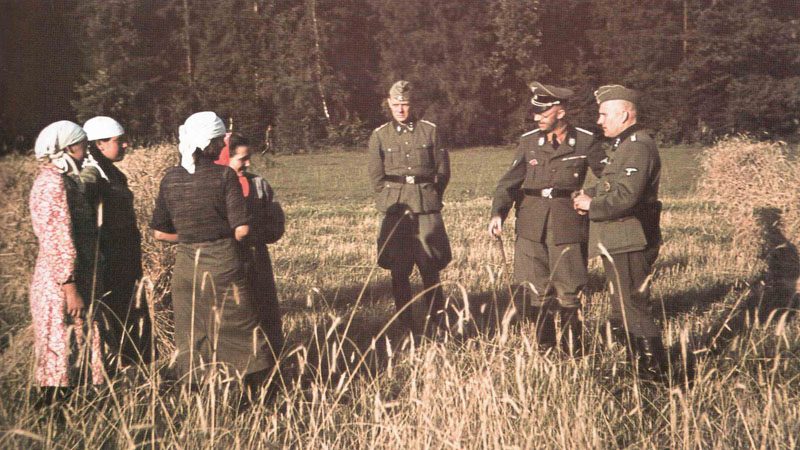
The infamous ‘Borghild Project’ is said to have taken place in 1940. Hitler’s SS chief Heinrich Himmler had realised that the German soldiers in Paris were becoming too distracted.
In November 1940, he announced: ‘The greatest danger in Paris is posed by the wild prostitutes who ply their dark trade on the streets and in the cafés, restaurants, bars and entertainment centres. It is our job to make it easier for the soldiers to get rid of them’.
The real problem here, however, was not that the German soldiers had their occasional fun. Instead, an increased number of sexual diseases were found among the soldiers. The venereal disease syphilis in particular was doing the rounds at this time – and the German soldiers were not spared in Paris.
This gave rise to the idea of developing inflatable sex dolls. Although these were not to be life-size, as they would have to fit into the soldiers’ rucksacks, they were nevertheless intended to prevent the soldiers from getting involved with foreign women.
In this way, the soldiers could satisfy their lust without risking their health.
Hitler then gave his consent to design sex dolls for the German soldiers.
The design of the sex dolls
Franz Tschakert from the German Hygiene Museum was commissioned to produce the rubber dolls. He was to give the sex dolls an attractive design that would keep the soldiers away from the Parisian women.
Rumour has it that Tschakert asked the Hungarian actress Käthe von Nagy to model for the rubber dolls. He would have liked to model the Love Dolls on her appearance. However, when she rejected this bizarre suggestion, the decision was made to design a typical German doll with blonde hair and blue eyes instead.
Allegedly, this design was even tested in order to create a face that the German soldiers particularly liked. Ten different faces were designed and the most popular face was chosen for the design of the dolls.
It was also decided that a sex doll should have realistic skin and a satisfying pleasure cavity so that it could compete with a real woman.
The dolls were then to be produced in Dresden. When Tschakert presented the finished doll to Himmler in Berlin, he is said to have been so enthusiastic that he immediately ordered 50 dolls for the German troops.
But what is there really to these rumours?
Whether the production of sex dolls for German soldiers ever took place is something that is debatable. Although several sources prove that there was talk about it, at the time it was a secret project that was not supposed to be made public.
Therefore, there is no real evidence to support the Borghild project with leftover products. The factory where the dolls were supposedly made was destroyed in the attack on Dresden and with it any potential evidence. What a coincidence!
There are also various rumours as to how the story continued. Some people claim that Himmler cancelled production before the sex dolls were finished. This is said to have been for financial reasons, as the war was no longer going the way the Germans wanted it to.
According to other stories, the sex dolls were not very well received by German soldiers. The men were probably too shy to actually pack these dolls in their rucksacks.
According to rumours, the men were worried that the suggestive dolls could be found by the enemy if they were captured, for example. However, it is doubtful whether a sex doll is really something to worry about in this case.
It is also possible that the German soldiers simply found the idea absurd and were looking for excuses not to have to carry the toys with them. Because honestly, what man would prefer an artificial rubber doll when he can also have the beautiful French women?
And you can get rid of them quickly after an evening and don’t have to lug them around with you in war situations…
So it’s pretty clear that Himmler’s idea was not a realistic solution to the dangers in Paris. If this ever happened at all!
And even photos showing the sex dolls from the Borghild project have since turned out to be fake.
The Borghild project: more history
Ultimately, it is only debatable whether the production of sex dolls for German troops was ever planned or not. In any case, the evidence is insufficient and with a topic like this, you can imagine that it spread like wildfire – even if it was just a rumour.
After all, who wouldn’t chuckle at the fact that Hitler cared so much about the sexual satisfaction of his soldiers that he even designed them their own sex toys?
At this point, it is also debatable whether sex dolls had not existed before.
According to legend, Spanish sailors built artificial female bodies as early as the 16th century to satisfy their lust on long voyages. Dutchmen then recreated these models in the 17th century.
History therefore has no real evidence to prove that the Borghild project ever took place. Furthermore, Hitler’s government most likely did not invent sex dolls, as many claim.
For this reason, this myth should not be given any more attention than necessary. After all, it is nothing more than a nice story that, like many wartime rumours, cannot be proven!
The real history of sex dolls: From ancient origins to modern innovations
Sex dolls have existed longer than most people think. They have evolved from simple objects to realistic companions over centuries. While many believe that sailors created the first sex dolls (called “dames de voyage”) during long sea voyages, this widely accepted story lacks solid historical evidence.
Sex dolls as we know them today began to take shape in the late 20th century with companies like Abyss Creations, founded in 1997, which makes the RealDoll. These modern dolls offer realistic features and customization options for people seeking intimacy alternatives. The technology continues to advance, with newer models incorporating more lifelike characteristics.
Throughout history, the creation and use of sex dolls has been predominantly associated with straight men. However, the industry has expanded to include diverse options, including transgender dolls and various customizable features. These sexual devices reflect changing attitudes about intimacy and companionship in society.
Origins and Evolution of Sex Dolls
Sex dolls have transformed from simple objects to sophisticated companions over centuries. Their development reflects changing attitudes toward sexuality, technological advancements, and societal norms across different cultures and time periods.
Ancient Inceptions and Mythological References
The concept of artificial companions dates back to ancient civilizations. In Ovid’s “Metamorphoses,” the story of Pygmalion tells of a sculptor who fell in love with his ivory statue of a woman, which Venus then brought to life. This myth represents one of the earliest references to the desire for artificial companionship.
Ancient artifacts from various cultures show evidence of figurines that may have had erotic purposes. The Venus de Milo and other classical sculptures celebrated the human form, though they weren’t explicitly created for sexual use.
By the 17th century, more direct precursors to modern sex dolls appeared. These rudimentary objects were often made from cloth or leather and stuffed with materials like straw.
Sex dolls in the first half of the 20th century
The early 20th century saw significant developments in sex doll technology. Following the invention of vulcanized rubber in the late 19th century, more realistic “femmes en caoutchouc” (rubber women) became available. These inflatable dolls offered greater realism than their cloth predecessors.
During World War II, it’s reported that Nazi Germany developed the “Model Borghild” for German soldiers, though historical evidence for this project remains disputed. The post-war period saw greater commercial production of inflatable dolls.
Hans Bellmer, a German artist, created articulated dolls in the 1930s that explored eroticism and the human form. While not functional sex dolls, his work influenced later designs and highlighted the growing interest in realistic human replicas.
The Emergence of Modern Sex Dolls
The 1960s and 1970s marked a turning point with the introduction of vinyl and latex materials that allowed for more realistic features. The term “fornicatory dolls” became common in some markets, emphasizing their sexual function.
Sailors had long been associated with sex dolls, particularly the “dame de voyage” or “dames de voyage” used during ocean voyages. Dutch sailors were often mentioned in historical accounts as early adopters of these companions during long journeys at sea.
By the 1980s and 1990s, silicone and TPE (thermoplastic elastomer) materials revolutionized the industry, allowing for remarkably lifelike dolls with better durability and feel. These materials permitted customizable features and greater articulation, leading to the sophisticated designs available today.
Technological Advancements and Realistic Features
The sex doll industry has evolved dramatically through technological innovation. Materials have progressed from simple inflatable designs to sophisticated silicone models with lifelike features, while new technologies continue to push boundaries with robotic capabilities.
The Creation of Inflatable Dolls
Inflatable sex dolls emerged in the mid-20th century using vulcanized rubber technology. These early models were basic in design and functionality, offering a portable and affordable option for consumers.
The first commercially successful inflatable dolls appeared in the 1960s as manufacturing techniques improved. They featured simple anatomical designs and were primarily marketed as novelty items.
By the 1970s, improvements in plastic and vinyl materials created more durable products. However, these dolls still lacked realistic features and were prone to punctures and air leaks.
The Bild Lilli doll, originally a German adult novelty item, influenced design concepts despite not being created as a sex doll. This demonstrated consumer desire for more human-like aesthetics in adult products.
From Inflatable to Hyper-Realistic
The 1990s marked a turning point with the introduction of silicone and TPE (thermoplastic elastomer) materials. These substances revolutionized the industry by allowing for softer, more skin-like textures.
The creation of RealDoll in 1996 set new standards for realism. These dolls featured articulated metal skeletons covered with silicone skin, allowing for positioning and a more lifelike appearance.
Manufacturers began offering customization options including:
- Facial features
- Body types
- Skin tones
- Hair color and style
Modern production techniques now incorporate 3D scanning of real people to create exact replicas. Some high-end models include heating elements for body warmth and built-in sensors that respond to touch.
The Advent of Sex Robots
The early 2000s saw the first integration of electronic components into dolls. Basic voice recordings and simple movement mechanisms marked the beginning of interactive features.
By 2010, AI technology began appearing in premium models. These systems allowed for rudimentary conversations and personality simulation, responding to user input and learning preferences over time.
Current sex robots incorporate:
- Voice recognition
- Facial expressions
- Automated movement
- Personalized responses
- App connectivity
The development continues with machine learning algorithms creating more natural interactions. Some models can maintain “conversations” and remember details from previous interactions.
Ethical debates surround these advancements as the line between dolls and simulated companions blurs. Despite controversies, consumer desire for increasingly realistic features drives ongoing innovation in this technology sector.
Societal and Cultural Impact
Sex dolls have profoundly shaped societal attitudes about intimacy and relationships while reflecting changing cultural values. Their presence extends beyond mere objects to influential symbols in discussions about gender, representation, and technology.
Representations of Gender, Race, and Sexuality
Sex dolls overwhelmingly represent female forms, raising important questions about gender power dynamics. Most commercial models feature idealized female body types that reflect and potentially reinforce beauty standards.
Race representation in sex dolls has been particularly problematic. Many companies offer dolls with exaggerated racial features that critics argue perpetuate harmful stereotypes and fetishization of racial characteristics.
The sexuality depicted through these dolls often centers heterosexual male desire. This narrow focus has sparked debates about how such products might shape perceptions of consent and sexual agency.
Some manufacturers have begun creating more diverse products, including male dolls and non-binary options. This shift represents evolving attitudes about sexuality and gender expression in society.
Sex Dolls in Art and Popular Media
Artists have incorporated sex dolls into their work to explore themes of artificial companionship and objectification. Photographers like Elena Dorfman have created powerful series examining relationships between humans and dolls.
In film, movies like “Lars and the Real Girl” and “Air Doll” use these objects as central metaphors. These works often explore loneliness, connection, and the boundaries between real and artificial relationships.
Porn magazines and adult media frequently feature sex dolls, sometimes blurring lines between human and artificial subjects. This representation has evolved alongside technological advances in doll realism.
Television shows like “Westworld” explore futuristic concepts that parallel current discussions about AI-enhanced sex dolls. These stories reflect anxieties about technology and intimacy.
Academic Perspectives and Critiques
Scholars like Bo Ruberg have examined sex dolls through feminist and technological lenses. Their research explores how these objects might reinforce or challenge traditional gender roles.
Academic studies on sex dolls often focus on psychological aspects of users. Researchers investigate motivations beyond sexual gratification, including companionship and emotional connections.
Ethics committees and technology scholars debate the cultural implications of increasingly realistic sex dolls. Key questions include whether these objects affect how people view consent and human dignity.
Some academics argue these dolls provide valuable outlets for sexual expression. Others warn about potential social isolation and detachment from human relationships.
Religious and conservative critiques often center on moral concerns. Meanwhile, progressive academic perspectives typically focus on representation issues rather than outright condemnation.
Controversies and Ethical Considerations
Sex dolls have sparked intense debates throughout history, challenging social norms and raising questions about human relationships, objectification, and morality. These controversies reflect changing attitudes about sexuality and technology across different time periods.
Historical Controversies and Urban Legends
During World War II, an urban legend emerged that Adolf Hitler ordered the creation of sex dolls for German soldiers to prevent them from engaging with foreign women or contracting diseases. While this story lacks solid historical evidence, it demonstrates how sex dolls became entangled with propaganda and military history.
The use of “sailor’s dames” or “dame de voyage” by seamen in previous centuries also generated moral panic among religious authorities. These rudimentary dolls were seen as promoting “immoral” behavior among travelers.
Sex workers faced additional stigma when early dolls were marketed as “replacements” for human companionship. This messaging reinforced harmful stereotypes and devalued women’s autonomy.
People of color and queer people have historically been excluded from doll representations, reflecting broader patterns of discrimination and colonialism in how desire was commercialized and controlled.
Current Debates and Ethical Dilemmas
Modern sex dolls raise complex ethical questions about objectification and consent. Critics argue these products may reinforce harmful attitudes toward real people, particularly women, by presenting idealized, compliant bodies for consumption.
The emergence of childlike sex dolls has sparked particular outrage, with many countries implementing bans. Debate continues about whether such products could encourage harmful behavior or serve as a deterrent.
Privacy concerns have grown as dolls incorporate artificial intelligence and data collection features. Users may not fully understand how their intimate preferences are being recorded or potentially shared.
Some advocates highlight potential benefits for people seeking companionship, including those with disabilities or social anxiety. They argue dolls can provide meaningful connections for individuals with limited access to relationships.
Cultural attitudes vary significantly worldwide, with some countries embracing sex doll technology while others have implemented strict regulations or outright bans based on moral or religious grounds.
Frequently Asked Questions
Sex dolls have sparked curiosity across cultures and time periods. These commonly asked questions explore their evolution, cultural significance, technological advancements, controversies, media representation, and ethical considerations.
How have sex dolls evolved from their inception to the present day?
Sex dolls originated in the 17th century with simple fabric designs like the “Dame de Voyage” used by Dutch sailors on long voyages. These early versions were basic cloth and leather creations meant to provide companionship.
By the 20th century, inflatable dolls became popular, offering a more portable option. These dolls were mass-produced but lacked realism and durability.
The 1990s marked a significant turning point with the introduction of solid, more realistic dolls. Modern versions now feature silicone and TPE (thermoplastic elastomer) construction with detailed facial features, articulated joints, and customizable attributes.
Today’s high-end models incorporate advanced materials that mimic human skin texture and warmth. Some even integrate AI technology for interactive experiences, representing a dramatic evolution from their humble origins.
What cultural impacts have sex dolls had throughout their history?
Sex dolls have reflected changing attitudes toward sexuality across different societies. In some cultures, they’ve helped address issues of loneliness and provided companionship during periods of isolation.
The Japanese market has been particularly influential in normalizing and advancing sex doll technology. Cultural acceptance there has driven innovation and design improvements that eventually spread globally.
Sex dolls have challenged traditional views on relationships and intimacy. They’ve sparked debates about human connection and whether artificial companions can fulfill emotional needs beyond physical satisfaction.
These objects have also served as indicators of sexual liberation movements. Their increasing mainstream presence signals shifting societal comfort with discussing sexuality and personal pleasure.
How has technology influenced the development of sex dolls over the years?
Materials technology has dramatically transformed sex dolls. Early versions used simple fabrics, while modern dolls utilize medical-grade silicone and specialized polymers that closely resemble human skin.
Manufacturing advances have enabled increasingly detailed features. Modern production methods allow for realistic hair implantation, customizable body proportions, and facial expressions that were impossible decades ago.
Robotics and AI integration represent the latest technological frontier. Some contemporary models feature responsive heating elements, programmable personalities, and voice recognition capabilities.
3D printing has revolutionized customization options. This technology allows for highly specific features to be created based on customer preferences, making each doll potentially unique.
What are some controversial aspects in the history of sex dolls?
Gender representation has been a significant controversy, with critics noting most dolls perpetuate unrealistic female body standards. This has raised concerns about objectification and gender stereotyping.
The appearance of childlike sex dolls has created serious legal and ethical dilemmas. Many countries have banned these versions, while debates continue about their psychological impacts.
Some mental health professionals have questioned whether sex dolls might reinforce social isolation. Concerns exist about users potentially withdrawing from human relationships in favor of artificial companions.
Privacy issues have emerged with newer AI-enabled models. Questions about data collection, user information security, and potential surveillance capabilities remain largely unresolved.
In what ways have sex dolls been represented in art and media?
Films like “Lars and the Real Girl” and “Air Doll” have explored the psychological aspects of human-doll relationships. These works often examine loneliness, connection, and the nature of love.
Visual artists have incorporated sex dolls into exhibitions that question consumer culture and objectification. These pieces frequently challenge viewers to consider the boundaries between objects and intimate partners.
Literature has featured sex dolls as metaphors for artificial relationships. Authors have used these figures to explore themes of alienation in modern society and humanity’s increasing reliance on technology.
News media coverage has evolved from sensationalistic to more nuanced reporting. Early stories often emphasized shock value, while contemporary journalism increasingly examines the sociological implications of these products.
What legal and ethical considerations have arisen with the advancement of sex dolls?
Regulatory frameworks vary widely across countries. Some nations have implemented specific restrictions on design features, while others apply broader obscenity laws to their manufacture and sale.
Ethical questions about consent and representation remain unresolved. The increasing realism of dolls has prompted discussions about whether they influence perceptions of real-world consent and human autonomy.
Privacy concerns have grown with smart-enabled models. The potential for data collection during intimate moments raises questions about user confidentiality and information security.
Intellectual property issues have emerged around resemblance to real people. Some manufacturers have faced legal challenges when creating dolls that appear similar to celebrities or individuals without permission.