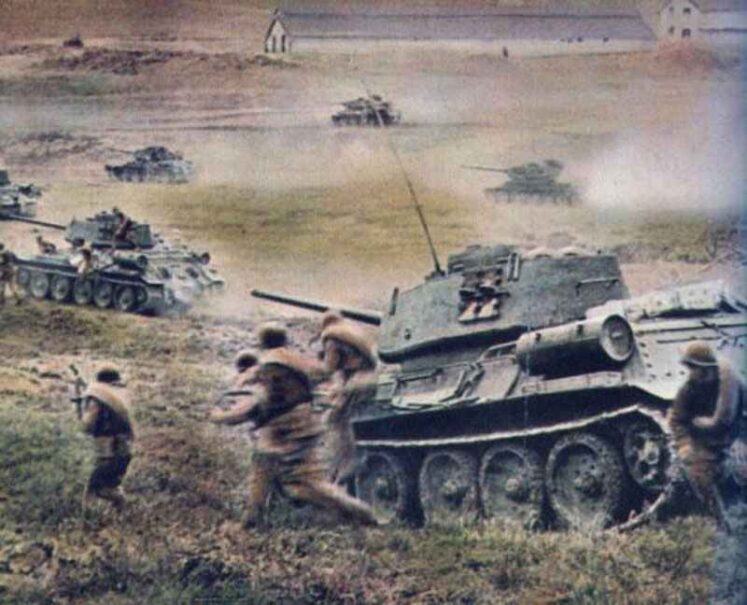
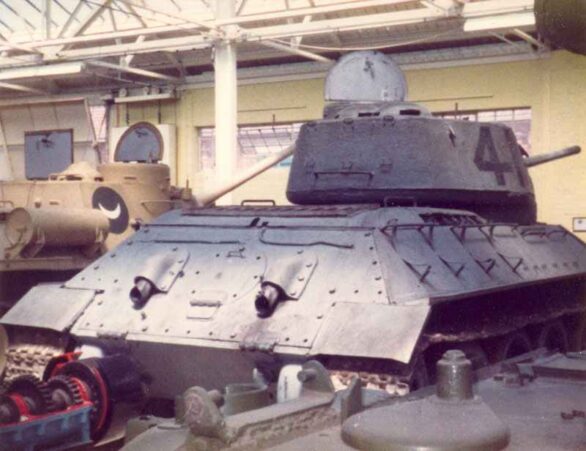
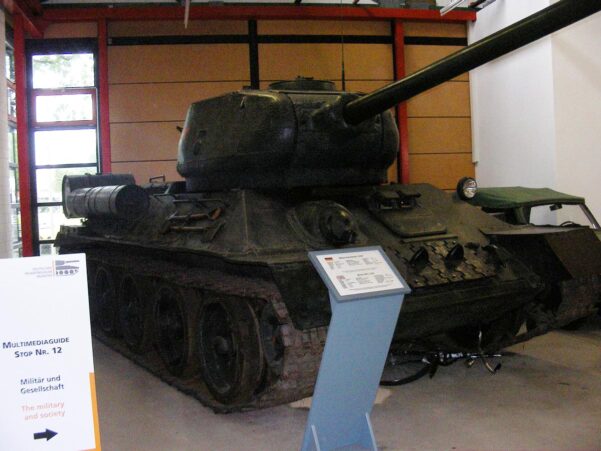
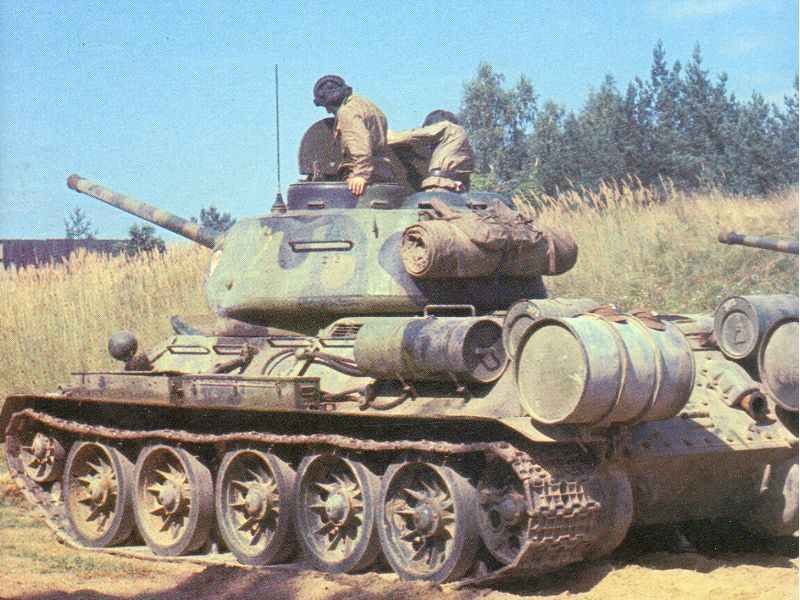
Soviet medium tank T-34 with 85-mm gun from the Second World War.
History, development, service, specification, pictures and 3D model of T-34-85.

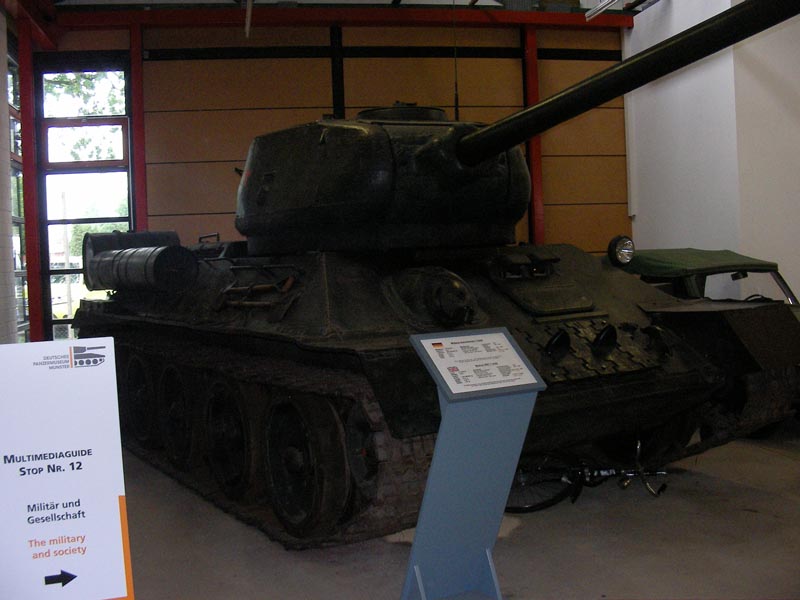
T-34 with 85mm gun
Table of Contents
T-34-85
Type: Russian medium battle tank.
The T-34-85 was a Soviet medium tank that served during World War II and beyond. It was an upgraded version of the earlier T-34 tank, which was introduced in 1940. The T-34-85 featured several improvements over its predecessor, making it one of the most effective and influential tank designs of the war.
Overview
Improved armament: The T-34-85 was equipped with an 85mm main gun, which provided better anti-tank capabilities compared to the 76mm gun of the original T-34.
Enhanced turret design: The turret was enlarged to accommodate the bigger gun and provide more space for the crew, improving their efficiency and comfort.
Stronger armor: The frontal armor of the T-34-85 was slightly thicker than that of the T-34, increasing its survivability on the battlefield.
Reliable and easy to produce: Like its predecessor, the T-34-85 was designed for mass production and easy maintenance, allowing the Soviets to quickly replace combat losses.
Versatility: The T-34-85 was effective in various roles, including infantry support, exploitation, and anti-tank warfare.
The T-34-85 first saw combat in early 1944 and played a crucial role in the Soviet offensives that ultimately led to the defeat of Nazi Germany. Its success influenced post-war tank designs, and the T-34-85 remained in service with various countries for decades after the war. Many experts consider the T-34 series, including the T-34-85, to be one of the best tank designs of World War II.
History

The inability of the T-34 Model 1943 adequately to deal with the new German armor, like the Panzer V Panther and Panzer VI Tiger, forced the NKTP to accept the fact that major improvements in Russian tank design would have to be accepted no matter what disruption they caused the tank industry. The GKO intervened, having been deluged by complaints from the field that Soviet tanks needed ‘a longer arm’ to reach out and smash German armor.
Four gun design teams were assigned to a crash program to field an up-armed T-34. Besides the Grabin and Petrov teams already working on 85 mm guns, Grabin’s bureau at Zavod No 92 in Gorki was turned over to 23-year-old A. Savin when Grabin was shifted to the Central Artillery Design Bureau (TsAKB) in Moscow, and K. Siderenko’s team also began design work on their S-18 85 mm gun. The new guns were tested at the Gorokhovieskiy Proving Grounds outside Gorki, where Grabin’s ZiS-53 was declared the winner.
Unfortunately, the new turret, designed by V. Kerichev at Krasnoye Sormovo in Gorki, did not mate properly with the new gun, apparently being designed around Petrov’s D-5 gun which had been available earlier since it was already in production for the SU-85.
Two unarmed T-34-85s were completed on 15 December 1943, and the GKO approved the type for Army service despite the problems. To circumvent any further delays, the NKTP ordered the T-34-85 into production on an interim basis, using the runner-up D-5T gun. This entered production at Zavod Nr. 112 Krasnoye Sormovo in December 1943. In the meantime, Grabin’s gun was adapted to fit the new turret by Savin, who incorporated other improvements. The modified gun was designated ZiS-S-53, in acknowledgment of Savin’s contributions to the design. It supplanted the D-5T on the new T-34-85 Model 1944 in the spring of 1944.

The T-34-85 Model 1943 and T-34-85 Model 1944 differed in a number of respects. The most obvious external difference was the gun mantle, but the Model 1944 also had the commander’s cupola moved back to give more room to the gunner and to allow the radio to be moved from its previous position near the hull machine-gunner up into the turret in front of the commander so that he had more control over it.
The T-34-85 represented not only an important leap forward in firepower, but finally the T-34 turret was reconfigured for a three-man crew with full vision facilities for the tank commander and with full radio equipment. T-34-85 production did not completely supplant production of the T-34 Model 1943 armed with the 76-mm gun at all factories, but did make up the bulk of the 1944 production.
Users: Russia/Soviet Union.
Animated 3D model T-34-85 Model 1944
Specifications for T-34-85 Model 1944
Specifications:
T-34-85 Model 1944 | Specification |
|---|---|
Type | medium battle tank |
Engine | 12 cylinders V-2 with 500 hp |
Gearbox | ? |
Crew total | 5 |
Turret crew | 3 |
Length | 8.15 m |
Width | 3.00 m |
Height | 2.60 m |
Weight | 32.0 tonnes |
Maximum speed | 55 km/h |
Cross-country speed | ? |
Fuel consumption per 100 km | 225 liters |
Fuel | 810 litres |
Road radius | 360 km |
Cross-country radius | 310 km |
Vertical obstacle | 0.79 m |
Trench crossing | 2.49 m |
Fording depth | c. 1.37 m |
Turning circle | ? |
Gradient | 30 % |
Armor:
T-34-85 Model 1944 | mm | angle |
|---|---|---|
Turret front | 90 | ? |
Turret side | 75 | ? |
Turret rear | 60 | ? |
Turret top | 20 | ? |
Superstructure front | - | - |
Superstructure side | - | - |
Superstructure rear | - | - |
Superstructure top | - | - |
Hull front | 47 | ? |
Hull side | 60 | ? |
Hull rear | 47 | ? |
Hull top | 20 | ? |
Hull bottom | 21 | ? |
Gun mantlet | ? | ? |
Armament and Equipment:
T-34-85 Model 1944 | Specification |
|---|---|
Main armament | 85-mm-gun M1944 ZIS-S-53 L/51 |
Rounds | 60 |
Traverse | 360° |
Elevation | ? |
Muzzle velocity Arnour piercing (APCBC) | 792 m/s |
Muzzle velocity Arnour piercing (DS) | 1,200 m/s (only limited available) |
Muzzle velocity High-explosive fragmentation | 792 m/s |
Shell weight Armour piericing (APCBC) | 9.02 kg |
Shell weight Arnour piercing (DS) | 4.9 kg |
Shell weight HE-fragementation | 9.2 kg |
Secondary armament | two 7.62 mm DT MG |
Radio | 9R (range 24 km) |
Telescopic sight | ? |
Penetration mm at 30° and 0° armor plates of 85-mm-gun M1944 ZIS-S-53 L/51:
Range | APCBC 30° | APCBC 0° | DS 30° | DS 0° |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Penetration 100 meters | ? | ? | ? | ? |
Penetration 500 meters | 103 mm | 111 mmm | c.110 mm | 138 mm |
Penetration 1,000 meters | 94 mm | 102 mm | c. 80 mm | 100 mm |
Penetration 1,500 meters | 86 mm | ? | - | - |
Penetration 2,000 meters | 77 mm | ? | - | - |
Production:
T-34-85 Model 1944 | figures |
|---|---|
Production | Spring 1944 - 1947 (continued from 1953 in Poland and Czechoslovakia). T-34-85 Model 1943 with 85-mm-D-5 gun December 1943 - Spring 1944 |
Combat delivery | Early 1944 |
Price per tank | 193,000 Rubels (Model 1942) |
Total production figure (all variants) | c.53,000 + 9,000 from 1953 in Poland and Czechoslovakia |
Service statistics of T-34-85’s:
Year | Available | Production | Losses |
|---|---|---|---|
before 1939 | - | - | - |
1939 | - | - | - |
1940 | - | - | - |
1941 | - | - | - |
1942 | - | - | - |
1943 | - | 100 | - |
1944 | 100 | 11,000 | ? |
1945 | ? | 18,330 | ? |
Total | - | 29,430 | ? |
Video from the action with the T-34-85 in video games
A typical action with the T-34-85E (field modification with additional armor against strikes by the Panzerfaust) in a realistic ground battle of the F2P game War Thunder:
Please click on the start button for this c.5 min video !
More about the Russian Bias in the F2P game War Thunder here !
Who does not know the F2P tank and plane war game War Thunder can download it from here for free:
References and literature
Soviet Tanks and Combat Vehicles of World War Two (Steven J. Zaloga, James Grandsen)
Fire and Movement (RAC Tank Museum)
Krieg der Panzer (Piekalkiewicz)
















