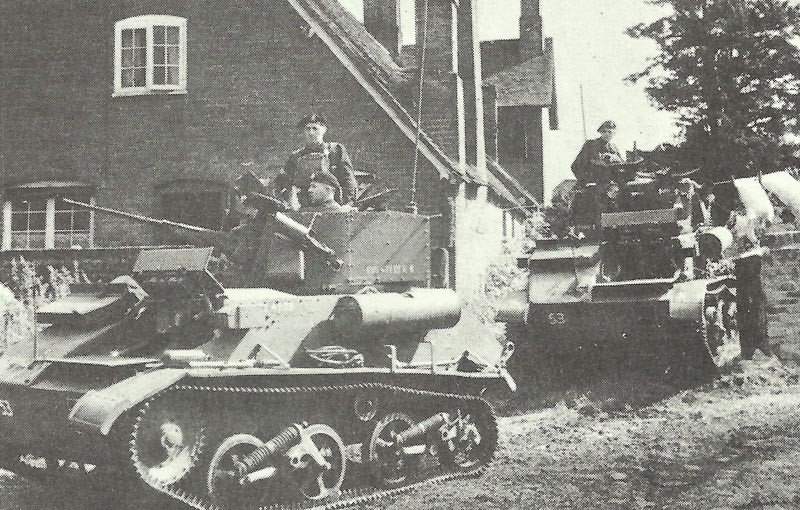
British Light Tanks Mk VIA, VIB, VIC from the beginning of WW2.
History, development, service, specifications, statistics, pictures and 3D model.

Vickers Mark I-VI, VIA, VIB, VIC.
Type: Light tank.
History:
Table of Contents
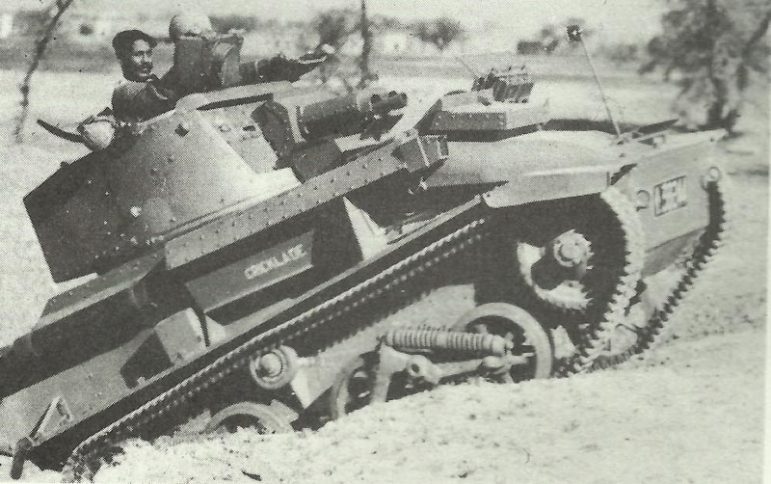
Right after the Mk V light tanks, the Mk VI was similar in every way’s aside from the turret that has been even more remodeled to provide space within the back for the new wireless equipment. In the Mk VIA the solitary return roller was taken from the top of the primary bogie and connected to the hull sides. The Mk VIB became a tank mechanically just like the VIA, however with characteristic variations to streamline manufacturing. These alterations incorporated a one-piece armored louvre above the radiator (rather than a two-piece louvre) along with a simple round cupola instead of the faceted model of the VIA.
The Light Mk VIB Indian version, manufactured for the Indian Army, was similar to the regular version aside from the removing of the commander’s cupola to be replaced by an ordinary hatch in the turret top.
The Mk VIC, final of the models, furthermore didn’t have the commander’s cupola and was more strongly armed than its predecessors, owning co-axial 15 mm and 7.92 mm Besa machine guns instead of the .303 and -.5 Vickers machine guns of the previously versions. Additionally, it had larger bogies and 3 carburetors in the power plant to provide increased speed.
The Mk VI light tanks went into manufacturing in 1936 and VIC manufacturing ended in 1940.
The tanks were in extensive service with the British Army at the beginning of WW2 in 1939, the VIB staying manufactured and employed in the most significant figures. The majority of British tank power in 1940, in France, in the Western Desert, and anywhere else was basically made up of Mk VI light tanks, and they were usually used to work in the ‘cruiser tank’ function instead of the reconnaissance purpose for which they were designed – typically with significant losses to themselves.
After Dunkirk, these light tanks were furthermore commonly used to prepare armored divisions in the United Kingdom and continued to be in really extensive ‘first line’ service as late as 1942, even though at that time becoming succeeded by later tanks and directed to exercising.
Versions:
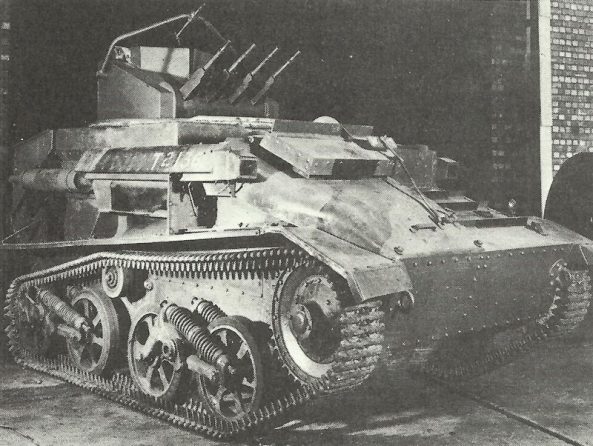
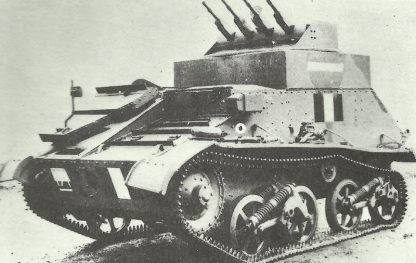
Tank Light AA Mk I: Encounter under the Blitzkrieg war during the German attack of France and Belgium in May 1940, when the British troops initially stumbled upon combined air attacks supporting assaults by German Panzer divisions, resulted in the quick creation of professional anti-aircraft tanks. Experimental variants, depending on the Mk V chassis, were tested. Production tanks had a power-operated turret with 4 x 7.92 mm Besa MGs placed in an altered superstructure. The initial version, Tank, Light AA Mk I, was on the Mk VIA platform.
Tank Light AA Mk II: This was basically the just like the Light AA Mk I, but had upgrades by means of superior sights and a roomier, more accessible, turret. In addition, it had an exterior ammunition bin installed on the hull back. The Tank, Light AA Mk II was constructed on the Light Mk VIB chassis. A troop of 4 Anti-aircraft tanks was along with every regimental HQ squadron.
Tank Light Mk VIB, with revised suspension: Only a few Mk VIBs were equipped with bigger size sprocket wheels and individual idlers at the back (as in the Light Mk II) to be able to provide extended ground contact and much better cruise. This particular customization was just for trials, nevertheless, and it was definitely not put into practice as common.
Tank Light Mk VI, Bridgelayer: A single chassis was transformed by MEXE in 1941 to transport a light foldable scissors bridge. Transported to the Middle East Forces for battle studies, it was obviously lost on the way and no further report of it is available.
Users: Great Britain, Australia, Canada, South Africa, Italy.
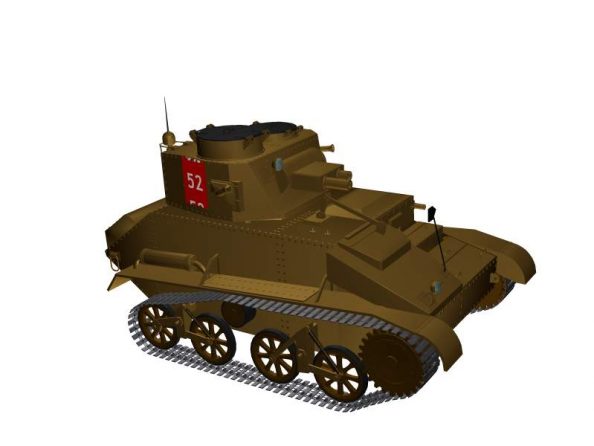
Animated 3D model Vickers Mk VIB in Western Desert
Specifications for Light Tank Mk VIB
Specifications:
Mk VIB | Specification |
|---|---|
Type | Light tank |
Engine | Meadows 6cylinder 88HP |
Gearbox | ? |
Crew | 3 |
Turret crew | 2 |
Length | 12ft 11.5in (3.99m) |
Width | 6ft 9in (2.05m) |
Height | 7ft 3.5in (2.23m) |
Weight | 11,740lb (5,283kg) |
Maximum speed | 35 mph (56 km/hr) |
Cross-country speed | c.25 mph (41 km/hr) |
Fuel consumption per 100 Kilometers | ? |
Fuel | ? |
Road radius | 130 miles (208 km) |
Cross-country radius | ? |
Vertical obstacle | 2 ft (0.61m) |
Trench crossing | 5 ft (1.52m) |
Fording depth | 2 ft (0.61m) |
Turning circle | ? |
Climbing power | 60° |
Armor:
Mk VIB | mm | angle |
|---|---|---|
Turret front | 15 | ? |
Turret side | 15 | ? |
Turret rear | 12 | ? |
Turret top | 10 | ? |
Hull front | 12 | ? |
Hull side | 8-14 | ? |
Hull rear | 8-14 | ? |
Hull top | 10 | ? |
Armament and Equipment:
Mk VIB | Specification |
|---|---|
Main armament | 1 x Vickers .5 MG |
Rounds | 400 |
Traverse | 360° |
Elevation | ? |
Secondary armament | 1 x Vickers .303 MG coaxial (2,500 rounds) |
Radio | available, type unknown |
Telescopic sight | ? |
Production:
Mk VI | figures |
|---|---|
Production | 1936 - 1940 |
Price per tank | ? |
Total production figure | c. 1,000 |
References and literature
Panzer und andere Kampffahrzeuge von 1916 bis heute (Christopher F. Foss, John F. Milsom, Colonel John Stafford Weeks, Captain Georffrey Tillotson, Richard M. Ogorkiewicz)
Krieg der Panzer (Piekalkiewicz)
British and American Tanks of World War II (Peter Chamberlain, Chris Ellis)