Throughout history, firearms have played a pivotal role in shaping the outcomes of wars, revolutions, and conflicts across the globe. From their early development to their modern iterations, firearms have continuously evolved, influencing military strategies, geopolitical landscapes, and technological advancements.
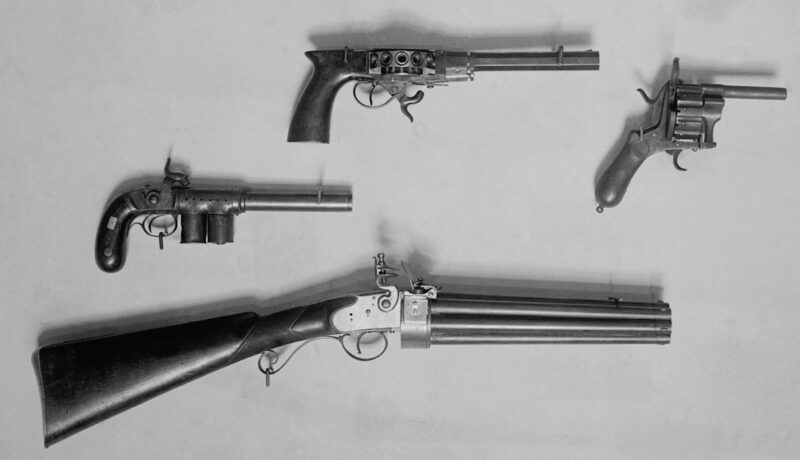

At Pathfinder Militaria, we recognize the historical significance of firearms and their impact on warfare. Understanding their role in historical conflicts provides valuable insight into how warfare has changed over time and how these weapons have shaped societies.
The Evolution of Firearms in Warfare
Table of Contents
Early Firearms (15th – 17th Century)
The introduction of gunpowder in warfare revolutionized combat, replacing traditional melee and archery-based fighting techniques. Early firearms such as the arquebus and matchlock musket allowed armies to strike from a distance, reducing the dominance of armored knights on the battlefield. Notable conflicts that saw the rise of early firearms include:
- The Hundred Years’ War (1337–1453) – The use of early hand cannons gradually influenced European warfare.
- The Spanish Conquest of the Americas (16th Century) – Firearms, combined with steel weapons and disease, played a crucial role in the Spanish conquest of the Aztec and Inca empires.
- The English Civil War (1642–1651) – Muskets and early flintlocks became the primary infantry weapons.
- The Battle of Lepanto (1571) – One of the largest naval battles where firearms played a decisive role.
Flintlock Era and the Rise of Organized Armies (17th – 18th Century)
The flintlock musket replaced the matchlock, improving reliability and ease of use. This period saw the emergence of standardized military tactics, with formations such as line infantry becoming dominant. Key historical conflicts include:
- The Thirty Years’ War (1618–1648) – Marked the widespread use of muskets and field artillery.
- The American Revolutionary War (1775–1783) – Flintlock muskets like the Brown Bess were standard among soldiers.
- The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) – Mass musket volleys and bayonet charges defined battlefield tactics.
- The Seven Years’ War (1756–1763) – The global conflict demonstrated the effectiveness of organized musket formations.
The Industrial Revolution and Rifled Firearms (19th Century)
Advancements in metallurgy and manufacturing led to the development of rifled muskets and breech-loading firearms, significantly increasing accuracy and rate of fire. This era introduced:
- The American Civil War (1861–1865) – Rifled muskets and early repeating rifles, such as the Henry Rifle, changed battlefield strategies.
- The Crimean War (1853–1856) – Demonstrated the impact of rifled weapons and modern artillery.
- The Franco-Prussian War (1870–1871) – Showcased the effectiveness of breech-loading rifles like the Dreyse Needle Gun.
- The Boer Wars (1880–1902) – Guerilla tactics combined with long-range rifles reshaped military engagements.
The Age of Automatic Weapons and Modern Warfare (20th Century – Present)
The 20th century saw rapid advancements in firearm technology, leading to the widespread adoption of automatic weapons, assault rifles, and machine guns. The role of firearms in major conflicts included:
- World War I (1914–1918) – The introduction of fully automatic machine guns, bolt-action rifles, and trench warfare tactics.
- World War II (1939–1945) – Widespread use of submachine guns (MP40, Thompson) and semi-automatic rifles (M1 Garand).
- The Cold War and Beyond (1947–Present) – The AK-47 and M16 became symbols of ideological conflicts, from Vietnam to Afghanistan.
- The Gulf War (1990–1991) – Advanced firearms combined with modern tactics and precision-guided munitions.
The Impact of Firearms on Warfare and Society
- Tactical Evolution – The transition from massed infantry formations to mobile, precision-based combat.
- Geopolitical Influence – Firearms shaped colonial expansion, revolutions, and power shifts between nations.
- Technological Advancements – Innovations in firearm design led to the development of new military strategies and defensive measures.
- Civilian and Resistance Movements – Firearms played a crucial role in uprisings and revolutions, such as the French Revolution and guerrilla warfare in modern conflicts.
- Cultural and Economic Impact – The global arms industry has influenced economic power dynamics and technological advancements in various nations.
Conclusion
Firearms have been a defining factor in military history, influencing how wars are fought and won. From the early matchlocks to modern automatic weapons, their impact on battlefield tactics, national security, and societal change remains profound. As technology continues to evolve, the role of firearms in future conflicts will undoubtedly shape the course of history, just as they have for centuries. The study of these advancements and their consequences allows for a deeper understanding of military strategies and the shifting nature of global power structures.