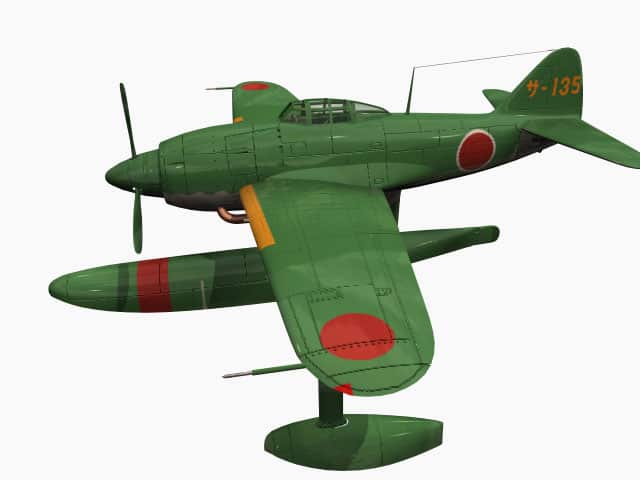
German Luftwaffe fighter plane Messerschmitt Bf 109 F of World War II.
History, development, service, specifications, pictures and 3D model.
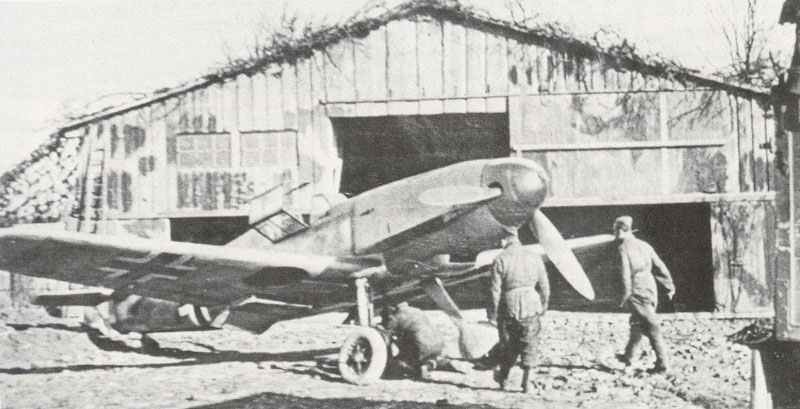

Messerschmitt Bf 109 F (Friedrich)
Table of Contents
Messerschmitt Bf 109 F
Type: German Luftwaffe fighter plane.
The Messerschmitt Bf 109F, often referred to as the ‘Friedrich’, was a German World War II fighter aircraft. It was a variant of the famous Bf 109 series and was introduced in 1941.
Overview
Improved aerodynamics: The Bf 109F had a more streamlined cowling, redesigned wings, and a new radiator design, which enhanced its speed and maneuverability compared to earlier variants.
Armament: It was typically armed with a 15 mm or 20 mm cannon firing through the propeller hub and two 7.92 mm machine guns in the upper engine cowling.
Engine: The Bf 109F was powered by a Daimler-Benz DB 601E or DB 601N engine, producing around 1,300 horsepower.
Performance: The aircraft had a maximum speed of approximately 390 mph (628 km/h) and a service ceiling of 37,890 ft (11,550 m).
Variants: Several subvariants of the Bf 109F were produced, including the F-1, F-2, F-3, and F-4, with differences in armament and other minor details.
Service: The Bf 109F served on all fronts where the Luftwaffe operated, including the Eastern Front, Western Europe, North Africa, and the Mediterranean.
Pilots: Many notable German fighter aces flew the Bf 109F, including Hans-Joachim Marseille and Erich Hartmann.

The Messerschmitt Bf 109F was a formidable fighter aircraft that played a significant role in the early years of World War II. It was eventually replaced by later variants of the Bf 109, such as the Bf 109G ‘Gustav’.
History
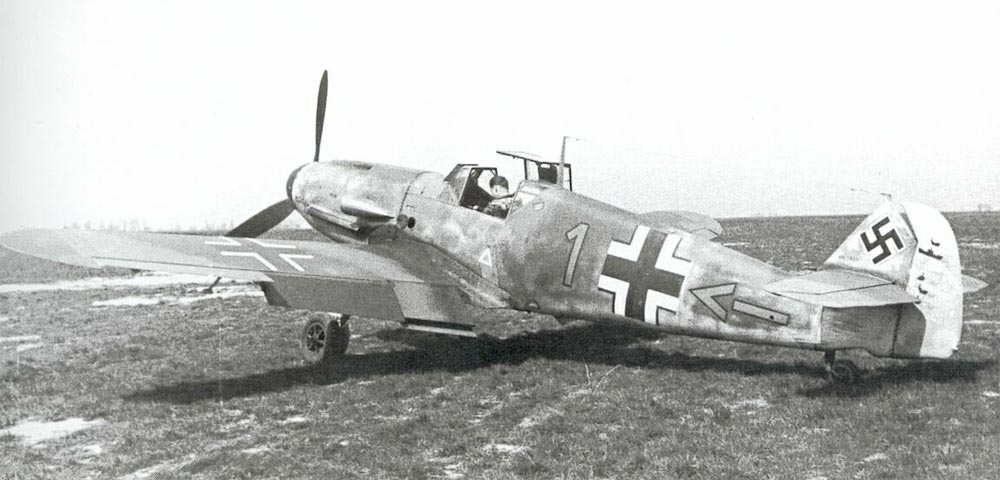

During the period of the manufacturing of the Me 109 E for the German Luftwaffe, Messerschmitt was creating what was to turn into the best of the many variants, the Me 109 F. Operated by either a 1,200hp DB 601N or a 1,350hp DB 601E power plant, the Me 109 F shown significant progress over previously models when it comes to both performance and cleanliness of line, and finally offered the Luftwaffe a fighter that could outmaneuver the Spitfire V.
The complete fuselage had been better aerodynamically, concluding in a more curved rudder, an unbraced tailplane along with a retractable tail-wheel; the wings, of marginally improved span, were curved off at the tips; and performance at all altitudes was superior to that of previous versions.

Manufacturing series ran from F-1 to F-6, with a variety of sub-types. Several F-series planes were utilized as test beds, the products examined including BMW 801 (radial) and Jumo 213 motors, a V-type tail device, rocket weapons, and a nose wheel landing gear.
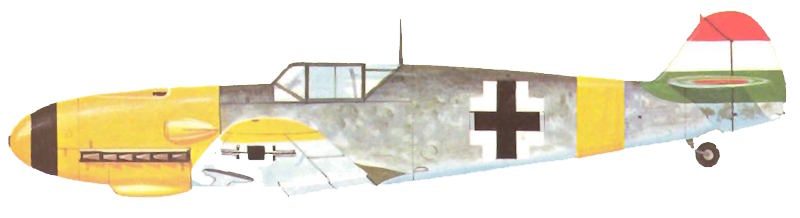
A prototype never flown, but nonetheless of fascination, was the Me 109 Z of 1943, by which a pair of Me 109 F’s were ‘twinned’ by linking them by a fresh, common wing center-section and tail plane, the single pilot being intended to take up a cockpit in the port fuselage.
By 1942 the Me 109 F had been replaced in manufacturing and service by the most numerous model, the Me 109 G, called ‘Gustav’.
Users: German Luftwaffe (for Bf 109 F).

Animated 3D model Me 109 F
Specifications Messerschmitt Bf 109 F-4
Specifications:
Me 109 F-4 | Specification |
|---|---|
Type | single-seat fighter |
Power plant | one 1,350 hp Daimler Benz DB601E-1 inverted-vee-12 liquid-cooled engine |
Accommodation | 1 |
Wing span | 32 ft 6.7 in (9.92 m) |
Length overall | 29 ft 0.3 in (8.84 m) |
Height overall | 8 ft 6.0 in (2.59 m) |
Wing area | 174.38 sq/ft (16,20 m²) |
Weight empty equipped | 5,269 lb (2,390 kg) |
Weight loaded | 6,393 lb (2,900 kg) |
Maximum wing loading | 36.66 lb/sq ft (179.01 kg/m²) |
Maximum power loading | 4.73 lb/hp (2.14 kg/hp) |
Maximum speed | 388 mph at 21,325 ft (625 km/hr at 6,500 m) |
Cruising speed | 355 mph at 16,405 ft (585 km/hr at 5,000 m) |
Time to height | 16,405 ft (5,000 m) in 5.2 min |
Service ceiling | 39,375 ft (12,000 m) |
Range | 528 miles (850 km) with 300-liters drop tank |
Armament:
Me 109 F-4 | Specification |
|---|---|
above engine | 2 x 15.1mm MG151 machine guns (700 rpm, velocity 3,131 ft/sec) |
through propeller hub | 1 x 20mm MG FF (540 rpm) |
optional in fairings under wings | 2 x 20mm MG151/20 machine guns (720 rpm, velocity 1,920 ft/sec) |
Service statistics:
Me 109 F | figures |
|---|---|
First flight prototype | July 1940 |
Production delivery | 1941 |
Service delivery | Spring 1941 |
First combat reports | May 1941 |
Final delivery | 1942 |
Price per unit | RM 100,000 = c. $45,000 = c. £ 11,250 |
Total production figure (all) | 35,000+ (of these 30,480 during WW2) |
Accepted by Luftwaffe 1/39-12/44 (all) | 29,350 |
Production 1941 (all variants) | 2,764 |
Production 1942 (all variants) | 2,665 |
Me 109's in First Line Units 20.9.42 | 1,074 |
Me 109's in First Line Units 31.12.42 | 700 (still 90 Me 109 F) |
References and literature
The Encyclopedia of Weapons of World War II (Chris Bishop)
Combat Aircraft of World War II (Bill Gunston)
Technik und Einsatz der Kampfflugzeuge vom 1. Weltkrieg bis heute (Ian Parsons)
Das große Buch der Luftkämpfe (Ian Parsons)
Luftkrieg (Piekalkiewicz)
Flugzeuge des 2. Weltkrieges (Andrew Kershaw)
German Aircraft of World War 2 in Colour (Kenneth Munson)
Warplanes of the Luftwaffe (David Donald)
The Luftwaffe Album, Bomber and Fighter Aircraft of the German Air Force 1933-1945 (Joachim Dressel, Manfred Griehl)
Luftwaffe Handbook (Dr Alfred Price)









