History of the French heavy tank Char B1 and its service in the computer game War Thunder.
History, development, service, specifications, statistics, pictures and 3d model.
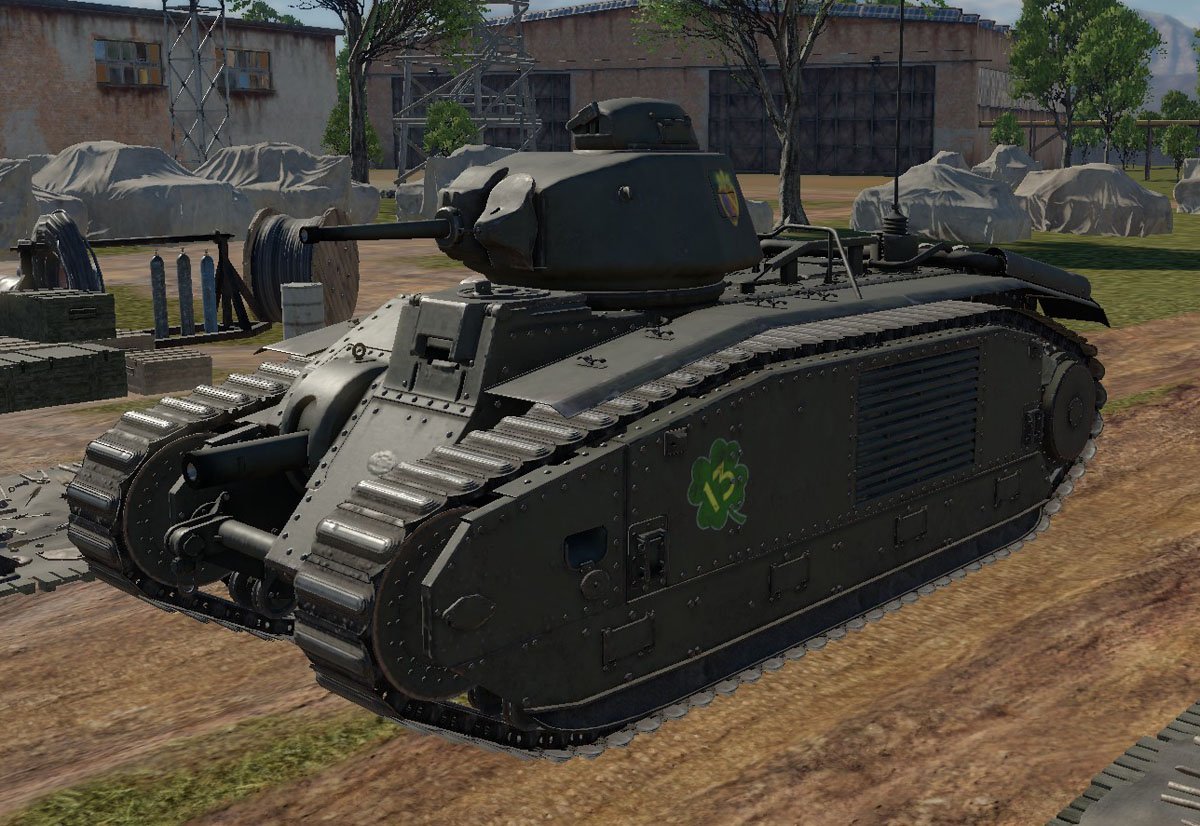

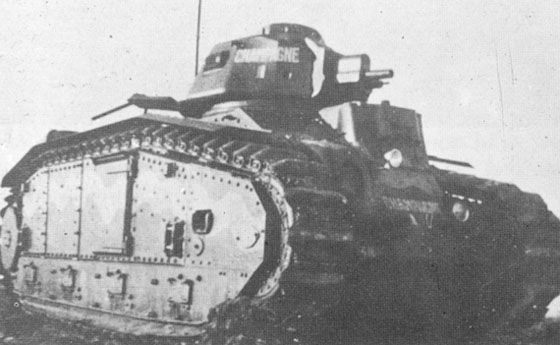
French heavy tank Char B1
Table of Contents
Char B1
Type: heavy tank.
History
The series of tanks known as the Char B definitely had a World War One look like they were designed for. So it is not surprising that the traces of their development can be traced back to 1921, to the aftermath of the ‘Great War’ of 1914-18.
The leading French tank expert, General Estienne, as head of the Section Technique des Chars de Combat, demanded a design for a new tank from five companies. What was demanded at that time was a tank with a 75 mm cannon mounted in a ‘gun port’ in the front of the hull. In 1924, four different vehicles were presented at Rueil.
In 1927, the companies FAMH (Forges et Chantiers de la Marine et d’Homecourt), FCM (Forges et Chantiers de la Mediterranee) and Renault-Schneider each received the order to build one tank. These were completed between 1929 and 1931 and were designated Char B.
This heavy tank had a weight of about 25 tons. Delays in development and tight budgets in France meant that the series version was not released until 1935 as the Char B1.
This Char B1 was a powerful tank for its time, as it was armed with a 47 mm cannon in the turret and a 75 mm cannon in the lower hull front. The limited traverse of the heavy cannon was partly compensated by a complex control system, which enabled the vehicle to be quickly aimed in a different firing direction.
The archaic appearance was deceptive in that the Char B had many very advanced design features ranging from self-sealing fuel tanks to grouped lubrication of the numerous bearings. There was also an electric starter and much attention was paid to internal fire protection.
However, the four-man crew was scattered inside the vehicle in a way that made it difficult for them to communicate with each other and led to many problems in the field. The crew of the Char B1 therefore had to consist of a highly qualified group of specialists in order to make the best possible use of the vehicle’s potential combat power. In 1940, however, very few crews met these requirements.
The final production model was the Char B1-bis, which had a reinforced armor plating of maximum 65 mm (2.56 in) and minimum 14 mm (0.55 in), compared to the Char B1 of maximum 40 mm (1.57 in) and minimum 14 mm (0.55 in). The B1-bis also had a revised turret design and a more powerful engine.
Later production models had an even more powerful aircraft engine for propulsion and additional fuel capacity.
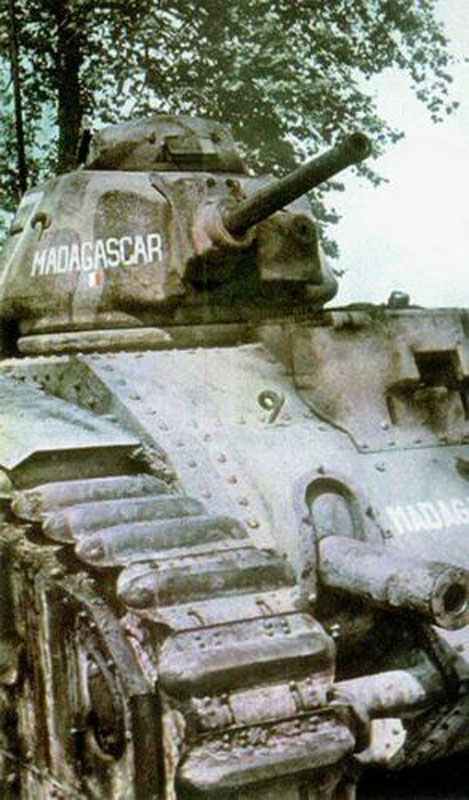
The production of the Char B1-bis started in 1937 and until 1940 about 400 Char B of all types were delivered. Of these, 66 were with the 1st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th DCR (Division Cuirassee de Reserve) and another 57 were with various independent units.
At that time the Char B1 and Char B1-bis were the most numerous and most powerful of all French heavy tanks and the basic version was the main battle tank of the few tank formations of the French Armed Forces.
Until the armistice in June 1940, 35 Char B1, 365 Char B1-bis and 5 Char B1-ter were built.
The excellent armor of the Char B1-bis could practically only be penetrated by the German 88 mm gun Flak.
Its hull consisted of bolted castings and the driver had his place in the front left and steered the vehicle with an ordinary steering wheel, which operated a hydraulic system.
To the right of the driver was the short-barreled 75 mm SA-35 cannon with caliber 17.1 and an elevation of -15° to +25° degrees. Since the cannon could not be traversed sideways, the driver had to aim with the whole tank. The cannon also had a fan which blew the powder gases out of the barrel. A 7.5 mm Chatellerault machine gun was installed a little below the 75 mm cannon, which could be operated by both the driver and the commander.
The crew consisted of four men. The commander had to lead the vehicle and was also the gunner and loader for the turret gun, which was a considerable disadvantage to his German pedant in tank combat.
The loader gunner also had his hands full, since he had to supply the turret gun from the tank’s stores as well as the 75 mm cannon in the hull. The radio operator was located near the turret.
The driver had his entry and exit hatch above his seat in the front left of the hull, while the other crew members usually entered the tank through an armored door on the right side of the hull. There was also a hatch in the turret roof and as emergency exits a hatch in the hull floor and in the roof of the engine compartment.
Engine, transmission and fuel tanks were in the rear part of the hull. Besides the electric starter there was also a compressed air starter. A gyro direction indicator was driven by the blower.
Of the 16 track rollers of the crawler, 12 ran in groups of four in three wheel frames, which were damped by vertical coil and leaf springs. Three other rollers were located in a wheel frame at the front, while one individual roller was located at the rear on a leaf spring.
The guide wheel, which functioned at the same time as a tension wheel by means of a coil spring, was located at the rear and the drive wheel at the front.
Although the German soldiers had great respect for the Char B1, whose 75 mm cannon could even take out the Panzer IV, the potential effect of the French heavy tank was reduced by various factors in May 1940.
One of the reasons was that the Char B1 was a complex beast and therefore required a lot of careful maintenance. Under the conditions of the ‘Blitzkrieg’, therefore, many simply broke down on the way to the battle area and were captured by the Germans undamaged.
The possible potential of the type in combat was also somewhat diminished by the fact that it required a well-trained crew, and the disadvantage that applies to all French tanks was that the commander had to command the vehicle and crew in addition to operating the turret cannon.
Finally, the Char B1 was also used by the French High Command, as was the case for all other of their tank formations, fragmented into small units for local defense tasks instead of being used in a massive strike against the German tank advance.
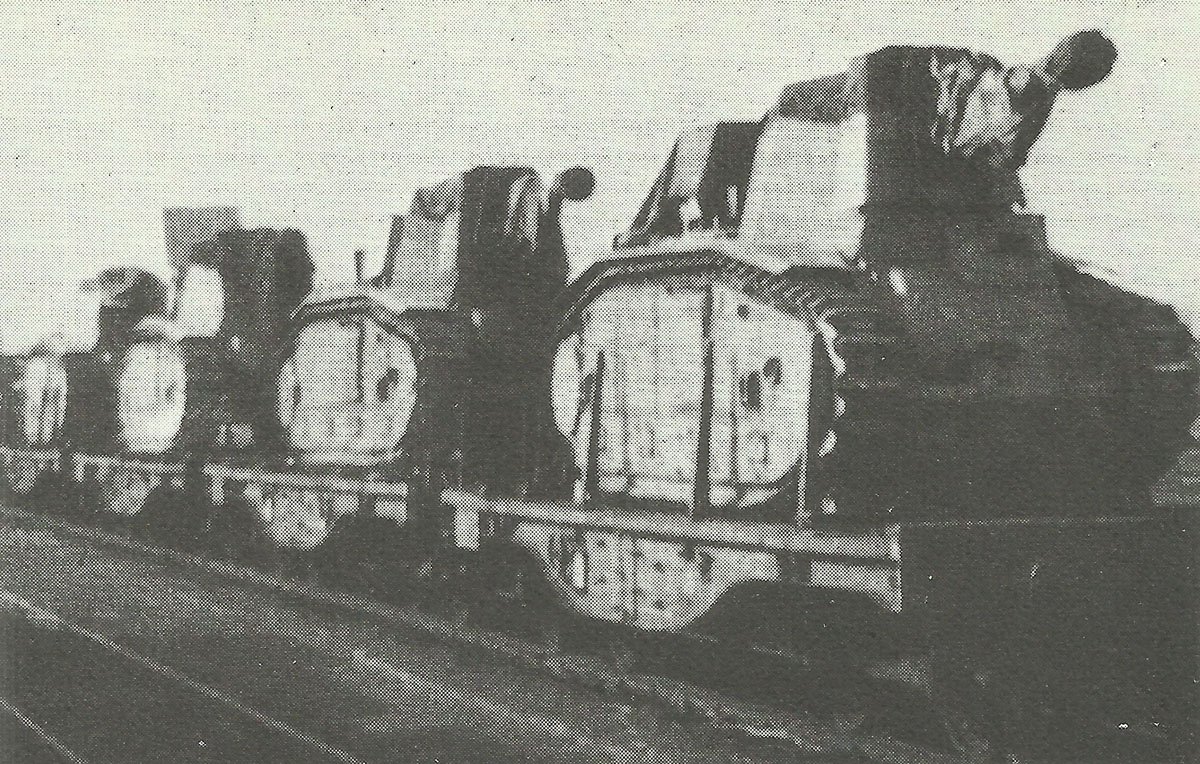
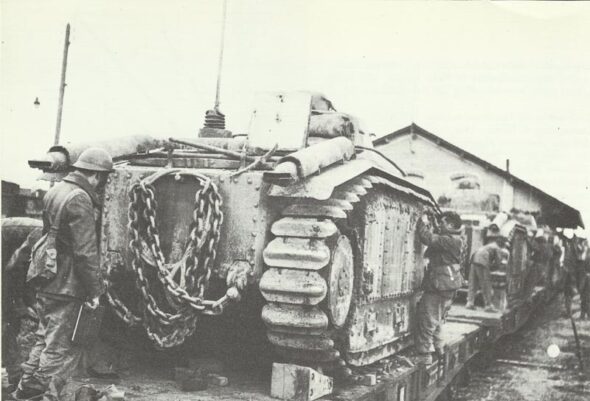
The Wehrmacht took over the captured Char B1-bis as PzKpfw B1-bis 740(f) and used them for a variety of purposes.
Many Char B1s were distributed unchanged to occupying troops in France and some were still standing around in the occupied British Channel Islands at the end of the war. Four went with the 223rd Panzer Company to the Eastern Front and seven with the SS-Division Prinz Eugen to the Balkans.
Others were used as school vehicles and 16 were converted to artillery self-propelled guns in 1942. 60 were equipped with flamethrowers and became the PzKpfw Flammwagen(f).
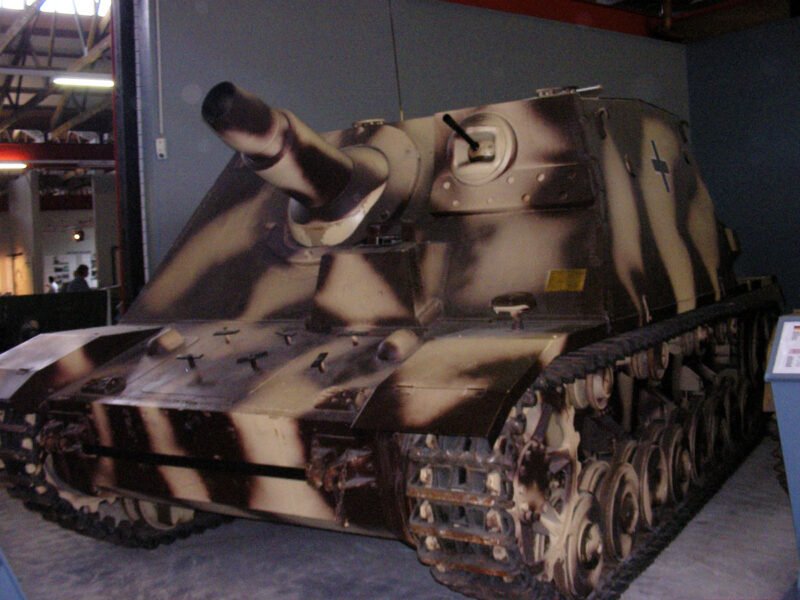
In 1944 some of them were reconquered by the Allies and were again used by the French army, but by 1945 only a handful of them were left. Today there are still three of them in museums.
Users: France, Germany.
Char B1-ter
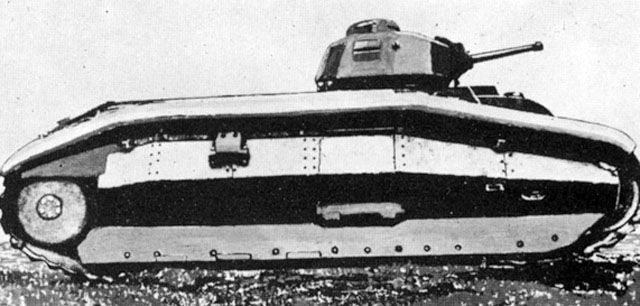
When the budget for the production of the Char B1-bis was released in 1935, an order was also placed to develop a version of the Char B with up to 75 mm armor.
The opportunity was taken to change the design of the hull and to make room for a fifth crew member, who was to serve as a mechanic in the tank.
The armament remained the same, but practical experience had shown in the meantime that it was a disadvantage to aim the 75 mm cannon in the hull mainly by turning the tank. Therefore, this cannon was given a limited traverse range of 5° in each direction in the new design.
A prototype of the new tank, named Char B1-ter, was demonstrated in front of Daladier at Satory in 1937. However, only five vehicles of this type were produced, while production was concentrated on the Char B1-bis.
Char B1 in War Thunder
Status of the information: June 2020.

In the F2P game War Thunder, the Char B1-ter is a premium vehicle and located on the ‘Battle Rating’ (short BR) 2.3. The freely playable variant is the standard Char B1-bis with weaker armor, engine and lacking traverse range for the main gun on BR 2.0.
Once you get used to aiming with the main gun in the hull by the alignment of these heavy tanks, the double fire together with the turret gun is devastating for most enemy vehicles. But what you should be aware of, especially in higher-rated battle ratings, is the limited penetrating power of the cannons, making accurate targeting of weak points unavoidable.
But if the Char B1-ter is thrown into battle with a good ‘Battle Rating’, it can hardly be penetrated by most of the enemy tanks, can be driven or positioned against the enemy without any cunning and almost ‘blindly’ and can decide the game without further ado.
For the composition of your vehicle line you should always have a replacement voucher for the Char B1-ter ready and also have the standard Char B1-bis as a third entry. So you can throw three of these heavy tanks into battle one after the other if necessary !
As a good addition to a line with a total of nine slots for France on BR 2.3 the following vehicles are recommended:




Video of the action with Char B1-ter in War Thunder
Here you can see an approximately 12-minute video of a Char B1-ter mission, where this heavy tank takes a lot of punishment without paying much attention to the opponent’s vehicles, achieved seven kills, three assists, two CAP conquests and uncounted hits without being destroyed and finally wins a battle that would almost certainly have been lost without it:
Victory rate and BR’s
I have played the French deck of BR 2.3 with the two Char B1 tanks 48 times so far. Of these, 16 fights (i.e. 37 %) were on the best BR of 2.3, 9 (or 21 %) on BR 2.7, 8 (or 19 %) on BR 3.0 and 15 (or 35 %) on the worst BR 3.3.
There were a total of 27 victories (56%) and 129 enemy vehicles were destroyed, which was about 2.69 kills per battle.
The individual statistics for the Char B1-ter are as follows: Victory rate 54 %, 109 kills and 42 times destroyed, 277.000 earned in-game currency SL (Silver Lions) and 38.700 generated research points.
If you don’t know this F2P tank and plane game yet, you can download War Thunder here for free and will receive extra 50 Golden Eagles premium currency as well as a Rank I premium plane or tank:
Specifications
Specifications:
Char B1-bis | Specification |
|---|---|
Type | Heavy tank |
Engine | Renault 6cyl 16.5lit 307 hp at 1.900 rpm |
Gearbox | 5 forward, 1 reverse |
Crew total | 4 |
Turret crew | 1 (Commander, simultaneous gunner and loader for turret gun) |
Length | 20 ft 10.8 in (6.37 m) |
Width | 8 ft 2.4 in (2.50 m) |
Height | 9 ft 1.8 in (2.79 m) |
Weight | 31,5 tonnes (32 t) |
Maximum speed | 17.4 mph (28 km/hr) |
Cross-country speed | ? |
Fuel consumption per 100 miles | ? |
Fuel | ? |
Road range | 93 miles (150 km) |
Cross-country radius | ? |
Vertical obstacle | 3 ft 1 in (0.93 m) |
Trench crossing | 9 ft (2.74 m) |
Fording depth | ? |
Turning circle | ? |
Gradient | 50 % |
Armor:
Char B1-bis | Armor (mm) | Angle |
|---|---|---|
Turret front | 56 | 0° |
Turret side | 46 | 22.5° |
Turret rear | 46 | 22.5° |
Turret top | 30 | 72.5° and 90° |
Superstructure front | 60 | 20° |
Superstructure side | 60 | 0° |
Superstructure rear | 55 | 0° |
Superstructure top | 25 | 80° and 90° |
Hull front | 60 | 45° |
Hull side | 60 | 0° |
Hull rear | 55 | 43° |
Hull bottom | 20 | 90° |
Gun mantlet | 56 | round |
Armament and Equipment:
Char B1 | Specification |
|---|---|
Main armament | 75-mm-SA-35 L/17.1 gun (in hull) |
Rounds | 74 |
Traverse | 0° |
Elevation | -15° to +25° |
Secondary gun | 47-mm L/34 gun in APX turret |
Rounds | 50 |
Traverse | 360° (electric) |
Elevation | -18° to +18° |
Secondary armament | 7.5 mm MG coaxially in the turret (own traverse -10° to +10°), one 7.5 mm MG below the 75 mm gun in the hull |
Radio | FuG5 (4 km range) in vehicles used by the Wehrmacht |
Telescopic sight | ? |
Penetration of guns unknown.
Service statistics:
Figures | Char B1 |
|---|---|
Production | 1937-1940 |
First combat | May 1940 |
Price per tank | ? |
Total production figure | 405 (35 Char B1, 365 Char B1-bis, 5 Char B1-ter) |
References and literature
Krieg der Panzer (Piekalkiewicz)
The Encyclopedia of Weapons of World War II (Chris Bishop)
Panzer und andere Kampffahrzeuge von 1916 bis heute (Christopher F. Foss, John F. Milsom, Colonel John Stafford Weeks, Captain Georffrey Tillotson, Richard M. Ogorkiewicz)
Panzerkampfwagen des 1. und 2. Weltkrieges (Andrew Kershaw)
French Infantry Tanks: Part I – Chars 2C, D and B (Major James Bingham)
French Tanks of WWII