U.S. arms production during WW2 from 1939-1945.
U.S. arms production in WW2
Table of Contents
During World War 2, the United States underwent a massive industrial mobilization to produce armaments and supplies for itself and its allies. This effort was often referred to as the “Arsenal of Democracy.”
Overview
– 300,000 aircraft
– 124,000 ships
– 41 billion rounds of ammunition
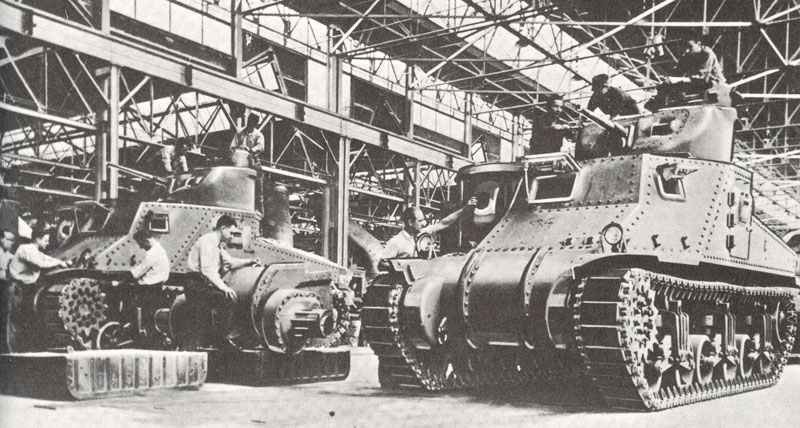
– 100,000 tanks
– 2.4 million military trucks
Conversion of civilian industries: Many civilian factories were converted to produce military goods. For example, automobile manufacturers switched to producing tanks, aircraft engines, and other military vehicles.
New facilities: The government invested in building new production facilities, such as shipyards and aircraft factories.
Scientific advancements: The war spurred technological innovations, including radar, jet engines, and nuclear weapons.
Lend-Lease program: The US supplied vast amounts of equipment to its allies, particularly the UK and Soviet Union, through the Lend-Lease program.
Women in the workforce: With many men serving in the military, women entered the workforce in unprecedented numbers to support production efforts.
Standardization: The US focused on mass-producing standardized designs to increase efficiency and output.
Key products:
– Aircraft: B-17 and B-24 bombers, P-51 Mustang fighters
– Ships: Liberty ships, aircraft carriers, destroyers
– Tanks: M4 Sherman
– Vehicles: Jeeps, trucks, half-tracks
Economic impact: The massive production effort helped end the Great Depression and positioned the US as the world’s leading economic power after the war.
Coordination: The War Production Board was established to coordinate the conversion of civilian industries to military production and allocate resources.
This unprecedented industrial mobilization played a crucial role in the Allied victory in World War 2, cementing the United States’ position as a global superpower.
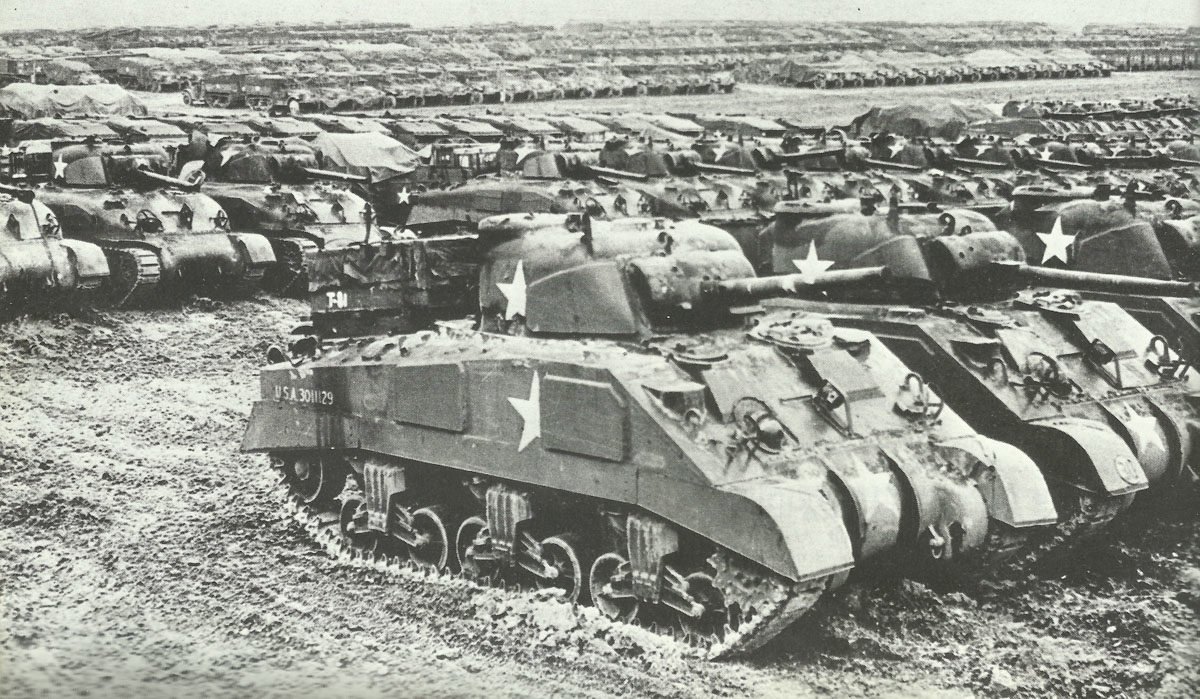

U.S. arms production by weapon types
Following are tables of the annual U.S. arms production (excluding ammunition) and a comparison of the necessary strategic raw materials.
Annual U.S. production figures of the main arms and military equipment (without ammunition) during WW2 from 1939-1945:
Armaments:
Type of Weapon | 1939 | 1940 | 1941 | 1942 | 1943 | 1944 | 1945 | TOTAL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Tanks and Self-propelled guns | - | 331 | 4,052 | 24,997 | 29,497 | 17,565 | 11,968 | 88,410 |
Artillery (including anti-tank and anti-aircraft guns) | 257,390 (1939-45) | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | 257,390 |
Mortars | 105,054 (1939-45) | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | 105,054 |
Machine-guns (without sub-machine guns) | 2,679,840 (1939-45) | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | 2,679,840 |
Infantry rifles | c.11,750,000 (1939-45) | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | c.11,750,000 |
Sub-machine guns | c.1,956,000 (1939-45) | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | ? | c.1,956,000 |
Military trucks and Lorries | 32,604 (1939-40) | ? | 183,614 | 619,735 | 621,502 | 596,963 | 327,893 | 2,382,311 |
Fighter planes | ? | 1,162 | 4,416 | 10,769 | 23,988 | 38,873 | 20,742 | 99,950 |
Light and medium bombers | ? | 623 (incl. heavy) | 4,115 (incl. heavy) | 10,012 | 19,740 | 18,672 | 9,282 | maximum 62,444 |
Four-engined bombers | ? | ? (in light and medium) | ? (in light and medium) | 2,615 | 9,615 | 16,331 | 6,805 | minimum 35,366 |
Reconnaissance planes | ? | 63 | 727 | 1,468 | 734 | 259 | 667 | 3,918 |
Transport planes | ? | 164 | 532 | 1,984 | 7,012 | 9,834 | 4,403 | 23,929 |
Trainers and miscellaneous military types | ? | 1,794 | 9,373 | 17,631 | 19,939 | 7,577 | 1,309 | 57,623 |
Aircraft carriers (all types) | - | - | - | 18 | 65 | 45 | 13 | 141 |
Battleships | - | - | - | 4 | 2 | 2 | - | 8 |
Cruisers | - | - | 1 | 8 | 11 | 14 | 14 | 48 |
Destroyers | - | - | 2 | 82 | 128 | 74 | 63 | 349 |
Escorts (Corvettes, Frigates) | - | - | - | - | 298 | 194 | 6 | 498 |
Submarines | - | - | 2 | 34 | 55 | 81 | 31 | 203 |
Merchant shipping tonnage | 376,419 | 528,697 | 1,031,974 | 5,479,766 | 11,448,360 | 9,288,156 | 5,839,858 | 33,993,230 |
Raw material production for the military weapon production above:
Annual strategic raw material production (m. metric tons):
Year | 1939 | 1940 | 1941 | 1942 | 1943 | 1944 | 1945 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Coal | ? | ? | ? | 528.5 | 535.3 | 562.0 | 523.9 |
Ore | ? | ? | ? | 107.6 | 103.1 | 96.0 | 90.2 |
Steel | ? | ? | ? | 80.6 | 82.2 | 85.1 | 86.6 |
Aluminium (in 1,000 metric tons - especially important for aircraft production) | ? | ? | ? | 751.9 | 1,251.7 | 1,092.9 | 1,026.7 |
References and literature
World War II – A Statistical Survey (John Ellis)
Chronology of World War II (Christopher Argyle)










Any idea where I can locate information relating to how and where phosphorus incendiary devices were put together and stored during WWII? I can locate no information or references.
Thanks
Charles